|
| CHIANTI |
| An Atomic Database for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of Astrophysical Plasmas |
| USER GUIDE - Version 5.0 - 18 August 2005 |
| Written by Giulio Del Zanna |
| with contributions from Peter Young and the team members. |
which_line pop_processes(see the example section).
The changes introduced to speed the calculations were made necessary by the increasingly larger atomic models now available in CHIANTI, that made the running time of the software of the previous version too long.
The software is backward-compatible, i.e. can be used together with previous versions of the database.
-Added detailed descriptions of the data file contents.
-Replaced the continuum plot, that was created with the corrupted version of the itoh.dat file.
-Corrected instructions for installation within Windows.
This document describes the general characteristics of the new Version 4.0 of the CHIANTI package (database and IDL procedures).
A considerable number of new features, both in the database and the software, have been added (see Young et al., 2003). We have tried to keep a distinction between the previous and the new features in this document.
Users of previous versions, please NOTICE:
The main new features described in this guide are
Backward compatibility has been assured for almost all cases. In practice, previous users of CHIANTI will be able to use the new V.4 software as before, with just minor changes. On the other hand, software versions prior to 4 are not compatible with the v.4 database.
This document replaces the previous CHIANTI guide (Version 1.0).
CHIANTI is a collaborative project involving researchers based at the Naval Research Laboratory (NRL, Washington DC, USA), Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (RAL, UK), the University College London (UCL, UK), the University of Cambridge (UK), the George Mason Univerity (GMU, USA) and the University of Florence (Italy).
The CHIANTI package consists of a critically evaluated set of atomic data (energy levels, wavelengths, radiative transition probabilities and excitation data) for a large number of ions of astrophysical interest. It also includes a number of ancillary data and a suite of Interactive Data Language (IDL) programs to calculate optically thin synthetic spectra and to perform spectral analysis and plasma diagnostics.
Plasma emission codes have long been used to study UV and X-ray spectral lines emitted from solar or stellar atmospheres. A comparison of the theoretical line intensities with the observed intensities allows a determination of the physical parameters for the plasma (cf Mason and Monsignori Fossi, 1994 and Del Zanna, Landini and Mason, 2002).
It is very important, now that high accuracy atomic data are available, to improve and keep up-to-date the plasma codes.
The CHIANTI database has been used extensively by the astrophysical and solar communities to analyse emission line spectra from astrophysical sources.
The CHIANTI package is freely available at one of the CHIANTI homepages:
or at
As with any atomic data package, CHIANTI has been developed to suite some specific applications in astrophysics, and users should read the CHIANTI papers and the documentation to find out the ranges of applicability of the package.
Currently, some of the main assumptions and limitations of the data and programs are:
A correction to the level populations due to ionization and recombination is included, but it is only valid up to densities above which metastable level populations begin to be non-negligible.
The continued development of the CHIANTI database is dependent on continued funding which is generally available if we can demonstrate that the CHIANTI database is of use to astrophysical research. If you use CHIANTI, we only ask that you acknowledge it appropriately in any publications:
Write in the text of any publication the reference to the CHIANTI paper associated with the particular VERSION you have used:
We would appreciate if you also write in the acknowledgements of any
publication the following:
CHIANTI is a collaborative project involving NRL (USA), RAL (UK), and the following Universities: College London (UK), of Cambridge (UK), George Mason (USA), and of Florence (Italy).
If a detail work on a particular ion is done, it would be appropriate to also refer to the original publication. References can be found at the end of each data file or on the WWW.
CHIANTI data are included into other databases. It would be appropriate to make that clear to the users so they can trace back the results they use to the original calculations.
Users should be aware of what is included in the database, of the approximations applied, and of the atomic data used. The CHIANTI results should not be blindly considered valid in all cases. For example, the CHIANTI predicted emissivities should not be used when considering temperatures outside of the validity ranges.
Any contributions and suggestions to CHIANTI are welcomed. We would appreciate a short description of how you employ CHIANTI.
The CHIANTI project was originally set up by Dr. Ken Dere of the Naval Research Laboratory (Washington, USA), Dr. Helen Mason of the Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics at the University of Cambridge (UK), and Dr. Brunella Monsignori-Fossi of the Arcetri Astrophysical Observatory (Florence, Italy). Former students of Dr. Monsignori-Fossi (Dr. Enrico Landi) and Dr. Mason (Dr. Peter Young) helped in the creation of the database. The sad and unexpected death of Dr. Monsignori-Fossi in January 1995, led to Prof. Massimo Landini, a close associate of Dr. Monsignori-Fossi, becoming a new CHIANTI representative (University of Florence).
Additional collaborations have involved Dr. Dave Pike of the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (RAL), who has written CHIANTI routines to run within the environment of the SOHO/CDS software (and within SolarSoft), and with Dr. Gordon Bromage, Dr. Barbara Bromage and her former student Dr. Giulio Del Zanna of the University of Central Lancashire.
Dr. Enrico Landi, now at the Naval Research Laboratory, Dr. Peter Young, now at RAL, and Dr. Giulio Del Zanna, now at UCL, have continued to be active collaborators in the CHIANTI project.
Young et al. (1998) used the CHIANTI database for a detailed comparison with observed EUV solar spectra to assess the diagnostic accuracy of the two data sets.
In November 2000 we have released a whole new CHIANTI package under SolarSoft.
The fitting procedure for excitation data, both electrons and protons, has been extended to allow 9 point spline fits in addition to the previous 5 point spline fits. This allows higher quality fits to data from close-coupling calculations where resonances can lead to significant structure in the thermally-averaged collision strengths.
With the addition of H I, He I and N I, the first neutral species have been added to CHIANTI.
Many existing ion data-sets have been updated, in particular most ions of the nitrogen and beryllium isoelectronic sequences. Also, new ions have been added, including Ar IV, Fe VI and Ni XXI.
The continuum routines have been re-written, including a new relativistic free-free continuum, a new free-bound, and a new two-photon continuum. New software has been written.
Minor releases of the database and the software normally include fixes and might occur a few times per year.
chianti_help@halcyon.nrl.navy.mil
The atomic data will continue to be updated regularly as new data are calculated or measured in the laboratory.
It is intended that these atomic data can be accessed and transfered into users own analysis programs, for more sophisticated applications.
The database has a tree structure, with the top directory designated with the IDL system variable !xuvtop (and named dbase within SolarSoft):
dbase/
In the top directory are the following files:
README_CHIANTI with the description of the current version.
VERSION with the version number.
Then, there is a series of subdirectories, one for each element present in the database.
Each element has a subdirectory for each ion.
The filename prefix for each ion follows spectroscopic notation.
For example, for He, we have He I and He II subdirectories:
he/
he_1/
he_2/
Then, we have a series of ancillary data that are contained in
various subdirectories:
masterlist/
has the list of the ions currently present
in the database
abundance/ with elemental abundance files.
continuum/ contains files for the continuum calculations.
dem/ has DEM files.
ioneq/ contains ionization fraction files.
ip/ has ionization potentials.
ancillary_data/instrument_responses/ with effective areas.
There are five primary ASCII files for each ion subdirectory. For example, for Fe XIV we have:
Specifies the energy levels in cm-1 and Rydbergs. It includes both experimental data and theoretical values of the levels energies.
The energy levels are obtained from NIST. Where necessary, these are supplemented by other laboratory and theoretical values.
Each column in the files has:
Note that the ordering of the levels does not follow any strict rule.
Contains the wavelengths, gf and A values of the transitions and the indices initial and final level corresponding to the indices of the levels as given in the fe_14.elvlc file. Wavelengths calculated from the theoretical energies are of an indeterminate accuracy and their values are presented as negative values of the calculated wavelength. The `observed' wavelengths in these files are based on the experimental energies and should be the best available.
The radiative data are taken from published literature and where necessary, supplemented by new calculations.
Each column in the files has:
contains the point spline fits to electron collision strengths scaled according to the the rules formulated by Burgess and Tully (1992), as described in Dere et al. (1997). All the atomic data in the CHIANTI database have been visually displayed and assessed for accuracy and any sporadic errors which sometimes creep into published results.
Accurate replication of the temperature averaged collision strength over a wide range of temperatures can be accomplished with the data in this file.
Each column in the files has:
This is analogous to the fe_14.splups file, and contains the point spline fits to proton collision strengths.
We created two new files that include the aion and arec rates. The names of these files follow the usual CHIANTI pattern, and have the .CILVL and .RECLVL suffixes, for ionization and recombination respectively.
Data in these files are tabulated as a function of temperature, at all temperatures for which they are provided.
Currently, all the rates for each ion are given at the same temperature. In the future this will be generalised.
The basic structure of the files is to put the data at the beginning of the file followed by comments.
The comments must be enclosed at the end of the file between two lines containing a single '-1'
The original sources are documented in each data file, where also additional and detailed comments written by the CHIANTI member that assessed that particular ion can be found. You can have direct access to the references via the WWW pages.
Some additional data files are needed in various calculations. The software allows the selection of these files, from either a 'standard' selection provided within the database, or by using user defined files that are included in the current working directory, provided they have the proper file extension. For example, it is possible to create a user defined 'myfile.dem'. If the file is in the working directory, then the file will automatically be appended to the list of available DEMs from the CHIANTI database. In other cases, it is possible to select the file by using a widget that allows the user to change directory.
Any user-defined file must have the same format as those already provided (also including a 'comment' section at the end of the file)
The list of the ions present in the database
A !xuvtop/masterlist/masterlist.ions file keeps the current list of all the ions in the database. This list is used as default by many routines (for example those that calculate line intensities).
In some cases, it is possible to instead use a user-defined list of ions, to speed the calculation, or to directly supply the routines with a list of ions, via the SNGL_ION keyword.
Elemental abundances
Files with various elemental abundances are provided in the directory !xuvtop/abund/ Element abundances are in the usual dex notation (Log10 values, relative to H, that has a Log10 value of 12).
Options are available within the routines to choose different elemental abundances. User-defined abundance files can also be used, and should have a .abund file extension.
Be aware that any element missing in the elemental abundance file will also be missing in any output created by any software that reads the elemental abundance file.
There is a great deal of controversy over the variation of the elemental abundances in the solar and stellar atmospheres. See the reviews of Meyer (1985, 1993), Widing and Feldman (1992), Mason (1992), Raymond et al. (2001). Also, it should be kept in mind that different analyses can lead to very different results. For example, the ionisation balance, the selection of lines, and the spectroscopic method used can each account for a variation of a factor of two or more in the derived element abundances (see Del Zanna et al., 2002 and references therein).
Ionisation Fractions
Files giving collisional ionization equilibria are provided in the !xuvtop/ioneq directory. User defined ionisation files should have a .ioneq file extension.
Be aware that most CHIANTI software uses the temperatures in these files as a base for the calculations. For example, if DEM(T) values are supplied, they are first interpolated at the temperatures in the ionization fraction, and the calculations are done at those temperatures.
The ionisation fractions have been taken from the tabulated values in the published literature (e.g. Arnaud & Raymond, 1992; Arnaud & Rothenflug, 1985; Mazzotta et al., 1998).
Be aware that any ion missing in a ionisation fraction file will also be missing in any output created by the software.
Also, be aware that any line missing a temperature overlap with the chosen ionisation fraction would have zero emissivity and will not be output by the software.
Be aware that large differences between different tabulations are present, and that large uncertainties are associated with these calculations. It should be noted that the ionisation equilibrium plays a major role not only in the derivation of the DEM, but also in that one of the elemental abundances. In this respect, it is important to be aware of the fact that a number of ions, in particular those of the Li and Na isoelectronic sequence, present anomalous behaviour (see Del Zanna et al., 2002, and references therein).
Differential Emission Measure
Files specifying various standard differential emission measures (DEM) distributions for different solar features are provided in the !xuvtop/dem directory. Additional files for stellar atmospheres will also soon be added. Each file contains the Log10 T and Log10 DEM values in two columns, ordered with increasing temperature.
User-defined DEM files should have a .dem file extension and must have the same format and ordering of the files provided.
Be aware that any line missing a temperature overlap between the ion fraction and the chosen DEM distribution would have zero emissivity and will not be output by the software.
The emission measure distribution in the solar atmosphere is a complex issue. Starting with the pioneering work by Pottasch (1964), spectra in the UV wavelength range have been used to determine the distribution of material as a function of temperature, following various methods. More details can be found in Section 9.16.
Other files
Other files are in other miscellaneous directories. For example:
!xuvtop+'/ip/chianti.ip' has the ionization potentials for all the ions;
!xuvtop+'/continuum/ contains data used by the routines that calculate the continuum. For example, gffgu.dat contains the free-free gaunt factors of Sutherland (1998).
A number of Interactive Data Language (IDL) procedures are also provided as part of the CHIANTI package. These include routines to read the various CHIANTI database files, calculate level populations, line intensities, and temperature dependent and density dependent line intensity ratios.
Most of our efforts have gone into developing well-documented user-friendly IDL routines that meet readily apparent needs. We welcome contributions to the software.
CHIANTI has been run mainly on Sun, Dec Unix workstations and on PCs with Linux. CHIANTI also runs (with some small limitations) under Windows NT and in VMS. Please report to us any problems you might find.
All the IDL routines have been documented with extensive headers
giving detailed descriptions and
examples. Please read them carefully.
The CHIANTI routines can be grouped into three classes:
The CHIANTI routines are organised in a tree structure. The main level contains some high-level procedures and the HISTORY file, where all modifications to the software are logged.
Now, a description of the various high-level routines that are present within the CHIANTI software tree is given.
Compared to previous releases, significant changes occurred. Please read Sect. for details.
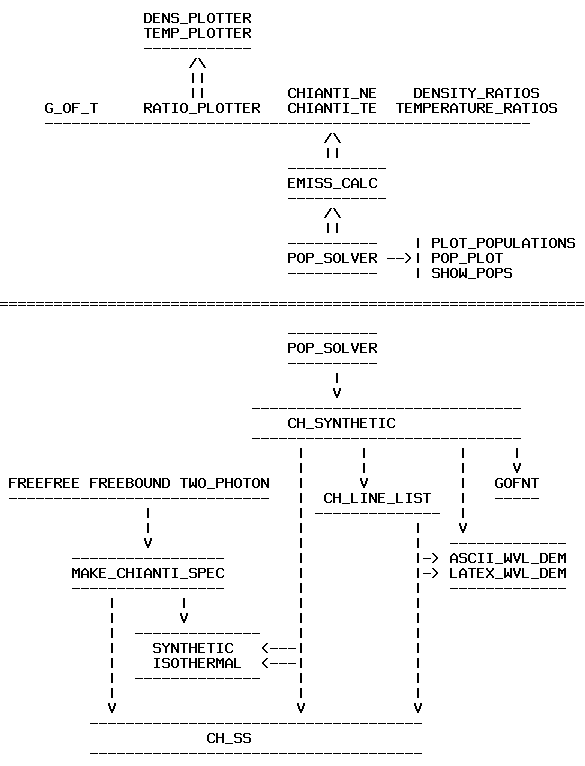
A new set of high-level and higher-level routines has been written for Version 4. The major change for V.4, aside from those already mentioned, has been the way to calculate synthetic spectra and handle line intensities (see Fig. 1):
Other routines that previously were only available within SolarSoft are also included now. The users therefore now have various different routines to choose from.
We have kept the older high-level routines, so the user can still use them as before (with slight modifications/additions of keywords). We have updated them and re-written as wrapper routines (essentially that call the newly-written routines) as follows:
| Synthetic spectra | ||
| ch_ss |
| |
| synthetic |
| |
| synthetic_plot |
| |
| isothermal |
| |
| make_chianti_spec |
| |
| Line intensities | ||
| ascii_wvl_dem |
| |
| latex_wvl_dem |
| |
| ch_synthetic |
| |
| ch_line_list |
| |
| Line emissivities | ||
| emiss_calc |
| |
| gofnt |
| |
| g_of_t |
| |
| Density-sensitive line ratios | ||
| dens_plotter |
| |
| density_ratios |
| |
| chianti_ne |
| |
| plot_chianti_ne |
| |
| Temperature-sensitive line ratios | ||
| temp_plotter |
| |
| temperature_ratios |
| |
| chianti_te |
| |
| plot_chianti_te |
| |
| Continuum | ||
| freefree |
| |
| freebound |
| |
| two_photon |
| |
| Level populations | ||
| plot_populations |
| |
| pop_plot |
| |
| show_pops |
| |
| pop_processes |
| |
| Miscellaneous | ||
| rad_loss |
| |
| max_temp |
| |
| plot_ioneq |
| |
| chianti_dem |
| |
| plot_dem |
| |
| integral_calc |
| |
| ch_read_fits |
| |
| ch_write_fits |
| |
|
For the first two classes of routines, by simply typing the name of the routine, a description of how to call the routines, with examples, is printed. For example,
IDL > temperature_ratios IDL > temperature_ratios,ion,wmin,wmax,Log10(tempmin),Log10(tempmax),$ IDL > temperature,ratio,description,$ IDL > [pressure= ,density= , psfile= , outfile= ] IDL > IDL > i.e.: IDL > temperature_ratios,'c_5',40.,50.,5.,7.,temp,rat,desc
In any case the best way to understand what a routine does and how it works is to read the header documentation with e.g.:
IDL > xdoc,'ch_synthetic' IDL > doc_library,'ch_synthetic'
Another way to quickly see the keywords of a routine is to use:
IDL > chkarg,'temperature_ratios ..... ---> Call: pro temperature_ratios,ions,wmin,wmax,tempmin,tempmax,$ temperature,ratio,description,$ density=density,psfile=psfile, $ outfile=outfile,noprot=noprot, $ radtemp=radtemp,rphot=rphot,photons=photons, $ ioneq_file=ioneq_file, abund_file=abund_file, $ VERBOSE=VERBOSE
CHIANTI is currently distributed in two ways:
http://www.lmsal.com/solarsoft/
for details on how to download and install the package. The database and the software are organised in a self-contained package
$SSW/packages/chianti/
with the following tree structure:
dbase/ (database) doc/ (documentation, in particular the USER GUIDE) idl/ (IDL software) setup/ (supplementary setup files)
The contents of the SolarSoft CHIANTI package are
mirrored daily from a master tree.
Normally, only small fixes to the existing
software can occur rather frequently.
All modifications to the software are logged in the $SSW/packages/chianti/idl/HISTORY file.
Modifications to the database are much less frequent. They are described in the $SSW/packages/chianti/dbase/README_CHIANTI file.
We send an e-mail to the CHIANTI user group every time we make a minor release of the database available.
Note that the contents of the SolarSoft package change on a frequent timescale normally to fix bugs caused by the use of new IDL releases.
We recommend that you use CHIANTI within the SolarSoft framework and that you setup in your site a mirror in order to have automatic upgrades. It is easy to follow the instructions to download and setup the package.
Currently, the data and the software are distributed in two separate tar files. The tar files have a similar tree structure as the SolarSoft distribution.
E.g. the data are in CHIANTI_4.0_data.tar that contains a copy of $SSW/packages/chianti/dbase.
CHIANTI_4.0_pro.tar contains doc/, a copy of $SSW/packages/chianti/doc/ and idl/, a copy of $SSW/packages/chianti/idl/, plus idl/gen/, a copy of the $SSW/gen/ routines. This is because some routines of the $SSW/gen/ directory are needed to run some of the CHIANTI programs.
CHIANTI is a package, in the sense that database and progams are to be used together. The current version of the database must be used with the current version of the programs. Backward compatibility does not always apply.
To run any CHIANTI IDL procedure, the following is needed:
If you are using SolarSoft you should have the setup already organised so as to have the path of the CHIANTI IDL procedures added to IDL_PATH, the !xuvtop and the other IDL system variables defined. This is done automatically by using
unix> setssw chianti unix> sswidl or unix> sswidl IDL > ssw_packages,/chianti
After this, you will be able to run the CHIANTI routines.
Users of previous versions, please NOTICE:
The procedures to install CHIANTI have changed in small but important ways.
Download the CHIANTI files
Download the CHIANTI data tar file (e.g. CHIANTI_4.0_data.tar.gz) and the CHIANTI IDL procedures tar file (e.g. CHIANTI_4.0_pro.tar.gz) and put the tar files into a directory (for example, /data1/chianti/dbase for the data and /data1/chianti/ for the software) and then do the following:
unix> gunzip [file_name].tar.gz unix> tar xvf [file_name].tar
This will copy all the CHIANTI data files into /data1/chianti/dbase and create the /data1/chianti/idl and /data1/chianti/doc/ directories.
Define the IDL paths and the system variables
There are two ways of doing the above. The first is to define the system variables within IDL, the second is outside IDL. We suggest the first option. Once IDL is started, there are three steps:
unix > idl
Unix: IDL> !PATH = '+/data1/chianti/idl:'+!PATH Windows: IDL> !PATH = '+C:\data1\chianti\idl;'+!PATH VMS: IDL> !PATH = '+/data1/chianti/idl,'+!PATH
IDL> !PATH = EXPAND_PATH(!PATH)The '+' and the EXPAND_PATH are needed since the IDL routines are organised into subdirectories. The second option involves writing (UNIX) the following statement in your /.cshrc (or /.login) file:
setenv IDL_PATH /usr/local/rsi/idl_4/lib:+/data1/chianti/idl
(assuming you have the main IDL directory in /usr/local/rsi/idl_4).
Unix: IDL> use_chianti, '/data1/chianti/dbase' Windows: IDL> use_chianti, 'C:\data1\chianti\dbase'
After following the above steps, it will be possible to run the CHIANTI routines from any directory. use_chianti also allows you to set your default abundance and ionization equilibria files with the abund and ioneq keywords.
Previous CHIANTI users should check the note below.
We suggest that you add the three above calls to your IDL_STARTUP file (say /.idl_startup). If this file does not exist then it should be created. In UNIX, this can be done if you add the following line to your .login file:
setenv IDL_STARTUP ~/.idl_startup
(Note that the changes to the .login file mean that you should do a source ~/.login before running IDL).
Alternatively, you can write the three statements above in a file, say start_chianti.pro:
!PATH = '+/data1/chianti/idl:'+!PATH !PATH = EXPAND_PATH(!PATH) use_chianti, '/data1/chianti/dbase' ENDand run
IDL> .r start_chianti
Note to previous CHIANTI users:
If you had already defined the CHIANTI system variables
before entering IDL or in your IDL STARTUP file you
should remove those definitions.
Alternatively, instead of using use_chianti, '/data1/chianti/dbase', you have to make sure you have in your IDL STARTUP file something like this:
!PATH = '+/data1/chianti/idl:'+!PATH !PATH = EXPAND_PATH(!PATH) defsysv,'!xuvtop', '/data1/chianti/dbase' defsysv,'!ioneq_file','/data1/chianti/dbase/ioneq/mazzotta_etal.ioneq' defsysv,'!abund_file','/data1/chianti/dbase/abundance/cosmic.abund' defsysv,'!BCOLOR',0 defsysv,'!ASPECT',1.0
For a review on Spectroscopic Diagnostics in the EUV for Solar and Stellar Plasmas see e.g. Mason and Monsignori Fossi (1994).
The intensity I(lij), of an optically thin spectral line of wavelength lij (frequency nij = [ c/(h lij)]) is
| (1) |
where i, j are the lower and upper levels, Aji is the spontaneous transition probability, Nj is the number density of the upper level j of the emitting ion and h is the line of sight through the emitting plasma. In low density plasmas the collisional excitation processes are generally faster than ionization and recombination timescales, therefore the collisional excitation is dominant over ionization and recombination in populating the excited states. This allows the low-lying level populations to be treated separately from the ionization and recombination processes.
For allowed transitions we have Nj(X+m) Aji ~ Ne. The population of the level j can be expressed as:
| (2) |
See the routine PROTON_DENS described in Sect. B.5 for details on how to calculate N(H)/Ne.
In the `standard model' for interpreting line intensities there are three fundamental assumptions that serve to simplify the problem considerably:
The atomic data contained in the CHIANTI database are particularly suited to the analysis of emission lines via this model, and the following discussion outlines this approach. No attempt is made to discuss non-equilibrium conditions.
With the first of the assumptions, the
population of ions lying in a
given state is constant and so the number of ions leaving this state
per unit time must exactly balance the number arriving into that
state. If we denote the number of transitions leaving the state i to
a state j taking place per unit time per unit
volume by aij, then steady state implies
| (3) |
| (4) |
| (5) |
Now our second assumption means that the processes that
affect the ionisation state of the plasma do not affect the quantity
ni. Eq. 5 thus becomes
| (6) |
For the basic CHIANTI model these processes are simply electron and proton excitation and de-excitation, and the generalised radiative decay:
| (7) |
Cije is given by:
| (8) |
| (9) |
where wi is the statistical weight of level i, k is
Boltzmann's constant, T the electron temperature, and qij
the electron excitation rate coefficient which is given by:
| (10) |
The solution of Eq. 6 is performed by the CHIANTI routine pop_solver.pro, which gives the fraction of ions in the state i.
The level populations for a given ion can be calculated and displayed with plot_populations.pro (but also see pop_plot.pro).
We rewrite the intensity as:
| (11) |
where the function
| (12) |
called the contribution function, contains all of the relevant atomic physics parameters and is strongly peaked in temperature.
gofnt.pro calculates these contribution functions (see also g_of_t.pro for a slightly different way of calculating contribution functions).
Please note that in the literature there are various definitions of contribution functions. Aside from having values in in either photons or ergs, sometime the factor [ 1/(4p)] is not included. Sometimes a value of 0.83 for N(H)/Ne is assumed and included. Sometimes the element abundance factor is also included. Any of the above (or any other) variations also affect the definition of a line intensity in terms of the contribution function and the DEM. In the following we will refer to the functions C(T,lij,Ne) and G(T,lij,Ab(X),Ne) = Ab(X) C(T,lij,Ne) ( i.e. the contribution function that contains the abundance factor ).
If we define, assuming that is a single-value function of the temperature, the differential emission measure DEM (T) function as
| (13) |
the intensity can be rewritten, assuming that the abundance is constant along the line of sight:
| (14) |
The DEM gives an indication of the amount of plasma along the line of sight that is emitting the radiation observed and has a temperature between T and T+dT.
The IDL routine chianti_dem.pro described in Sect. 9.16 calculates the Differential Emission Measure DEM(T) using the CHIANTI database, from a given set of observed lines.
Routines such as ch_synthetic.pro (see Sect. 9.1 and Sect. ) calculate line intensities without the abundance factor, that is only included at a later stage.
In the isothermal approximation, all plasma is assumed to be at a single temperature (To) and the intensity becomes:
| (15) |
where we have defined the column emission measure
| (16) |
ch_synthetic.pro in the isothermal approximation calculates I = C(To, lij, Ne) òNe NH dh, while isothermal.pro and ch_ss.pro (see examples in Sect. 9.1) can be used to create synthetic spectra (with the abundance factor).
It is also possible to calculate intensities and spectra with a multi-temperature model, by providing an array of To, EMh values.
Please note that in the literature many different definitions of Differential Emission Measures, Emission Measures and approximations can be found (see Del Zanna et al., 2002 for some clarifications).
In the stellar case, the theoretical flux of an optically thin spectral line is:
| (17) |
where C(Ne, T, lij) has the
same expression as above, d is the star's distance,
dV is the volume element, and V is the entire source volume.
A volume Differential Emission Measures DEM is often defined:
| (18) |
| (19) |
At the moment CHIANTI does not include volume emission measures. In the near future we will modify the software and the definition of the DEM in order to include volume emission measures.
However, any volume Differential Emission Measures can be rescaled to column DEMs and used within the software to produce synthetic spectra for stellar coronae. One way of doing this is to assume spherical symmetry, and that the emitting region is a layer dh distributed over the entire star's disk, i.e. dV=4pR2* dh (R* is the star's radius). If the star's radius and distance are known, a volume DEM can be scaled with the factor [(4pR2*)/(d2)] to obtain a column DEM.
If this is used, the outputs will have flux units, i.e. ergs cm-2 s-1 (or photons cm-2 s-1) and not ergs cm-2 s-1 sr-1.
An example of scaled DEM is provided in the file AU_Mic.dem, in the CHIANTI distribution.
Column DEMs and EMs are assumed when the spectra are folded with effective areas (see Sect. 9.1). The effective areas are assumed to have units of counts photons-1 cm+2, so the output units of the spectra will be counts s-1 pixel-1.
Also note that corrections to interstellar absorption are not presently included in CHIANTI.
For each ion for which proton rates are available, an additional file is required in the database to contain the fits to the rate coefficients. The file has the suffix .PSPLUPS, and is exactly analogous to the .SPLUPS file for the electron fits. All of the proton transitions included in CHIANTI are forbidden transitions taking place between levels within the same configuration. Many of the transitions required 9-point splines (see Sect. C) in order to provide adequate fits. The number density of protons, Np, is calculated with the IDL routine proton_dens.pro (see Sect. B.5).
By default, all routines will include proton rates in the calculation of the ion level balance. A keyword /NOPROT can be used to switch off the proton rates.
Within CHIANTI the assumption of Maxwellian electron and proton distributions is implicit through the storage of Maxwellian-averaged electron and proton collision strengths in the .SPLUPS and .PSPLUPS data files. To model emission from plasmas with general, non-Maxwellian particle distributions would require integrations of the original collision strengths with the new particle distributions, and this is outside of the scope of the CHIANTI database.
However, if the particle distributions can be expressed as a linear combination of Maxwellians of different temperatures, i.e.,
| (20) |
where the Maxwellian function fM(E, Ti) is given by
| (21) |
then such distributions can be modelled in a straightforward manner within the CHIANTI framework.
The generalized electron excitation rate coefficient for the transition j to k and for the particle distribution f of electron velocities is given by
|
where Ejk is the threshold energy for the transition, Qjk is the collision cross section, E (=mev2/2, me the electron mass) is the energy of the incoming electron, and Cjk(Ti) is the electron excitation rate coefficient for a Maxwellian particle distribution of temperature Ti (see, e.g., Burgess & Tully 1992).
The matrix Cjk replaces the usual Maxwellian-derived rate coefficient (Cjk) in the level balance equations solved by the CHIANTI software. The software routines for calculating emissivities and level populations have been modified to allow input of the non-Maxwellian parameters ai through the keyword SUM_MWL_COEFFS. The temperatures Ti are specified through the standard temperature input to the routines. The temperatures are assumed to apply to both proton and electron distributions.
This prescription for treating non-Maxwellian distributions is not compatible with the treatment of ionization and recombination since an equilibrium ionization balance described by a single temperature is required for these processes. In such cases the ionization and recombination processes described in Sect. are switched off when calculating the level populations if the ai coefficients are specified in CHIANTI.
See Sect. 9.8 for an example.
Within CHIANTI, we presently model the Photoexcitation and Stimulated Emission by assuming a a blackbody radiation field of temperature T*. The generalized photon rate coefficient in this case is:
| (25) |
where Aji is the radiative decay rate and W(R) is the radiation dilution factor which accounts for the weakening of the radiation field at distances R from the source center.
We also assume an uniform (no limb brightening/darkening) spherical source with radius R*:
| (26) |
where
| (27) |
It is important to remember the assumptions in our formalism for radiation processes. For a given ion, only very specific wavelengths in the radiation continuum will affect the ion's level balance. If there are significant deviations from a blackbody spectrum at any of these wavelengths (perhaps due to a deep absorption line) then CHIANTI does not model the ion entirely correctly.
Examples of specific uses of the extra radiation processes include modeling of coronal emission lines above the surface of the Sun and other cool stars when the coronal electron density falls to low enough values that electron collisions lose their potency.
For the Sun, photoexcitation is very important for the infrared coronal lines. Photoexcitation is also important for modelling nebular ions that are irradiated by a hot star, such as in planetary nebulae, symbiotic stars and Wolf-Rayet stars.
No additions or modifications to CHIANTI data files are required for photoexcitation and stimulated emission as their rates are entirely determined from the radiative decay rates, level separation energies, and statistical weights - information already contained in CHIANTI. It is only necessary to specify the radiation field temperature and the dilution factor. These are specified as inputs to the IDL procedures through the new keywords RPHOT and RADTEMP. RPHOT specifies r = [ R/(R*)], while RADTEMP gives the blackbody radiation temperature in K.
By default, photoexcitation and stimulated emission are not included in the level balance equations unless the keywords are set.
Version 4 of CHIANTI introduced the possibility of including photoexcitation and stimulated emission through an external blackbody radiation field into the level balance equations. With version 5 the software has been modified to allow an arbitrary, user-defined radiation field to be specified.
The user must create an IDL routine that calculates the energy density per unit wavelength, Ul, as a function of wavelength. The photoexcitation rate for a transition i® j is related to Ul by the expression
| (28) |
where W(R) is the dilution factor defined as in Young et al. (2003), Aji is the Einstein coefficient for spontaneous radiation from j to i, wj and wi are the statistical weights of levels j and i. or example, Ul for a blackbody of temperature, T, is given by
| (29) |
thus giving the photoexcitation rate for a blackbody of
| (30) |
For reference we note that the energy density is related to the specific intensity, Il, by
| (31) |
The user-defined radiation field function is implemented through a keyword
RADFUNC='user_function, a, b' in the CHIANTI IDL routines SHOW_POPS and
EMISS_CALC. The optional coefficients a and b can be used to modify the
radiation field, e.g., by specifying a relative velocity between the
radiation field and incident ion.
See Sect. 9.7 for an example.
In Version 5 of CHIANTI, we have included ionization and recombination into level populations. The CHIANTI model for ionization and recombination assumes that the plasma can be described under the Coronal Model Approximation, where the total population of the excited levels of an ion is negligible compared to the population of the ground level. In this case, recombination and ionization processes can be included in a relatively straightforward way, since they can be treated as a correction to the case where populations are calculated neglecting them.
To illustrate this method, we will consider the simplified atomic model of an ion X+q with abundance nq composed of the ground level and one excited level only. In case ionization and recombination contributions to level populations are negligible, the relative population of the upper level is obtained by solving the equation:
| (32) |
where Cg® i is the collisional excitation rate and Ai® g is the Einstein coefficient for spontaneous radiative decay. Collisional de-excitation is neglected in the coronal model approximation. In case ionization and recombination provide significant contribution, Equation 32 needs to be modified to include the rate coefficients for ionization (aion) and recombination (arec):
| (33) |
where nq-1,nq,nq+1 are the ion fractions for the ions Xq-1, Xq and Xq+1, respectively. The population of the excited level can then be expressed as
|
where the correction À is given by
|
The correction À is temperature sensitive and can be large when the collisional excitation rate is small or when the abundance of the ion q is much smaller than the abundances of the adjacent ions. The correction due to ionization and recombination can have significant effects on intensities of observed X-ray lines.
The only limitation of this approach lies in the breakdown of the coronal model approximation at high densities for a few ions. This occurs at densities above which metastable level populations begin to be non-negligible, compared to the ground state (cf. Landi et al. 2005).
The CHIANTI software has been modified to allow calculation of the correction factor À for the ions for which aion and arec are provided.
The inclusion of ionization and recombination effects in level population has required some more changes. New files have been created (.CILVL and .RECLVL) to store the ionization and recombination rates necessary for this process (see Sect. 5.1.1 for details).
A new routine (READ_IONREC.PRO) has been created to read these files and store their data in the input to the routine POP_SOLVER.PRO. This latter routine has been modified to include the correction to the level populations. In case the .CILVL and .RECLVL files are not available, a flag is set in the programs and these processes are ignored. The impact of this new process on the running time is negligible.
However, the introduction of ionization and recombination effects on level population has had a side effect. In previous versions of CHIANTI, the contribution to the intensity of spectral lines from levels below the ionization potential due to cascades from levels above the ionization potential was taken into account in the ``dielectronic'' .WGFA files, which included radiative transitions from the former, populated by cascades from the latter. For the ions for which the complete .RECLVL and .CILVL files are now available (Fe XVII to Fe XXIV), cascades from levels above ionization are now taken into account directly, so that the cascade contribution calculated by the ``dielectronic'' .WGFA files is not anymore necessary. To avoid double-counting this contribution, the transitions from levels below the ionization threshold in the ``dielectronic'' .WGFA files have been given a null wavelength, so they can be removed from the spectrum without having to change the way the ``dielectronic'' level population are handled.
An IDL routine to include the two photon continuum has been added to CHIANTI, while the free-bound and free-free continuum (bremsstrahlung) routines have been revised. See Young et. al. (2002) for more details.
Note that the output units of the continuum routines are by default 10-40 ergs sr-1 s-1 Å-1 per unit emission measure òNe NH dh.
On the other hand, the SolarSoft routine CONFLX outputs a continuum in photons s-1 Å-1 assuming an emission measure òNe2 dh = 1050.
The two-photon continuum is calculated with two_photon.pro.
Transitions in hydrogen-sequence ions
The first excited level (2s 2S1/2) of the hydrogen iso-electronic sequence ions can decay only by means of forbidden magnetic dipole and two-photon transitions. The importance of the competing magnetic dipole transition increases with Z but for nickel (Z=28), the two-photon transition rate is roughly 5 times that of the magnetic dipole rate.
The spectral emissivity (erg cm-3 s-1 sr-1 Å-1) for optically-thin two-photon emission at wavelength l is given by:
| (36) |
where Aj,i (sec-1) is the Einstein spontaneous emission coefficient (A value); Nj(X+m) is the number density of the level j of the ion X+m; f is the spectral distribution function; and l0 is the wavelength corresponding to the energy difference between the excited and ground level.
Two-photon continuum transitions in helium-sequence ions
For the helium iso-electronic sequence, the second excited level (1s2s 1S0) decays through a forbidden magnetic dipole and two-photon transitions.
The bremsstrahlung emission is calculated with freefree.pro. This routine has been rewritten ex-novo. It now includes the Itoh et al. (2000) and Sutherland (1998) gaunt factors.
Itoh et al. (2000) have provided an analytical fitting formula for the relativistic thermal bremsstrahlung gaunt factors, and this is now added to CHIANTI. The fitting formula is valid for the ranges 6.0 £ log T £ 8.5 and -4.0 £ log (hc/klT) £ 1.0. For temperatures below log T=6.0 we retain the non-relativistic Gaunt factors of Sutherland (1998) for computing the continuum. The condition log (hc/klT) £ 1.0 results in some of the low wavelength points being inaccurately represented by the Itoh et al. fitting formula. For these wavelengths the Gaunt factors of Sutherland (1998) are used to compute the continuum level.
The relativistic free-free continuum is almost identical to the non-relativistic continuum at low temperatures. At T=1×108 K (the maximum temperature permitted by the ion balance calculations contained in CHIANTI) the relativistic continuum is around 1% higher near the peak of the distribution.
The free-bound continuum emission is calculated with freebound.pro. This routine has been rewritten. The new routine uses the the Karzas and Latter (1961) approximation to the photoionization cross-sections and calculates free-bound gaunt factors for levels n=1-6. Additional data files have been created for this purpose. For example, free-bound radiation produced by recombination of an electron onto C IV to produce C III will use the data in the c\_3.fblvl file.
In what follows we review the main points about the new software. We hope you find it useful and enjoy using it !
For an user-friendly, widget-based approach the best option is to use CH_SS:
IDL >ch_ss
This widget allows the user to calculate synthetic spectra in two basic steps. Basically, you follow the various widgets from top left to lower right to set the desired parameters. First calculate the line intensities. These values can be saved for later use. Next, specify further parameters such as the elemental abundances and instrumental spectral resolution and then calculate and plot the spectrum. These values can also be saved for later use. The HELP buttons in the widget provide short descriptions of the required information. More details are given below.
Alternatively, for e.g. background jobs, the
routine CH_SYNTHETIC can be used.
ch_synthetic.pro
calculates line intensities assuming
constant pressure or density (or a model T,N),
without the abundance factor.
One of the reasons why element abundances are not
included in the line intensities calculation is so that it is easier
for the user to see how modifying abundances affects their spectra in
e.g. ch_ss.pro.
The calling sequence is:
IDL> ch_synthetic, wmin, wmax, output=output, err_msg=err_msg, msg=msg, $
pressure=pressure, density=density, $
model_file=model_file, all=all,sngl_ion=sngl_ion, $
photons=photons, masterlist=masterlist, $
save_file=save_file , verbose=verbose,$
logt_isothermal=logt_isothermal, logem_isothermal=logem_isothermal,$
goft=goft, ioneq_name=ioneq_name, dem_name=dem_name, $
noprot=noprot, rphot=rphot, radtemp=radtemp, progress=progress
The routine has many KEYWORDS (see Sect. for a full list) A series of parameters must be set:
Wmin, Wmax: minimum maximum of the desired wavelength range in Angstroms
Pressure: pressure in emitting region (Pe, cm^-3 K).
Only a single value is accepted, and the calculation is
performed at constant pressure.
Density: density in emitting region (Ne, cm^-3).
Only a single value is accepted, and the calculation is
performed at constant density, unless LOGT_ISOTHERMAL is
defined. In this case, DENSITY can be an array of values, but
has to have the same number of elements as LOGT_ISOTHERMAL.
model_file Full path of the (Te,Ne) file if defined.
This file should have two columns, one with the Te (K)
values, and one with the Ne (cm^-3) values. If these
values are not sorted in ascending order of Te, the
routine does sort them.
The line intensities are calculated either in the isothermal approximation, in which case the following has to be defined:
LOGT_ISOTHERMAL: Array of logarithmic temperatures. LOGEM_ISOTHERMAL: Array of logarithmic emission measures (0 by default).
or by folding the G(T) with a differential emission measure DEM contained in the file specified by DEM_NAME. The program will prompt the user to select one if not defined.
Example:
IDL> ch_synthetic, 10,20., output=str , pressure=1.e+15,$
ioneq_name=concat_dir(concat_dir(!xuvtop,'ioneq'),'mazzotta_etal.ioneq'),$
dem_name=concat_dir(concat_dir(!xuvtop,'dem'),'flare.dem'),$
/photons, /noprot, /all, sngl_ion=['fe_17','fe_18']
Creates an output structure str that contains the line intensities of only Fe XVII and Fe XVIII in the 10-20 Å range calculated at constant pressure of 1015, with the ionization balance in mazzotta_etal.ioneq and the DEM values in flare.dem in the standard CHIANTI distribution (if not supplied these files can be selected with a widget). Line intensities are in photons cm-2 s-1 sr-1 (KEYWORD photons), the proton rates are not included (KEYWORD noprot), and all the lines in the database (KEYWORD all) are included (also the lines with only theoretical energy levels).
You can see the contents of the structure with e.g.
IDL> help, str,/st IDL> help, str.lines[0],/stThe last command shows the first structure associated with the first spectral line.
The CHIANTI line intensities structure can be saved and later restored from the command line in various ways. We suggest two:
IDL> savegen, file='ch_int_10_20_fe.genx', struct=str IDL> restgen, file='ch_int_10_20_fe.genx', struct=str
to save and restore the IDL structure str in the file ch_int_10_20_fe.genx.
Please note that we discourage the use of e.g.:
IDL> save, file='output.save', output IDL> restore, file='output.save'since IDL save files generated with later versions of IDL are usually not readable with earlier versions.
IDL> ch_write_fits, str, 'output.fits' IDL> ch_read_fits,'output.fits', str
to save and restore the IDL structure str in the FITS file output.fits. Aside from an introductory HEADER, the contents of the IDL structure are converted into two binary tables. Extensive comments are added.
In either case, the structure saved in the .genx and .fits files can be restored via CH_SS to later create a spectrum.
For an user-friendly approach the best option is to use CH_SS:
IDL >ch_ss
Alternatively, if you have already calculated a line intensity structure (as shown above), you can use CH_LINE_LIST. This program creates a latex or an ascii file of predicted spectral line intensities and wavelengths corresponding to selected parameters.
The routine has many KEYWORDS. Please read the header or read Sect. for details. The calling sequence is:
IDL> ch_line_list, transitions, outname, latex=latex, ascii=ascii, $
wmin=wmin,wmax=wmax,$
SPECTRUM=SPECTRUM, abundfile=abundfile, min_abund=min_abund, $
minI=minI,photons=photons,kev=kev, $
all=all,no_sort=no_sort, sngl_ion=sngl_ion
Example:
IDL> restgen, file='ch_int_10_20_fe.genx', struct=tran
IDL> ch_line_list, tran, 'ch_line_list.tex', /latex,$
abundfile=concat_dir(concat_dir(!xuvtop,'abundance'),'cosmic.abund'),$
mini=1e13
This creates a latex file ch_line_list.tex where only lines with an intensity greater than 1013 (KEYWORD mini) are included, and the allen.abund file in the standard CHIANTI distribution is used (if not supplied it can be selected with a widget).
Then, you have to latex the file three times, and optionally xdvi it:
unix> latex ch_line_list unix> latex ch_line_list unix> latex ch_line_list unix> xdvi ch_line_list
If you do not have it already, you will need the package longtable.sty that is distributed as part of ftp://cam.ctan.org/tex-archive/macros/latex/required/tools.tar.gz
You will obtain a table that looks like:
| Line List * tab:obs | ||||
| Ion | l (Å) | Transition | Tmax | Int |
|
| ||||
| Ion | l (Å) | Transition | Tmax | Int |
| Fe XVII | 12.1227 | 2p6 1S0 - 2p5 4d 1P1 | 6.9 | 1.11e+14 |
| Fe XVII | 12.2639 | 2p6 1S0 - 2p5 4d 3D1 | 6.9 | 9.81e+13 |
| Fe XVII | 13.8231 | 2p6 1S0 - 2s 2p6 3p 1P1 | 6.9 | 6.25e+13 |
| Fe XVIII | 13.9540 | 2s2 2p5 2P3/2 - 2p4 (1S) 3d 2D5/2 | 6.9 | 2.06e+13 |
| Fe XVIII | 14.1519 | 2s2 2p5 2P3/2 - 2p4 (1D) 3d 2D3/2 | 6.9 | 1.35e+13 |
Alternatively, you can also create a latex file with a list of line identifications and intensities using the wrapper routine LATEX_WVL_DEM:
IDL > latex_wvl_dem,100.,200., pressure=1.e+15,mini=1.However, latex_wvl_dem calls ch_synthetic and ch_line_list, and if you want to modify some of the parameters of ch_line_list (e.g. the minimum intensity) you will have to redo the calculation which will take some time. Windows will pop up so that you can select the abundance, the ionization equilibrium and the differential emission measure files. This will create by default a file linelist.tex in the user's working directory, by default.
To create an ascii file with the line details you can follow a similar approach, i.e.:
IDL> restgen, file='ch_int_10_20_fe.genx', struct=tran
IDL> ch_line_list, tran, 'ch_line_list.ascii', /ascii,$
abundfile=concat_dir(concat_dir(!xuvtop,'abundance'),'allen.abund'),$
mini=1e13
Alternatively, you can also use the wrapper routine
IDL > ascii_wvl_dem,100.,200.,pressure=1.e+15,mini=1.However, ascii_wvl_dem calls ch_synthetic and ch_line_list, and if you want to modify some of the parameters of ch_line_list (e.g. the minimum intensity) you will have to redo the calculation which will take some time.
For example, to calculate the free-free, free-bound and two-photon continuum at a temperature of 5 × 106 K, for wavelengths at 1 Å intervals between 1 and 50 Å:
freefree,5.e+6,findgen(50)+1.,ff freebound,5.e+6,findgen(50)+1.,fb two_photon,5.e+6,findgen(50)+1.,tp window,0 plot,findgen(50)+1.,ff+fb+tp,xtit='Wavelength (A)' oplot, findgen(50)+1.,ff,line=2 oplot, findgen(50)+1.,fb,line=3 oplot, findgen(50)+1.,tp,line=4
|
Note that the intensities are in units of 10-40 ergs cm3 s-1 sr-1 Å-1 per unit emission measure òNH Ne dh (cm-5).
If DEM values are passed to the routines (via the keyword DEM_INT), it is assumed that they are given as NH Ne dh/dT . The units are 10-40 ergs cm-2 s-1 sr-1 Å-1 in this case.
The structure created by CH_SYNTHETIC can be restored via CH_SS to create a spectrum. Alternatively, it can be used as an input to the program MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC. This program creates the CHIANTI SPECTRUM structure (read Sect. E.2 for details), an OUTPUT structure similar to the structure created by CH_SYNTHETIC, with some additional tags. The calling sequence is:
IDL> make_chianti_spec, TRANSITIONS, LAMBDA, OUTPUT, BIN_SIZE=BIN_SIZE, $
INSTR_FWHM=INSTR_FWHM, BINSIZE=BINSIZE, $
WRANGE=WRANGE, ALL=ALL, continuum=continuum, $
ABUND_NAME=ABUND_NAME, MIN_ABUND=MIN_ABUND, $
photons=photons, file_effarea=file_effarea, $
err_msg=err_msg, verbose=verbose
The routine has many keywords and options. Please read Sect. for details.
IDL> restgen, file='ch_int_10_20_fe.genx', struct=tran
IDL> make_chianti_spec, tran, lambda, struct,/CONTINUUM, $
BIN_SIZE=0.01, instr_fwhm=0.1, WRANGE=[10.,19.],$
abund_name=concat_dir(concat_dir(!xuvtop,'abundance'),'cosmic.abund')
|
Some Caveats:
You may find that the calculation is slow. This is usually due to the continuum calculation. In general, it is advisable not to calculate spectra over large wavelength ranges. In any case you can speed up the continuum calculation by reducing the numbers of elements, using the KEYWORD MIN_ABUND.
To see the contents of the structure:
IDL> help, struct,/st IDL> help, struct.lines[0],/st
While to show the spectrum and the main contributing lines:
IDL> window,0 & plot,struct.lambda,struct.spectrum
for i=0,n_elements(struct.lines) -1 do $
if struct.lines[i].peak gt 7e5 then $
xyouts, struct.lines[i].wvl, struct.lines[i].peak, struct.lines[i].snote
It may be useful to save the SPECTRUM structure, that can be later inspected with the widget CH_SS:
IDL> savegen, file='ch_spectrum_10_20_fe.genx', struct=struct IDL> ch_write_fits, struct, 'ch_spectrum_10_20_fe.fits'
Alternatively, the wrapper routine SYNTHETIC (see Fig 1) can also be used to calculate CHIANTI line intensities. For example:
IDL > synthetic, 150., 200., 1., pressure=1.e+15, wvl, spectrum, list_wvl, list_ident
will create a synthetic spectrum with a resolution of 1 Å between 150 and 200 Å for a specified set of abundances and differential emission measure at a constant pressure of 1.e+15 (Ne T cm-3 K). The output arrays wvl, spectrum contain the wavelengths and the intensities (in erg cm-2 s-1 sr-1 Å-1 by default). The output arrays ist_wvl, list_ident contain the list of wavelengths and descriptions of the lines that made up the spectrum.
Windows will pop up so that the user can select the abundance file, the ionization equilibrium and the differential emission measure. A spectrum is created by convolving with a Gaussian profile with a FWHM of 1 Å. If the /CONTINUUM keyword had been set, then the continuum would also have been calculated and added to the spectrum. To plot the spectrum and interactively identify lines:
IDL > synthetic_plot, wvl, spectrum, list_wvl, list_ident, 2.
by clicking the left mouse button, a list of predicted lines within 2 Å of the selected wavelength will be printed out along with their predicted intensity. Clicking the right mouse button will exit the procedure.
For an user-friendly approach the best option is to use CH_SS:
IDL >ch_ss
Alternatively:
IDL > isothermal, 150., 200., 1., [1.e6], wvl, spectrum,$
list_wvl, list_ident, edensity=1.e9,$
ioneq_name=!xuvtop+'/ioneq/mazzotta_etal.ioneq',$
abund_name=!xuvtop+'/abundance/cosmic.abund'
IDL> synthetic_plot, wvl, spectrum, list_wvl, list_ident, 1.
calculates an isothermal synthetic spectrum with a resolution of 1 Å between 100 and 200 Å for a specified set of abundances and differential emission measure at a constant density Ne = 109 cm-3. The output arrays wvl, spectrum contain the wavelengths and the intensities (in erg cm-2 s-1 sr-1 Å-1 by default). The output arrays ist_wvl, list_ident contain the list of wavelengths and descriptions of the lines that made up the spectrum. synthetic_plot can then be used to view the spectrum.
Note: isothermal now is a wrapper routine that calls ch_synthetic . It has particular features. Please read the header documentation.
|
CH_SS is an user-friendly multi-purpose (see Fig 1) widget that allows the calculation of line intensities (calling CH_SYNTHETIC) and of a synthetic spectrum (calling MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC) by merging line intensities and continua. The parameters can be interactively set, and the results visually inspected. Line intensities can be saved and restored in various ways. The results can also be stored in various ways, ranging from output plots to tables of line details (using CH_LINE_LIST) or save files.
CH_SS replaces the CHIANTI_SS procedure. The calling sequence is:
IDL> ch_ss, font=font
Note that if the widget appears too large you can change the font. The widget is organised into four Sections:
This can be done in two ways:
1-Restore a save file with the CHIANTI line intensities already calculated. This is done with the RESTORE button. .genx and .fits files can be restored.
2-Calculate CHIANTI line intensities with a call to CH_SYNTHETIC.
In this case, A series of parameters must be set:
If set to no, then it is possible to select a list of ions with a widget
If set to yes, also the lines that do not have corresponding observed energy levels are included. In this case, the wavelengths are calculated from the theoretical energy levels, and might not be very accurate.
If set to yes, then the user is requested to enter one or more temperatures (as logarithmic values - Log T ) and correspondent column emission measures EM logarithmic values. NOTE: if more than one value is entered, then the sequence must be separated by commas (e.g.: 6.0, 6.5, 7.), and both Log T and Log EM must have the same number of values
Once all the parameters have been defined, the user should click on the "Calculate intensities" button to start the calculation (which calls CH_SYNTHETIC).
Once the calculation is finished, an IDL structure is loaded into memory. It is then possible to save it for later use by clicking on the "SAVE" button.
Once the IDL structure with the line intensities is in the memory, it is then possible to calculate and plot a spectrum (SECTION 2).
This section controls the parameters that are needed to fold the line intensities and the continua into a synthetic spectrum. These parameters are used by MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC.
Before this is done, a set of line intensities MUST be in the program memory. This is done either by calculating the intensities or by restoring a save file with previously calculated values (SECTION 1). Setting the parameters:
Also note that to have the correct output units (counts s-1 bin-1) the appropriately scaled DEM (or EM) values must be provided.
After this, by clicking on the "Calculate and plot" button the program calculates and plots the synthetic spectrum.
Once the spectrum is displayed, it is then possible to view the details of the lines by clicking with the mouse in the plot window, and to perform various operations by clicking on the buttons in SECTION 3
This Section allows the user to select a few parameters for the plotting, and to create different types of OUTPUT.
NOTE that only the line details and portion of the spectrum shown will be output.
Finally, SECTION 4 is a text information window, where various messages are printed.
Clicking the cursor on any part of the displayed spectrum will give a listing of the lines within a range of Angtroms of that wavelength. Text information on the lines is printed.
The radiation function used in Sect. 2.2 of the v.5 CHIANTI paper for studying the O VI Doppler dimming problem is defined below.
FUNCTION o6_lines, lambda, a ; Vernazza & Reeves (1978) give the quiet Sun O VI 1032 flux to be ; 305.28 erg/cm2/sr/s. The 1038 line is blended with C II, so I take ; it to be half of the 1032 line. I assume the FWHMs of the lines are ; 0.2 angstroms. ; ; A Velocity (km/s) relative to emitting ions of the structure emitting ; the radiation field. A positive velocity implies a redshift. IF n_elements(a) EQ 0 THEN a=0. siz=size(lambda) spectrum=dblarr(siz[1],siz[2]) cc=2.998d5 ; speed of light, km/s p1=305.28/0.2 p2=p1/2. c1=1031.914 c1=c1+ (a/cc * c1) ; c2=1037.615 c2=c2+ (a/cc * c2) w=0.2/2.35 i=where(abs(lambda-c1) LE 6.*w) IF i[0] NE -1 THEN spectrum[i]=p1*exp(-(lambda[i]-c1)^2/2./w^2)*4.*!pi/2.998d10 i=where(abs(lambda-c2) LE 6.*w) IF i[0] NE -1 THEN spectrum[i]=spectrum[i]+p2*exp(-(lambda[i]-c2)^2/2./w^2)*4.*! pi/2.998d10 return,spectrum END
This function can then be used in show_pops or emiss_calc as follows:
IDL> show_pops,8,6,radfunc='o6_lines, 20',rphot=1.1
where 'o6_lines, 20' indicates that the velocity A is set to 20 km/s. A zero velocity can be set simply by using radfunc='o6_lines'. RPHOT specifies the distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
The effects of many different velocities can be studied by doing, e.g.,
v=findgen(11)*10. for i=0,10 do begin radfunc_string='o6_lines, '+trim(v[i]) show_pops,8,6,radfunc=radfunc_string,rphot=1.1 endfor
Up to 2 input parameters are allowed for radfunc and are specified by, e.g., radfunc='radfunc, a, b'.
Currently the RADFUNC= keyword is only available for the routines show_pops and emiss_calc.
Another example of radfunc is a blackbody
function udens_bb, lambda t=6d3 ; temperature of Sun, 6000 K ee=1.439d8/lambda/t result=8.*!pi*1.986d-8/lambda^2*(1d8^3)/lambda^3/((exp(ee)-1)) return,result END
which is specified to show_pops as
IDL> show_pops,8,6,radfunc='udens_bb',rphot=1.1
The user should verify that this gives the same results as using the standard CHIANTI inputs
IDL> show_pops,8,6,radtemp=6000.,rphot=1.1
The following commands reproduce the numbers in Table 3 of the v.5 CHIANTI paper (Landi et al. 2005). Basically, we want to study the effects of non-Maxwellian distributions on two key line ratios of O VI, involving the strong lines at 1032 Å, 173 Å and 150 Å. We consider a distribution comprised of two Maxwellians at log T=5.5 and log T=6.0, with the coefficients [a1,a2]=[0.75,0.25].
IDL> em=emiss_calc(8,6,temp=[5.5,6.0],sum_mwl_coeff=[0.75,0.25],dens=9.0)
IDL> em150=em[40].em
IDL> em173=em[43].em
IDL> em1032=em[77].em
IDL> print,em150/em1032,em173/em1032
0.030072876
0.043500302
The effects of non-Maxwellians on level populations can be demonstrated with the show_pops routine, e.g.,
IDL> show_pops,8,6,lev=-8 Log10 density: 10.0 Log10 temperature: 5.5 1 1s2.2s 2S1/2 1.00e-00 2 1s2.2p 2P1/2 2.30e-07 3 1s2.2p 2P3/2 4.52e-07 4 1s2.3s 2S1/2 5.07e-11 5 1s2.3p 2P1/2 7.26e-12 6 1s2.3p 2P3/2 1.44e-11 7 1s2.3d 2D3/2 5.30e-12 8 1s2.3d 2D5/2 7.96e-12 IDL> show_pops,8,6,lev=-8,temp=[5.5,6.0],sum_mwl_coeffs=[0.75,0.25] Log10 density: 10.0 Using a sum of Maxwellians 1 1s2.2s 2S1/2 1.00e-00 2 1s2.2p 2P1/2 2.26e-07 3 1s2.2p 2P3/2 4.43e-07 4 1s2.3s 2S1/2 8.93e-11 5 1s2.3p 2P1/2 1.60e-11 6 1s2.3p 2P3/2 3.16e-11 7 1s2.3d 2D3/2 1.13e-11 8 1s2.3d 2D5/2 1.69e-11
where it can be seen that the n=3 level populations are enhanced by factors 2 by the high temperature component to the distribution.
To plot the populations of the first 4 levels of Si III as a function of density at a temperature of 3 x 104 K:
IDL > plot_populations,'si_3',3.e+4,4
|
Optionally, output files can be created.
Alternatively, SHOW_POPS can be used. This routine has a large range of features implemented via keywords.
To assess the contributions of the different physical processes to the population of a specified level within an ion, use POP_PROCESSES.
IDL> pop_processes,'fe_13',lev=4
Level: 3s2.3p2 1D2
Log10 Temperature: 6.2
Log10 Density: 10.0
Population leaving level 4
rad. decay: 1.60e+01 42.50%
e de-exc: 3.29e-01 0.87%
e exc: 2.10e+01 55.88%
p de-exc: 2.44e-01 0.65%
p exc: 3.75e-02 0.10%
stim. emiss: 0.00e+00 0.00%
photoexc: 0.00e+00 0.00%
--------
TOTAL 3.77e+01
Population entering level 4
rad. decay: 3.50e+01 92.98%
e de-exc: 3.38e-02 0.09%
e exc: 1.47e+00 3.92%
p de-exc: 2.81e-03 0.01%
p exc: 1.13e+00 3.01%
stim. emiss: 0.00e+00 0.00%
photoexc: 0.00e+00 0.00%
--------
TOTAL 3.77e+01
which shows that the level population is dominated by electron excitation and cascading into the level, and by radiative decay out of the level.
Note that the rates for each physical process are multiplied by the population of originating level (this results in the totals for entering and leaving the level to balance).
If you want to list the lines within one ion around some wavelengths, you can use WHICH_LINE. For example,
IDL> which_line,'o_6',1032
Wavelength i j Lower level Upper level A-value
* 1031.914 1 3 1s2.2s 2S1/2 - 1s2.2p 2P3/2 4.28e+08
1037.615 1 2 1s2.2s 2S1/2 - 1s2.2p 2P1/2 4.21e+08
Prints a list of atomic transitions and wavelengths for lines from O VI within 1% of the input wavelength (1032 Å).
If you are interested to see the differences between the various ionisation equilibria for e.g. Mg, you can use:
IDL > plot_ioneq,'Mg'
You will be able to select one of the files, and optionally create a postscript file of the plot.
|
If you are only interested in e.g. the Mg VIII, Mg IX, Mg X ions, you can type:
IDL > plot_ioneq,'Mg', ion=[8,10]
If, instead, you are interested in obtaining the temperature at the maximum ionisation fraction for e.g. Mg X, you can use:
IDL > print, max_temp ('Mg X')
You will be asked to select an ionisation equilibrium file.
Spectroscopic diagnostic line ratios in the UV wavelength range have been used extensively to determine the electron density and temperature in the solar atmosphere (cf Dere and Mason, 1981, Gabriel and Mason, 1982, Mason, 1991, Mason and Monsignori Fossi, 1994). The theoretical intensity ratios from individual ion species provide a measurement of electron density which is independent of any assumptions about the volume of the emitting region. This is of particular importance in the transition region and coronal structures. The electron density (which determines the electron pressure) is an essential parameter in the study of energy transfer mechanisms. The routines that can be used are described below.
DENS_PLOTTER and TEMP_PLOTTER are high-level widgets for the analysis of density- and temperature-sensitive ratios of lines from the same ion. They allow inclusion of proton rates and photoexcitation. The calling sequence is simple:
IDL > dens_plotter,'o_5'
to study O V.
IDL > temp_plotter,'c_4'
to study C IV.
Alternatively, you can use the command-line routines, DENSITY_RATIOS and TEMPERATURE_RATIOS. They also allow inclusion of proton rates and photoexcitation via KEYWORDS.
The routine DENSITY_RATIOS plots the variation of line intensities with electron density, allowing density diagnostics to be studied. As an example, we can look for density sensitive line ratios of O V in the 1000 to 1500 Å wavelength region for densities between 108 and 1013 cm-3:
IDL > density_ratios,'o_5',1000.,1500.,8.,13.,den,rat,desc
two windows will open and plot the relative intensities of a few O V lines. To choose the ratio of 1371.294 to 1218.393 Å line, select first the 1371.294 Å line. Another widget will appear to select the denominator. Select the 1218.393 Å line. This will chose the ratio of 1371.294 to 1218.393 which will be plotted in a new window. Values of the density and intensity ratio will be put into the variables den and rat and desc will contain a descriptive string.
IDL > print, desc IDL > CHIANTI V. 4.0 O V 1371.2939 (Å)/1218.3929 (Å) T = 2.51e+05 (K)
The DENSITY_RATIOS procedure also allows to calculate the ratio at user-defined value of constant temperature. Blends are accounted for via a selection of lines.
To calculate temperature sensitive line ratios of C IV for lines between 100 and 1600 Å for temperatures between 104 and 106 K:
IDL > temperature_ratios,'c_4',100.,1600.,4.,6.,temp,rat,desc
As with density_ratios, a widget will appear that will allow you to select the numerator. Select the 384.175 and 384.190 Å lines as these will typically be blended in most spectrographs. Select the 1550.775 Å line for the denominator. The ratio of (384.175 + 384.190 Å) to the 1550.775 Å line as a function of temperature will be plotted and stored in the variables rat and temp, respectively. The TEMPERATURE_RATIOS procedure also allows to calculate the ratio at user-defined values of either constant pressure or constant density.
IDL > print, desc IDL > CHIANTI V. 4.0 C IV 384.1750+384.1900 (Å)/1550.7750 (Å) Ne = 1.00e+10 (cm!e-3!n)
The IDL procedure which calculates line intensity ratios as a function of electron density is called CHIANTI_NE. Another IDL procedure to calculate ratios sensitive to electron temperature is called CHIANTI_TE. For example,
IDL > chianti_te
Or
IDL > chianti_ne
User interactions with the main widget setup the wavelength range and other parameters that are described individually below. On the left hand side are controls for wavelength and electron density or temperature selection and on the right hand side for ion selection.
Ion selection
Select first the element and then the ion stage using the pull-down menus. Only those elements and ions currently available in the CHIANTI database are displayed for selection.
Wavelength ranges
There are up to 4 wavelength ranges that can be defined in order to restrict the calculation (and the number of lines). At least one should be defined. Default is to calculate all lines from 1 to 1700 Å.
Electron Density/Temperature Range
For CHIANTI_NE, select the electron number density range (Log10Ne) over which the intensity ratios are calculated. Default values are 106 to 1014 cm-3. The intensity ratios are calculated at constant temperature corresponding to the peak ionic abundance Tmax, unless the value of the temperature is typed in.
For CHIANTI_TE, select the electron temperature (Log10Te) over which the intensity ratios are calculated. Default values are 104 to 108 K. The intensity ratios are calculated at a constant electron number density corresponding to 108 cm-3, unless a different value is typed in.
minimum intensity ratio
The relative intensity of all the lines found in the wavelength range is calculated. Only the lines that have an intensity (relative to the brighter one) greater than 0.0001 (by default) are selected and displayed.
Units for the ratio plot
The ratios can either be calulated from the relative intensities in ergs (default) or photons.
Controlling the procedure
The action of both CHIANTI_NE and CHIANTI_TE is controlled via the buttons in the central panel of the display. From left to right these are:
QUIT - click on this to exit from the program, all plot windows are also deleted.
CALCULATE LINE INTENSITIES - using the wavelength ranges as defined in the widgets above. Two plots will apear in the window - on the left the Ni*A/Ne and on the right the intensity ratios, where Ni is the level population and A is the radiative transition probability (s-1). A list of spectral lines in the given wavelength range for that ion is displayed in the message window. The reference index is in the first column, then the wavelength, intensity and transition.
PLOT RATIO - prompts for and then plots specific line intensity ratios, using line indices available from the list. The ratios within a particular ion can be stored for later use using the SAVE button. To allow for blended lines in the observed spectra, multiple line indices can be given for the numerator and denominator. The format is fairly flexible but the nominator and denominator specification must be separated by a '/'. Otherwise the line indices can be separated by spaces or commas. The ratio values can be plotted either with a linear or a log scale.
HARDCOPY - the menu under this button will allow a variety of hardcopy plots (ratio plots or intensity plots) and the line details (+refs), which gives a record of the input. A line ratio has to be defined.
SAVE - it is sometimes useful to save the plotted line intensity ratios to study several different ions. You will be asked to enter file name to store ratio data. A line ratio has to be defined.
In the CHIANTI_NE case, a .CH_NE will be appended. An IDL structure called NE_RATIO will be saved. It has the TAGS: DENSITY,RATIO, TEMPERATURE, UNITS, COMMENT, DESC. The first two have the arrays of the densities and ratios, TEMPERATURE has the value of the constant temperature used, while the last three have a description of the units used, how the calculation was performed, and a description of the lines used to defined the ratio.
In the CHIANTI_TE case, a .CH_TE will be appended. An IDL structure called TE_RATIO will be saved. It has the TAGS: TEMP, RATIO, DENSITY, UNITS, COMMENT, DESC. The first two have the arrays of the temperatures and ratios, DENSITY has the value of the constant density used, while the last three have a description of the units used, how the calculation was performed, and a description of the lines used to defined the ratio.
Please note that previous versions of the above routines did not create the TEMPERATURE (DENSITY), UNITS, COMMENT tags.
The save file can be restored and replotted outside of CHIANTI_NE and CHIANTI_TE using the procedures PLOT_CHIANTI_NE and PLOT_CHIANTI_TE respectively, or used within user-defined procedures.
DELETE PLOT WINDOWS - to clear the ratio plots from the screen.
The ratio values stored in the save files created with the CHIANTI_NE and CHIANTI_TE routines can be replotted outside of CHIANTI_NE and CHIANTI_TE using the procedures PLOT_CHIANTI_NE and PLOT_CHIANTI_TE respectively. For example,
IDL > plot_chianti_te
Or
IDL > plot_chianti_ne
If no files are specified, a widget allows you to select any '*.CH_NE' or '*.CH_TE' files.
A LOG keyword allows the user to have the plot in a log scale.
It is also now possible to interactively modify the X and Y ranges and to create a postscript file. Users can modify these routines to e.g. over-plot observed data points.
Note: If you are interested in determining an isothermal temperature by using the ratio of lines emitted by different ions (and/or elements), then a possible way is to first calculte the contribution functions of the lines you are interested, and then calculate their ratio. Note, however, that such determinations can be very inaccurate, since they depend on the ionisation equilibrium chosen (and eventually on the element abundance).
To calculate the contribution function ( erg cm3 s-1 sr-1 by default) vs. temperature at a specified abundance, ionization equilibrium and pressure or density for the Fe XXIV line at 255.1 Å:
IDL > gofnt,'fe_10',170.,180.,temperature,g,desc
temperature, g are the arrays with the temperatures and the G(T) values. It is possible to calculate the G(T) at either constant electron density or pressure, via the KEYWORDS DENSITY or PRESSURE.
The KEYWORDS ABUND_NAME, IONEQ_NAME allow to run the routine in the background, giving names of the abundance and ionization fractions files.
The routine GOFNT allows the user to select a number of lines. If this is done, then the total sum of the G(T)'s of the selected lines is returned and plotted.
Optional outputs can be created. The default units are erg cm3 s-1 sr-1, unless the KEYWORD /PHOTONS is set, in which case the units are photons cm3 s-1 sr-1.
A procedure ('RAD_LOSS') calculates the total radiative loss rate as a function of temperature for specified set of abundances and/or ionization equilibria:
IDL > rad_loss,temperature,loss_rate
|
Given a set of observed spectral intensities, the problem is to invert a system of integral equations like the previous one. The procedure CHIANTI_DEM solves the system and calculates the DEM(T).
The inversion problem itself is not simple and requires some assumptions about the nature of the solution. A series of workshops was sponsored in 1990/91 to study differential emission measure techniques (Harrison and Thompson, 1992). It was found that most codes eventually gave consistent results, but that the DEM derived depends rather critically on the methods used to constrain the solution and the errors in the observed intensities and atomic data.
It is advisable to select a number of well resolved, unblended lines which are not density sensitive, emitted by various elements over a wide temperature interval. Appropriate values of the pressure (or density) and the elemental abundances must be chosen according to the region of the Sun being observed. The pressure value can be obtained once the values of the temperature and the density are estimated. To estimate the electron density the procedure CHIANTI_NE can be used. The temperature can be estimated for example using the procedure CHIANTI_TE.
The contribution functions C (T,lij,Ne) can be calculated using CHIANTI_DEM either at constant pressure or at constant electron density. It is also possible to vary the elemental abundances before starting the fit to deduce the DEM.
Many papers have been written on solar elemental abundances. See e.g. Meyer (1993) Widing and Feldman (1992), Mason (1992, 1995). A possible approach in determining elemental abundances is to use the detailed shape of the DEM distribution for ions from the same element and apply an iterative procedure to normalize the curves for different elements (e.g. Fludra and Shmelz 1995, Del Zanna et al. 1995).
The CHIANTI_DEM procedure
The main IDL routine which has been written to perform a differential emission measure analysis of EUV spectra using the CHIANTI atomic database is CHIANTI_DEM. Other procedures required to run CHIANTI_DEM are GET_CONTRIBUTIONS , DEM_FIT, ZION2SPECTROSCOPIC and Z2ELEMENT. The resulting DEM may then be used by other procedures to calculate a synthetic spectrum.
This package of routines will be replaced in the future by new more versatile versions.
The main inputs required by CHIANTI_DEM are :
1) the observed wavelength lobs [Å].
2) The observed flux Iobs in ergs cm-2 s-1 sr-1.
3) The corresponding error sobs on the flux in ergs cm-2 s-1 sr-1.
4) The value of dl [Å]. All the theoretical lines that may have contributed to the observed lines, i.e. that have a theoretical wavelength ltheo in a lobs ±dl range will be searched for. This value should correspond to the spectral resolution of the instrument at that wavelength.
5) The identification, written as a string of up to 20 characters. For example:
171.114 4811.0 1443.0 0.25 Fe IX
174.604 4005.0 1202.0 0.25 Fe X
180.448 3877.0 1163.0 0.25 Fe XI bl Fe X
195.149 3443.0 1033.0 0.25 Fe XII
Once the file with the observed fluxes is read, another IDL procedure, GET_CONTRIBUTIONS, is called by CHIANTI_DEM in order to calculate the contribution functions C(T,lij,Ne) at the given constant density or pressure.
GET_CONTRIBUTIONS searches the CHIANTI database for all the theoretical lines that may have contributed to the observed lines, i.e. that have a theoretical wavelength ltheo in a lobs ±dl interval.
Then, for each theoretical line selected, it calculates the C values for the temperature interval log(T)= 4.0 - 8.0 in steps of log(T) = 0.1.
If a constant pressure is selected, for each ion the contribution function is calculated at an electron density Ne equal to the ratio of the pressure and the temperature of maximum ionization fraction.
The C(T) values are stored by GET_CONTRIBUTIONS in the output file output.contributions that can be used later, if required, to re-calculate the DEM, changing various parameters (e.g. the abundances), without having to start again and read the CHIANTI database, which can take a long time.
The observed lines with no theoretical counterparts are automatically excluded. If this happens, you might consider starting again with a larger dl, to see if there are theoretical lines in the vicinity of the observed one.
Then you are asked to select an *.abund file present in the CHIANTI database or in the working directory, and eventually edit it, if you want to change some abundances.
The G(T) are calculated, multiplying each theoretical line by the abundance factor. The theoretical lines contributing to each blend are sorted by intensity and then their G(T) can be plotted if the keyword PLOT_GT was activated. It is recommended to do this the first time, to check if there are some observed lines which are heavily blended with lines of other elements. It might be better to exclude such lines in a second run.
The G(T) for each blend are then summed and plotted, and the calculation of the DEM starts, using the fitting routine DEM_FIT. A series of parameters can change the result (DEM), especially the number and position of the mesh points of the spline that represents the DEM. The fitting procedure is based on Bevington's Data Reduction and Error Analysis for the Physical Sciences. fortran programs.
The iteration is controlled using key-words (see below).
A series of outputs are created, all having extensions of the output name. For example, using test as the output name:
The abundance file, the ionization equilibrium file and the pressure used are written at the beginning.
Then there is one line for each observed line, with the identification present in the input file, the observed wavelength lobs, the observed flux Iobs, the calculated flux Itheo , the error on the flux sobs, the value ([(Itheo - Iobs)/(sobs )] )2 and finally the value of [(Itheo)/(Iobs)]
After this line, there is one line for each theoretical line contributing to the blend, with the identification, the theoretical wavelength ltheo, the configuration and terms, and the contribution (as a percentage) of each line in the blend to Itheo.
The first one has the G(T) of all the lines then used for the fit, with all the contributions for each line summed ( the labels refer to the identifiacation given in the input file).
The file test_dem.ps has the DEM (T) with the scales set as in the interactive session. The points are plotted at the temperature where the product G(T)*DEM(T) has a maximum. It is possible to label the points with the comment string present in the input file, or to use the dominant ion in the blend.
The file test_4plots.ps has some additional plots. The upper-right figure of test_4plots.ps plots the values [(Itheo)/(Iobs)] versus the temperature where G(T) has it's maximum.
The action of CHIANTI_DEM is controlled via the following keywords.
The default units are ergs cm-2 s-1 sr-1.
The default units are ergs cm-2 s-1 sr-1.
If set, it has to specify the name of the file previously created by GET_CONTRIBUTIONS, where all the contribution functions C(T) are stored.
There are also some actions controlled via the keyboard.
When you are asked for an answer ( [y/N] ) yes or no you should either type in y or n. The capital letter in [y/N] means that the default choice is n which is what you get if you simply hit the return key. In case you have [Y/n], hitting the return key is the same as choosing y .
You must specify the output file name and the value of the pressure (or the density). The input file name is optional.
IDL > CHIANTI_DEM,OUTPUT='test',FILE_INPUT='test_obs',PRESSURE=1e16,/PLOT_GT
Select the ionization equilibrium file (e.g. Arnaud & Raymond). If there are no problems about N_MATCHES, the routine will select the lines having max( C(T) ) ³ 10-30 and write the C(T) values to the file test.contributions.
Then you'll be asked to select an abundance file and if you want to edit it. Pick up the Feldman abundances. Then the G(T) are calculated, multiplying each theoretical line by the abundance factor, sorted (within each blend) by their max( G(T) ) value, and plotted ( see Fig. 8).
|
It is recommended that you check the plots at least once, to see if there are some observed lines that it might be better to exclude in a second run, for example because they are blends. Also check if your identifications are consistent with the lines found in the CHIANTI database.
The G(T) for each blend are then summed, and plotted ( see Fig. 9).
|
At the end of the fit, the files test.dem, test.general, test.out are created.
Have a close look at these outputs, and check if there are emission lines not well represented by the fit or with no theoretical counterparts.
You can use the routine a second time, excluding some of the lines, and/or varying some of the fitting parameters. In particular, changing MESH_POINTS or starting from an appropiate DEM can affect the resulting DEM. For example:
IDL> CHIANTI_DEM,OUT='test',FILE_IN='test_obs',FILE_GT='test.contributions', $ IDL> EXCLUDE_OBS_WVL=[ 284.153 ] ,$ IDL > MESH_POINTS= [ 4.85, 5.6, 6.25, 7.0 ],N_ITER=40
The files test.dem, test.general, test.out will be created.
Eventually, also the files test_dem.ps test_4plots.ps may be created.
|
Fig. 10 shows the resulting DEM. The error bars on the points simply reproduce the error on the observed fluxes.
|
The Fig. 11 is self-explanatory. The DEM figure is repeated in the upper-left plot with the same scale of the previous plot.
The file test.out , toghether with test.dem, can be used to reproduce these plots using user-written software. If the only concern is the postscript output, then users just have to copy the routine in the working area and modify the top procedure PRINT2D_PLOT.PRO that controls the postscript device. The default is landscape.
This package is mostly intended to be a quick method to obtain a DEM which can then be used to calculate a synthetic spectrum, to be compared with the observed data.
Try to give as input lines covering a broad range in temperatures, and that are not density sensitive.
Try to adjust the location of the mesh points.
If the resulting DEM does not give a good fit to the data, it might be a good idea to start again calculating the G(T) with different abundances or to check the effect of blends.
Try a different DEM as a starting point, but be careful about the end points at lower and higher temperatures where usually there are no constraints (no observed lines).
Consider the possible effect on the DEM of different structures along the line of sight. It is important to realise that the DEM gives an indication of the amount of plasma at different temperatures along the line of sight, assuming constant density or pressure. It is not therefore possible to infer direct information about the variation of the temperature with height from this function. The inclusion of density-sensitive lines in the fit may also cause problems.
Send comments to : Giulio Del Zanna g.del-zanna@damtp.cam.ac.uk
The previous routines have been modified as described:
Compared to the previous version, these are the main changes:
1-Rewritten as a wrapper routine using the new procedures.
2-Now the PRESSURE value is a keyword.
3-The calculations can be done at constant DENSITY.
4-Energies (keV) can be output instead of wavelengths in Angstroms
5-MASTERLIST can now be used both as an input string or as a keyword.
Compared to the previous version, these are the main changes:
1-Rewritten as a wrapper routine using the new procedures.
2-Now the PRESSURE value is a keyword.
3-The calculations can be done at constant DENSITY.
4-MASTERLIST can now be used both as an input string or as a keyword.
Compared to the previous SYNTHETIC, these are the main changes:
1-Rewritten as a wrapper routine using the new procedures.
2-Now the PRESSURE value is a keyword as the DENSITY value
3-The keyword CONT is now renamed CONTINUUM
4-Added keywords
PHOTONS (If set, intensities are in photons instead of ergs)
DEM_NAME, ABUND_NAME, IONEQ_NAME, to run the routine in the
background, giving names of the
DEM, abundance and ionization
fractions files.
NOPROT (If set, then proton rates are not included.)
RADTEMP, RPHOT (to include photoexcitation)
5-MASTERLIST can now be used both as an input string or as a keyword.
6-The description of the line details now has the spectroscopic designation at the end.
Is left unchanged except for a few minor changes.
Aside from a few small fixes, these are the main changes:
1-Rewritten as a wrapper routine using the new procedures.
2-Added keywords
ABUND_NAME, IONEQ_NAME, to run the routine in the
background, giving names of the
abundance and ionization
fractions files.
NOPROT (If set, then proton rates are not included.)
RADTEMP, RPHOT (to include photoexcitation)
Compared to the previous routine, these are the main changes:
1-Rewritten as a wrapper routine using the new procedures.
2-Added keywords
ABUND_NAME, IONEQ_NAME, to run the routine in the
background, giving names of the
abundance and ionization
fractions files.
NOPROT (If set, then proton rates are not included.)
RADTEMP, RPHOT (to include photoexcitation)
EM Emission measure values.
Is not distributed nor supported anymore. Is now replaced by ch_ss.pro
Compared to the previous routine, these are the main changes:
1-Modified the plotting, adding information about the single lines.
2-Added keywords
NOPROT (If set, then proton rates are not included.) RADTEMP, RPHOT (to include photoexcitation)
Compared to the previous routine, these are the main changes:
1-Rewritten as a wrapper.
2-Added keywords
NOPROT (If set, then proton rates are not included.) RADTEMP, RPHOT (to include photoexcitation)
2-Added keywords
PHOTONS (If set, intensities are in photons instead of ergs) IONEQ_NAME The ionization fractions file. NOPROT (If set, then proton rates are not included.) RADTEMP, RPHOT (to include photoexcitation)
The call is the same, but the calculations are done using the fitting formulae of Itoh et al. (ApJS 128, 125, 2000) and Sutherland (MNRAS 300, 321, 1998). Also, a few bugs have been fixed.
Added the keyword
PHOTONS (If set, intensities are in photons instead of ergs)
-Added keywords
NOPROT (If set, then proton rates are not included.) RADTEMP, RPHOT (to include photoexcitation)
These routines are in the other/ subdirectory:
Unchanged.
Unchanged.
Widget unchanged but the low-level routine now uses emiss_calc.pro.
Unchanged.
Widget unchanged but the low-level routine now uses emiss_calc.pro.
Unchanged.
Changed the low-level routine that calculates the G(T), to account for the v.4 variations. The proton rates are included in the calculation of the level population.
Unchanged.
Routines in the extra/ subdirectory:
Is now a wrapper routine calling the widget RATIO_PLOTTER
Is now a wrapper routine calling the widget RATIO_PLOTTER
A few keywords have been added/ modified, mainly as an update for V.4.
A few keywords have been added/ modified, mainly as an update for V.4.
A few keywords have been added/ modified, mainly as an update for V.4.
A few keywords have been added/ modified, mainly as an update for V.4.
A few keywords have been added/ modified, mainly as an update for V.4.
This section describes the changes applied to the CHIANTI database and software in order to include the proton rates.
The proton rate data files have suffices .psplups and have the following format
2 3 2 0.000e+00 1.027e-02 8.000e+02-2.150e-13 1.052e-13 4.397e-12 \ 2.232e-11 5.389e-11 8.708e-11 1.014e-10 7.658e-11-2.805e-12
(The \ indicates a break in the line.) Note that the Z and spectroscopic number are not given for each ion, in contrast to the electron files. The rest of the line is the same as that for the electron files, except in this case there are 9 spline values as a 9-point spline was fitted to the data.
This is done by the routine read_splups.pro which loads the data into an IDL structure. The call is
IDL> read_splups_ns, filename, splstr, splref , /prot
The structure splstr has the following tags
.lvl1 lower level index
.lvl2 upper level index
.t_type transition type
.gf gf value
.de Delta-E for transition (rydbergs)
.c_ups the scaling parameter
.nspl number of spline points
.spl Vector of length 9, containing spline points
The routine pop_solver solves the set of linear equations that determine the level balance of the ion. To include proton rates, an extra matrix containing the proton rate coefficients needs to be added to the equations. This matrix is created within pop_solver from the splstr structure mentioned above.
Note also that the same routine is used to descale the spline fits into proton rates as to descale the electron spline fits. This routine is descale_all.pro and is called as
descale_all, temp, splstr, index, ups
where temp can be an array of temperatures.
User-written routines can be modified to include proton rates through two steps.
For routines which do not directly call pop_solver, the only changes are to add the keywords noprot=noprot, abund_file and ioneq_file to the routines' argument list, and to the call to the routine that calls pop_solver.
For routines that directly call pop_solver, the following steps need to be followed.
The first is to add the keyword noprot=noprot to the routine's argument list.
The second is to add a common block analogous to those that already exist for the energy level, radiative and electron collision data. This common block is
COMMON proton, pstr, pe_ratio
The third step is to add a line which will read the data. This is
if keyword_set(noprot) then begin
pstr=-1
endif else begin
read_splups, pname, pstr, pref, /prot
endelse
Before the call to pop_solver, the proton to electron ratio must be evaluated. This is done with
pe_ratio=proton_dens(temp)
where temp contains the logarithm of the temperatures that will be passed to pop_solver.
To include the proton rates in CHIANTI it is necessary to know the proton number density Np. This quantity is usually expressed in terms of the ratio relative to the electron density. For a standard solar plasma this is a constant for temperatures beyond log T=4.6 with a value around 0.85. Thus one option is to simply fix the ratio as a constant.
As we want CHIANTI to be applicable for low temperature plasmas, however, we have decided to explicitly calculate the ratio making use of the ion balance and abundance files, that uniquely determine Np. The relevant routine is PROTON_DENS.PRO. Np is calculated from the ion balance and element abundance files contained in CHIANTI through the following expression
| (37) |
where Ab is the element abundance, Ai is the ith element (i.e., A1=H, A2=He, etc.), Z is the charge on the ion, F(Ai+Z, T) is the fraction of ions of element Ai in the form Ai+Z at temperature T.
The ion fractions contained in CHIANTI are tabulated over the range 4.0 £ log T £ 8.0. Above and below these values, we set R(T) to the values for log T=8.0 and log T=4.0, respectively.
The use of this routine has some side effects. Some routines for which the ratio may have some effects in the results don't require you to select the ion balance or abundance files. E.g., DENSITY_RATIOS.PRO does not require the user to select these files, however, at low temperatures one may see significant changes take place in line ratios on account of the change in the proton-to-electron ratio. We deal with this effect by using the default !abund\_file and !ioneq\_file files to derive the proton-to-electron ratio, but allowing the files to be directly specified by the user through keywords if he/she needs to do this.
We have modified the CHIANTI routines so as PROTON_DENS.PRO is called once at the beginning of the routine and the ratio data are passed to POP_SOLVER.PRO through a common block.
The modifications due to the proton-to-electron ratio in user-defined procedures are as follows:
common proton, pstr, pe_ratio
COMMON elements,abund,abund_ref,ioneq,ioneq_t,ioneq_ref
pe_ratio=proton_dens(temp)
The call to PROTON_DENS.PRO thus does not take place within POP_SOLVER.PRO
This section describes the changes in the IDL software required to incorporate the 9-point spline fits.
The modification to the .splups file is simple. Any transitions which are fitted with a 9-point spline will simply have four extra numbers placed on the end of the data line. Transitions fitted with a 5-point spline will be output as normal. Both 5 and 9-point fits can be found in the same .splups file.
This section describes the changes to the read_splups routine, and also the changes required to routines that call directly or indirectly read_splups.
For some routines (such as synthetic, ...?) the reading of the data files is delegated to the routine setup_ion.pro. The data is then transferred to the main routine via common blocks.
Every routine that makes a call to read_splups.pro has to be modified. Two changes are needed:
The read_splups call used to be
read_splups,upsname,t_type,gfu,deu,c_ups,splups,upsref
The new call is
read_splups, filename, splstr, splref [, /prot]
where /prot should be set if proton rates are to be read.
The original common block had the form
COMMON upsilon,t_type,deu,c_ups,splups
The new one should be
COMMON upsilon, splstr
This reads data from .splups or .psplups files into an IDL structure (the previous version read data into several individual arrays). The call is
IDL> read_splups, filename, splstr, splref [, /prot]
The structure splstr has the following tags
.lvl1 lower level index
.lvl2 upper level index
.t_type transition type
.gf gf value
.de Delta-E for transition (rydbergs)
.c_ups the scaling parameter
.nspl number of spline points
.spl Vector of length 9, containing spline points
This routine directly replaces descale_ups.pro in the CHIANTI software. It is called as
descale_all, temp, splstr, index, ups
An important difference is that the temperature is specified directly whereas previously the scaled temperature was given. In addition, several temperatures can be given at once rather than just one.
Note that there is no difference in how this routine treats the descaling of proton rates.
The only place in the CHIANTI software where this routine is called is in pop_solver.pro.
The way electron excitation rates are included in pop_solver has been changed. Only a single for loop is required now as the routine goes through each line in the structure. In addition, the routine can now descale the upsilons for several temperatures simultaneously.
This section describes the features of the routines that are contained in the extra/ directory and that were contributed by Peter Young:
These routines, described in more detail in Sect. D.2 below, have slightly different units of outputs, compared to the other routines.
First of all, Sect. 8 gives the theory
behind the interpretation of optically-thin emission lines which
serves to set out the notation used here.
Going back to Eq. 2, we write
| (38) |
The emissivity of the emission line resulting from a j-to-i
radiative decay is defined as
| (39) |
| (40) |
In order to relate the emissivity to the actual observed intensity of
a line, we make use of the third assumption, which tells us that the
intensity is proportional to the emissivity of the plasma, and so
| (41) |
Expanding el using Eqs 38 and 39 gives
| (42) |
| (43) |
| (44) |
On account of the ionisation fraction F(T) this function is sharply peaked, and a common approximation (e.g., Pottasch [3], Jordan & Wilson [1]) is to assume that G(T) has a constant value over a narrow temperature interval around G(Tmax), where Tmax is the temperature of maximum ionisation for the ion. Here we will use the temperature of maximum emission or Tmem which is the temperature at which Gl has its maximum. Defining
| (45) |
| (46) |
| (47) |
| (48) |
| (49) |
Now, solar emission lines are often measured as intensity (or radiance), I, with units typically of erg cm-2 sr-1 s-1. This quantity is related to Pl by
| (50) |
where dA is the projected area of the emitting element. One thus relates the observed intensity to an emission measure by
| (51) |
where EM(s) is the column emission measure, where s is the line-of-sight depth of the emitting region.
Stellar emission lines are measured in flux (or irradiance), E, with units typically of erg cm-2 s-1. E is related to Pl by
| (52) |
where d is the distance to the object. The observed flux is then related to the emission measure by
| (53) |
If one treats the emitting region as a uniform, spherical shell of thickness h then dV=4pR2dh (R the distance from the star centre of the shell; typically R=R*, the radius of the star) and so the expression for E becomes
| (54) |
where EM(h) is the emission measure over height. The factor 1/2 denotes that half the photons from the shell are emitted towards the stellar surface and so are destroyed. Jordan and co-workers (see, e.g., Jordan & Wilson [1], Jordan & Brown [2]) utilise this definition and an assumption of spherical symmetry to deduce energy balance relations in solar and stellar atmospheres.
The routines are divided into primary and secondary routines. The secondary ones are called by some of the primary routines, and chances are that you won't have to use them too often. They are described in Sect. D.3.
All of the routines have headers which give more detailed information about how they work. This header can be read in the normal IDL way through, e.g., doc_library,'ratio_plotter'.
| (55) |
Example: For Fe XIII, select a line/blend from lines
in the range 200 to 205 Å
pop_plot,26,13,wrange=[200,205]
Note how no single line shows zero density dependence, and so care should be taking in using Fe XIII in emission measure analyses. Compare with Fe XVI:
pop_plot,26,13,wrange=[330,370]
where both the 335 and 360 lines are OK.
This routine calculates Cl, defined in Eq. 47. It displays both this value and the values of DE Cl and 4p/ DE Cl. For lines for which njAji ~ Ne, Cl is insensitive to Ne, but for other lines Ne should be specified. Note that for blended lines only åDE Cl and 4p/ åDE Cl are output. The routine also outputs the Tmem of the lines, accurate to 0.02 dex.
Example: Work out Cl for the Fe XIII lines
between 200 and 205 Å at a density of 109 cm-3.
integral_calc,26,13,wrange=[200,205],dens=9.
From Eq. 51, an observed line intensity of 100 erg cm-2s-1sr-1 for the 202.044 line implies a column emission measure of EM(s) = 100 ×1.614 ×1020 / Ab(Fe), where 1.614 ×1020 is taken from 4pi/DE*C_lambda column of the output.
For Fe XIV, one can do:
integral_calc,26,14,wrange=[210,220],dens=9.
and so to get the same column emission measure for Fe XIV l211.32, an intensity of 100 ×1.614 ×1020 / 2.280 ×1020 = 70.8 erg cm-2s-1sr-1 is required, where 2.280 ×1020 is the value of 4pi/DE*C_lambda for Fe XIV l211.32.
Both temp\_plotter.pro and dens\_plotter.pro call a widget-based routine (ratio_plotter, via the keywords /temp and /dens) that allows the thorough investigation of density or temperature sensitive ratios. Observed line intensities can be input for line ratios, and densities or temperatures derived.
Example: to study density sensitive ratios of Fe XIII, simply
type in
dens_plotter,'fe_13'
Try inputting some line intensities and errors from the SERTS-89 spectrum (Thomas & Neupert [4]), and comparing the derived densities with those found by Young, Landi & Thomas [5] in Table 20.
Gives percentage level populations for all levels within the specified ion that have populations greater than 0.01%.
Example: Compute level populations for Fe XIII at a
density of 1010 cm-3:
show_pops,26,13,dens=10
Eq. 44 gives the definition of the
contribution function as calculated by the g_of_t
routine.
In it's default setting g_of_t.pro actually calculates:
|
Examples:
result=g_of_t(26,13,dens=9.)
result=g_of_t(26,13,wrange=[200,205],/abund)
result=g_of_t(26,13,/no_de)
One can also use this routine to derive the Tmem of the emission line, by way of the ion_interp.pro routine, e.g.,
result=g_of_t(26,13,dens=9.)
ion_interp,t,result,ti,g_ti,10
print,ti(where(g_ti eq max(g_ti)))
result is tabulated at 0.1 dex intervals in temperature. ion_interp interpolates result and in this case gives it at 0.01 dex intervals.
These routines are called by the routines above.
Calculates the ion emissivity (Eq. 40) for all transitions within the CHIANTI model of the ion. The returned data is in the form of a structure. The default is to calculate emissivities for temperatures Tmax and log Tmax±0.15, and densities log Ne=8.0, 8.5, 9.0,....,12.0.
Example:
emiss=emiss_calc(26,13)
Allows the selection of lines/blends from the emiss structure created by emiss_calc.pro. This routine is useful if you want to access the emissivities of lines directly, e.g.,
emiss=emiss_calc(26,13) em202=emiss_select(emiss,wra=[200,205],sel_ind=sel_ind)In this example, calling emiss_select yields a widget that allows one to select a line/blend from the 200-205 Å range. The emissivities of this line blend will be contained in em202, while the emiss index/indices of this line/blend will be contained in sel_ind.
When reading the ionisation equilibrium files, you will receive an array with absolute (as opposed to log) ion fractions tabulated at 0.1 dex intervals from log T = 4.0 to 8.0. A common need is to interpolate this data and obtain the ion fraction tabulated at smaller intervals. As the ion fractions are generally sharply peaked, normal interpolation will lead to negative ion fractions at several temperatures, and so a more satisfactory method is to interpolate the log of the ion fraction. However, you need to take the log of only the non-zero values of the ion fraction.
The several lines of code required to perform the interpolation are straightforward but irritating (when typed on many occasions!), and so this routine performs the task.
Example: Use g_of_t to create a G(T) function for
one of the Fe XIII lines,
result=g_of_t(26,13,dens=9.)
ion_interp,t,result,ti,g_ti,5
The G(T) function is now tabulated at 0.02 dex intervals. Note that if t is not specified, it is assumed to be a vector going from 4.0 to 8.0 in 0.1 dex intervals.
More details are found in the program headers (see the html version of this guide).
The tags of the line intensities structure are:
.lines A structure containing information about the lines.
Its size is the number of lines in the spectrum. The
tags are:
.iz The atomic number of the elements (e.g., 26=Fe)
.ion The ionisation stage (e.g., 13=XIII)
.snote The identification of the ion (e.g., 'Fe XXIV d')
.ident The identification of the transition, configuration
and terms in text form.
.ident_latex
The identification of the transition, configuration
and terms in latex form.
.lvl1 The lower level of the transition (see .elvlc
file for ion)
.lvl2 The upper level for transition.
.tmax The temperature of maximum emission of the line.
If the G(T) are output, tmax is the maximum of G(T).
If the isothermal approximation is used tmax=0.
If a DEM is used, tmax is the maximum of the
emissivity that includes the product of the ion
fraction and the DEM.
Rounded to nearest 0.1
.wvl Wavelength of the transition, in Angstroms.
.flag A flag, =-1 if the line has only theoretical energy
levels. Otherwise flag=0.
.int Intensity of line (erg/cm2/s/sr or phot/cm2/s/sr),
divided by the element abundance (exclusive with .goft).
.goft The G(T) of the line (optional /exclusive with .int).
.ioneq_name The ion balance file used (full path).
.ioneq_logt The Log10 T values associated.
.ioneq_ref The references.
.dem_name The differential emission measure file eventually used
(full path).
.dem The Log10 DEM values
.dem_logt The Log10 T values associated.
.dem_ref The references.
.model_name A string indicating the model used:
1- Constant density
2- Constant pressure
3- Function (Te,Ne)
.model_file Full path of the (Te,Ne) file if defined. Null string otherwise.
.model_ne the Ne value(s).
- a scalar if 'Constant density' is selected.
- an array if 'Function' is selected.
- 0. if constant pressure is selected.
.model_pe the Pe value.
- a scalar if constant pressure is selected.
- 0. if 'Constant density' is selected.
- an array=density*temperature if 'Function' is selected.
.model_te the Te values if 'Function' is selected. Otherwise 0.
.wvl_units The wavelength units.
.wvl_limits The wavelength limits specified by the user.
.int_units The intensity units (erg/cm2/s/sr or phot/cm2/s/sr) if
intensities are calculated, otherwise the G(T) units
(erg cm3/s/sr or phot cm3 /s/sr)
.logt_isothermal
The Log10(T) values used.
.logem_isothermal
The Log10(EM) values used.
.date The date and time when the structure was created.
.version The version number of the CHIANTI database used.
.add_protons
A flag (0/1) to indicate whether proton data were used (1)
or not (0) to calculate the level population.
.photoexcitation
A flag (0/1) to indicate if photoexcitation was included (1)
or not (0).
.radtemp
The blackbody radiation field temperature used (if
photoexcitation was included).
.rphot
Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units
(if photoexcitation was included).
The spectrum structure output of MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC has the following ADDITIONAL tags (compared to the tags of the CHIANTI line intensities structure created by CH_SYNTHETIC:
LAMBDA The array of X-values
SPECTRUM The array of Y-values
UNITS The units of LAMBDA, SPECTRUM
WRANGE The wavelength range
INSTR_FWHM The Instrumental FWHM
BIN_SIZE Width of the Bins (fixed) in angstroms
ABUND_NAME The CHIANTI abundance file name
ABUND The abundance values
MIN_ABUND The minimum abundance value used
ABUND_REF The references
CONTINUUM The values of the continuum (if calculated)
FILE_EFFAREA The Effective Area File used (optional)
EFFAREA The array of effective area values
(optional - same size of LAMBDA)
.LINES An array of structures, for all the lines used
to calculate the SPECTRUM.
The tags are the same as those created by
CH_SYNTHETIC, plus
.PEAK The peak intensity of the line in the spectrum
(approx. value)
PROJECT
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME
CH_SS
PURPOSE:
Widget-based multi-purpose routine
to calculate CHIANTI line intensities and continua, to create a
synthetic spectrum, to make tables of lines, etc.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
IDL> ch_ss
PROCEDURE:
This routine calculates a synthetic spectrum by merging line
intensities and continua.
The widget is organised into four Sections:
SECTION 1:
-The Calculation of the CHIANTI line intensities.
This can be done in two ways:
1-Restore a save file with the CHIANTI line intensities already
calculated.
2-Calculate CHIANTI line intensities with a call to CH_SYNTHETIC.
In this case, A series of parameters must be set:
- Minimum and maximum wavelengths in Angstroms
- The model used for the calculation. Three are the options:
1) a constant density (cm^-3)
2) a constant pressure (cm^-3 K)
3) a general (Te,Ne) model. In this case, a file will be read.
This file should have two columns, one with the Te (K)
values, and one with the Ne (cm^-3) values.
- The ionization fraction file to be used. "*.ioneq" files
can be selected from either the CHIANTI database, the
working directory or selected via a widget.
- All ions ? If set to yes (default), then all the ions present in the
database will be included.
If set to no, then it is possible to select a list of ions
with a widget
- All lines ? If set to no (default), only the lines for which there are
observed energy levels are included
If set to yes, also the lines that do not have
corresponding observed energy levels are included. In this
case, the wavelengths are calculated from the theoretical
energy levels, and might not be very accurate.
- Isothermal ? If set to no (default), a DEM file must be selected.
"*.dem" files (i.e. files with a .dem extension)
can be selected from either the CHIANTI database, the
working directory or selected via a widget.
If set to yes, then the user is requested to enter one
or more temperatures (as logarithmic values - Log T )
and correspondent column emission measures EM
logarithmic values.
NOTE: if more than one value is entered, then the
sequence must be separated by commas (e.g.: 6.0,
6.5, 7.), and both Log T and Log EM must have the
same number of values
- Photoexcitation ?
If set to yes, you have to define:
Trad: The blackbody radiation field temperature
R/Ro: Distance from the centre of the star in stellar
radius units
Units: Photons or Ergs'
Protons: If set to Yes, the proton data are used to calculate the level population
Once all the parameters have been defined, the user should click on the
"Calculate intensities" button to start the calculation (which calls
CH_SYNTHETIC).
Once the calculation is finished, an IDL structure is loaded into
memory. It is then possible to save it for later use by clicking on the
"SAVE" button.
The RESTORE button is to restore previously saved files into an IDL
structure in memory.
Once the IDL structure with the line intensities is in the memory, it is
then possible to calculate and plot a spectrum (SECTION 2).
SECTION 2:
This section controls the parameters that are needed to fold the
line intensities and the continua into a synthetic
spectrum. These parameters are used by MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC.
Before this is done, a set of line intensities MUST be in the
program memory. This is done either by calculating the
intensities or by restoring a save file with
previously calculated values (SECTION 1).
Setting the parameters:
-Minimum and maximum wavelengths in Angstroms
-spectrum bin size in Angstroms. Disallowed if an Effective area
file is used.
-instrumental FWHM: Setting this to a non-zero value broadens
each of the spectral lines with a Gaussian of
the specified FWHM (in Angstroms) so
mimicking the effects of instrumental
broadening.
-continuum: Add continua to the binned spectrum:
free-free, free-bound and two-photon.
Please note that the continuum calculation takes some
time and you may want to define a minimum abundance
value to speed the calculations.
- All lines ? If set to no (default), only the lines for which there are
observed energy levels are included.
If set to yes, the "unobserved lines" will be added, but
only if they are present in the structure.
-elemental abundances
"*.abund" files (i.e. files with a .abund
extension) can be selected either from the CHIANTI database,
the working directory, or via a widget.
-select a minimum abundance value
If set not null, only the lines of those elements
which have an abundance greater than the value set are
selected. Also, the continuum is calculated only for
those elements which have an abundance greater than
the value set. This can significantly speed up the
calculations. By default, the minimum value in the
selected abundance file is used. To have an idea of
what minimum abundance should be set, the abundances
of Allen (1973) give:
abundance (H) = 1.
abundance (He) = 0.085
abundance (C) = 3.3e-4
abundance (O) = 6.6e-4
abundance (Si) = 3.3e-5
abundance (Fe) = 3.9e-5
Eff. Area: Yes/No
If you want to fold the spectrum with an effective area.
If set to Yes, you are requested to choose an input ascii file
with two columns, the wavelength and the effective area values
(cm^2).
The wavelenghts in the file (that might not be linear) are used
to create the spectrum, that is multiplied with the effective
area values.
Note that this option only works well if a sufficient number
of bins is given. The line intensities contributing to each
bin are summed, and subsequently convolved with a gaussian
of full-width-half-maximum FWHM, if FWHM is not set = 0.
Please note that the convolution might not work if a small
number of bins is defined.
Also note that to have the correct output units (counts s-1
bin-1) the appropiately scaled DEM (or EM) values must be provided.
After this, by clicking on the "Calculate and plot" button the
program calculates and plots the synthetic spectrum.
Once the spectrum is displayed, it is then possible to
view the details of the lines by clicking with the mouse in the
plot window, and to perform various operations by clicking on
the buttons in SECTION 3
SECTION 3:
This Section allows the user to select a few parameters for the
plotting, and to create different types of OUTPUT.
Labels ? : Setting this to yes plots a vertical line for each
spectral line in the spectrum, and also writes a label
above the strongest lines indicating the ion from
which the line arises.
Min.: Only lines which have an intensity greater than the
value set here will be listed and, if requested,
labelled and selected for inclusion in the various
outputs. Setting the value=0. will result in all
lines being listed and written in the outputs.
X,Y, XOOM, UNZOOM: It si possible to select a region of the
spectrum, by zooming with the use of the mouse
or by setting the X,Y ranges.
NOTE that only the line details and portion of
the spectrum shown will be output.
LINEAR/LOG To plot the spectrum in linear or log scale
Create PS file: A postscript file is created.
Hardcopy: the postscript file "idl.ps" is created and sent to the
default printer.
Save Line details (latex): The details of the lines shown in the
plot will be saved in a latex file.
Save Line details (ascii): The details of the lines shown in the
plot will be saved in an ascii file.
Save Spectrum (ascii): The X,Y values of the plot are saved in
an ascii file.
Save Spectrum (IDL/FITS): The details of all the lines and the arrays
of the X,Y values of the plot are saved into
an IDL or FITS file. The IDL structure
has the following tags:
.LAMBDA: The array of wavelength X values
.SPECTRUM: The array of spectrum Y values
.UNITS The units of LAMBDA, SPECTRUM
.INSTR_FWHM The Instrumental FWHM
.BIN_SIZE Width of the Bins (fixed) in angstroms
.ABUND_NAME The CHIANTI abundance file name
.ABUND The abundance values
.MIN_ABUND The minimum abundance value used
.ABUND_REF The references
.CONTINUUM The values of the continuum (if
calculated)
.EFFAREA The array of effective area
values (optional)
.FILE_EFFAREA The name of the effective area file used (optional).
.IONEQ_NAME The ion balance file used (full path).
.IONEQ_LOGT The Log10 T values associated.
.IONEQ_REF The references.
.DEM_NAME The differential emission measure file eventually used
(full path).
.DEM The Log10 DEM values
.DEM_LOGT The Log10 T values associated.
.DEM_REF The references.
.MODEL_NAME A string indicating the model used
(e.g. constant density or constant pressure).
.MODEL_NE the Ne value.
.MODEL_PE the Pe value.
.WVL_UNITS The wavelength units.
.WVL_LIMITS The wavelength limits specified by the user.
.INT_UNITS The intensity units
.LOGT_ISOTHERMAL
The Log10(T) values used.
.LOGEM_ISOTHERMAL
The Log10(EM) values used.
.TIME The date and time when the structure was created.
.VERSION The version number of the CHIANTI database used.
.ADD_PROTONS
A flag (0/1) to indicate whether proton data were used (1)
or not (0) to calculate the level population.
.PHOTOEXCITATION
A flag (0/1) to indicate if photoexcitation was included (1)
or not (0).
.RADTEMP
The blackbody radiation field temperature used (if
photoexcitation was included).
.RPHOT
Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units
(if photoexcitation was included).
THEN, FOR EACH LINE USED TO CALCULATE THE
SPECTRUM:
.LINES A structure containing information about the lines.
Its size is the number of lines in the spectrum. The
tags are:
.peak The peak intensity value
.iz The atomic number of the elements (e.g., 26=Fe)
.ion The ionisation stage (e.g., 13=XIII)
.snote The identification of the ion (e.g., 'Fe XXIV d')
.ident The identification of the transition, configuration
and terms in text form.
.ident_latex
The identification of the transition, configuration
and terms in latex form.
.lvl1 The lower level of the transition (see .elvlc
file for ion)
.lvl2 The upper level for transition.
.tmax The temperature of maximum emission of the line
(i.e., the temperature at which the product of
the emissivity and the ion fraction has its
maximum). Rounded to nearest 0.1, and zero in case
the isothermal approximation is used.
.fwhm
.wvl Wavelength of the transition, in Angstroms.
.flag A flag, =-1 if the line has only theoretical energy
levels. Otherwise flag=0.
.int Intensity of line (with the abundance factor multiplied)
Save Spectrum (FITS): The entire information contained in the
IDL structure is stored in a FITS file.
SECTION 4:
Here, text information messages are printed.
INPUTS
None.
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
The font
OUTPUTS:
Many.
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
FONT the font to be used. Can be useful to customize the appearance of
the widget.
CALLS:
CH_SYNTHETIC, CH_LINE_LIST, CH_DRAWBOX, MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC, CH_XMENU_SEL,
plus many other CHIANTI and SolarSoft routines.
PROGRAMMING NOTES
Within CH_SS, there are several other routines which are:
OPLOT_LINES This overplots lines and a label on the displayed
spectrum.
SYN_CURSOR When the mouse is clicked when on the spectrum window,
this routine prints out the list of nearby lines and
their IDs in the text window.
CALC_SYN_SPECTRUM
Calculates line intensities with a call to CH_SYNTHETIC
PLOT_SYN_SPECTRUM This calls make_chianti_spec to produce the
intensity vs. wavelength plot.
SYN_MAIN_EVENT This handles the widget operations
SYN_WID This creates the widgets.
COMMON BLOCKS:
many
RESTRICTIONS:
SIDE EFFECTS:
EXAMPLE:
IDL> ch_ss
CATEGORY:
spectral synthesis.
WRITTEN :
Ver.1, 7-Nov-01, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ) and Peter Young (PRY)
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
V.2, 7-Nov-01, GDZ . Fixed a small bug (now the spectrum plot is always
plotted within the widget), and modified the option to add continua.
Changed the suggested names of the outputs.
Corrected a bug when creating an IDL save file with the spectrum, when
no line details are present.
V.3 28-Jan-02 GDZ
fixed a bug in the density text widget, added a few buttons
and options, including the effective area.
Added noprot, rphot, radtemp keywords to the call to ch_synthetic
V 4, 18-Apr-2002, GDZ
Added photoexcitation, changed IDL save files to FITS files,
V.5, 21-May-2002, GDZ
fixed a few small bugs: checking min_abund before calculating the
spectrum; checking the ioneq file when
restoring the structure; changed the status of
all lines; chnaged the font system.
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V.6, 15-July-2002, GDZ - New major revision.
Changed the chianti top directory (for Effective areas).
Changed Linear/Log button.
Rearranged the sizes of the buttons and added a special cursor to
highlight the area where details of the lines will be given. Works
only in linear scale.
Added quite a lot of new checks to avoid crashes and
fixed the problem with the zoom/unzoom/change units.
V.7, 2-Aug-02, GDZ
Modified the output labels on the plot, inside and on the axis.
Also modified a few minor things like the appearance of the Log T,EM
values.
Fixed a bug when creating the latex output.
Now it restores at the end previous colors and settings.
V.8, 8-Aug-02, GDZ
Changed the CHIANTI system variables. Fixed.
Also fixed a problem with the element ab. file.
V.9, 13-Aug-02, GDZ
Restored the correct use of ch_line_int, now only the lines in the
plot window are listed, and the ALL keyword is in use.
Now the correct xrange is loaded into COMMON when line int. are
restored. Now it checks if all ions were in the structure, when
restoring the line intensities, and flags the widget button accordingly.
Added a device,decomposed=0. to remove problems with colors.
Corrected the use of the DEM, IONEQ and ABUND pulldown menus,
avoiding conflicts between files in the working and CHIANTI
directory having the same name.
Added printing of references for ancillary files, and a check on the
element abundances vs. the elements present in the structure.
V.10, 7-Nov-03 GDZ
Modified format e8.2 to e9.2 for Windows compatibility.
Replaced f9.4 with f11.4 format for the wavelengths.
Some minor modifications to the widget.
Added extended details in the ascii output spectrum.
Added more explanations in the HELP buttons.
V.11, 22-Jul-2005 GDZ
-Added keV option and a few more extra checks.
V.12, 2-Aug-2005 GDZ
put RETAIN=2 in the main plotting window.
TO DO LIST:
Control the range of Angstroms when clicking
kev
Allow plots in intensities instead of intensities A-1
VERSION : V.12, 2-Aug-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
CH_SYNTHETIC
PURPOSE:
to calculate CHIANTI line intensities or G(T) and output an IDL structure.
PROCEDURE:
This routine calculates as default line intensities for a user-specified
differential emission measure and ionisation balance. The actual
creation of a synthetic spectrum (i.e., wavelength vs. intensity)
is performed by other routines - see CH_SS.PRO and
MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC.PRO.
Note that this routine does not include the element abundances
in the line intensities, as this will be performed by
make_chianti_spec. One of the reasons why element abundances are not
included in the line intensities calculation is so that it is easier
for the user to see how modifying abundances affects their spectra in
e.g. CH_SS.PRO.
The calculations are performed at constant pressure or
at constant density.
The routine can also output line intensities calculated with an
isothermal approximation.
If the isothermal approximation is not used, then the user will be asked
to select two files, that can either be in the
standard CHIANTI database or in the working directory.
These files are:
- an ionization fraction file
- a differential emission measure (DEM) file.
The routine can also output the contribution functions G(T) of the lines,
instead of the intensities, if the keyword GOFT is used. In this case,
only the ionization equilibrium file needs to be selected.
The G(T), or intensity per emission measure, is calculated as:
G=(hc/lambda_ij)*A_ji*(N_j(X^+m)/N(X^+m))*(N(X^+m)/N(X))/ N_e /(4.*!pi)
where A_ji is the A-value of the transition;
(N_j(X^+m)/N(X^+m)) is the population of the upper level,
calculated by solving the statistical equilibrium equations;
(N(X^+m)/N(X)) is the ionization equilibrium
N_e is the electron density.
unless /PHOTONS is set, in which case the (hc/lambda_ij) factor
is not included.
If not specified otherwise, with the use of the MASTERLIST or SNG_ION
keywords, then the standard masterlist of the ions, which has
all the ions in the current CHIANTI database, is used.
PROGRAMMING NOTES
The DEM is not assumed to be specified at 0.1 logT intervals (which
is how the ion fraction are specified). Thus this routine reads
in the DEM vs. logT information and then uses the IDL spline
function to tabulate the DEM over 0.1 logT intervals. The minimum
and maximum temperatures are those in the DEM file, rounded up to
the nearest 0.1. The new DEM function tabulated over 0.1 logT
intervals is contained in 'dem_int'.
For some of the dielectronic files, radiative decays that were in
the standard .wgfa file will also be present in the dielectronic
version of the .wgfa file. In these cases the line intensity
produced from the latter file needs to be ignored and so we have a
check in ch_synthetic to do this. An example is the 1-7 decay in
the ca_19.wgfa and ca_19d.wgfa files. In the latter case, the
model of the ion does not include electron excitation to level 7
and so the model for the 1-7 decay is incorrect, hence we ignore
it.
CATEGORY:
spectral synthesis.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
IDL> ch_synthetic,wmin,wmax, output=output, pressure=pressure,$
[MODEL_FILE=MODEL_FILE, err_msg=err_msg, msg=msg, $
density=density,all=all,sngl_ion=sngl_ion, $
photons=photons, masterlist=masterlist, $
save_file=save_file , verbose=verbose, $
logt_isothermal=logt_isothermal,$
logem_isothermal=logem_isothermal,$
goft=goft, ioneq_name=ioneq_name, dem_name=dem_name,$
noprot=noprot, rphot=rphot, radtemp=radtemp, progress=progress ]
INPUTS:
Wmin: minimum of desired wavelength range in Angstroms
Wmax: maximum of desired wavelength range in Angstroms
PRESSURE: pressure in emitting region (Pe, cm^-3 K).
Only a single value is accepted, and the calculation is
performed at constant pressure.
OPTIONAL INPUTS :
DENSITY: density in emitting region (Ne, cm^-3).
Only a single value is accepted, and the calculation is
performed at constant density, unless LOGT_ISOTHERMAL is
defined. In this case, DENSITY can be an array of values, but
has to have the same number of elements as LOGT_ISOTHERMAL.
MODEL_FILE Full path of the (Te,Ne) file if defined.
This file should have two columns, one with the Te (K)
values, and one with the Ne (cm^-3) values. If these
values are not sorted in ascending order of Te, the
routine does sort them.
SNGL_ION: specifies a single ion (e.g. SNGL_ION='Fe_10' to include
only Fe X lines) or an array (e.g. SNGL_ION=['Fe_10','Fe_11']
to include only Fe X and Fe XI lines) of ions to be used
instead of the complete set of ions specified in
!xuvtop/masterlist/masterlist.ions
MASTERLIST: string of a specific masterlist file (full path).
If defined as a keyword (i.e. MASTERLIST=1 or /MASTERLIST)
then a widget allows the user to select a user-defined
masterlist file. Shortcut for SNGL_ION.
IONEQ_NAME: Name of the ionization equilization name to use. If not
passed, then the user is prompted for it.
DEM_NAME: Name of the DEM file to used. If not passed, then the user
is prompted for it.
LOGT_ISOTHERMAL
Array of logarithmic temperatures.
If defined, the emissivities are calculated with an
isothermal approximation. The values are sorted in ascending
order.
LOGEM_ISOTHERMAL
Array of logarithmic emission measures.
If defined, the emissivities are calculated with an
isothermal approximation. The values are sorted in ascending
order. If LOGT_ISOTHERMAL is specified without
LOGEM_ISOTHERMAL then the emission measures are set to 1
(logem_isothermal=0).
RADTEMP The blackbody radiation field temperature (default 6000 K).
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
OUTPUTS:
OUTPUT: The name of the structure containing the line intensities and
details.
The tags of the structure are:
.lines A structure containing information about the lines.
Its size is the number of lines in the spectrum. The
tags are:
.iz The atomic number of the elements (e.g., 26=Fe)
.ion The ionisation stage (e.g., 13=XIII)
.snote The identification of the ion (e.g., 'Fe XXIV d')
.ident The identification of the transition, configuration
and terms in text form.
.ident_latex
The identification of the transition, configuration
and terms in latex form.
.lvl1 The lower level of the transition (see .elvlc
file for ion)
.lvl2 The upper level for transition.
.tmax The temperature of maximum emission of the line.
If the G(T) are output, tmax is the maximum of G(T).
If the isothermal approximation is used tmax=0.
If a DEM is used, tmax is the maximum of the
emissivity that includes the product of the ion
fraction and the DEM.
Rounded to nearest 0.1
.wvl Wavelength of the transition, in Angstroms.
.flag A flag, =-1 if the line has only theoretical energy
levels. Otherwise flag=0.
.int Intensity of line (erg/cm2/s/sr or phot/cm2/s/sr),
divided by the element abundance (exclusive with .goft).
.goft The G(T) of the line (optional /exclusive with .int).
.ioneq_name The ion balance file used (full path).
.ioneq_logt The Log10 T values associated.
.ioneq_ref The references.
.dem_name The differential emission measure file eventually used
(full path).
.dem The Log10 DEM values
.dem_logt The Log10 T values associated.
.dem_ref The references.
.model_name A string indicating the model used:
1- Constant density
2- Constant pressure
3- Function (Te,Ne)
.model_file Full path of the (Te,Ne) file if defined. Null string otherwise.
.model_ne the Ne value(s).
- a scalar if 'Constant density' is selected.
- an array if 'Function' is selected.
- 0. if constant pressure is selected.
.model_pe the Pe value.
- a scalar if constant pressure is selected.
- 0. if 'Constant density' is selected.
- an array=density*temperature if 'Function' is selected.
.model_te the Te values if 'Function' is selected. Otherwise 0.
.wvl_units The wavelength units.
.wvl_limits The wavelength limits specified by the user.
.int_units The intensity units.
1) If LOGT_ISOTHERMAL is defined, we have two cases:
a) LOGEM_ISOTHERMAL is not defined, and is therefore
assumed to be 0 (EM=1). In this case, units are
'photons cm+3 sr-1 s-1' or 'erg cm+3 sr-1 s-1'.
b) LOGEM_ISOTHERMAL is defined. In this case, units are
'photons cm-2 sr-1 s-1' or 'erg cm-2 sr-1 s-1'.
2) If LOGT_ISOTHERMAL is not defined, we have two cases:
a) intensities are calculated. In this case, units are
'photons cm-2 sr-1 s-1' or 'erg cm-2 sr-1 s-1'.
b) Contribution functions G(T) are calculated. In this
case, units are
'photons cm+3 sr-1 s-1' or 'erg cm+3 sr-1 s-1'.
.logt_isothermal
The Log10(T) values used.
.logem_isothermal
The Log10(EM) values used.
.date The date and time when the structure was created.
.version The version number of the CHIANTI database used.
.add_protons
A flag (0/1) to indicate whether proton data were used (1)
or not (0) to calculate the level population.
.photoexcitation
A flag (0/1) to indicate if photoexcitation was included (1)
or not (0).
.radtemp
The blackbody radiation field temperature used (if
photoexcitation was included).
.rphot
Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units
(if photoexcitation was included).
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
SAVE_FILE: If defined, then an IDL save file is created, with the output
structure.
GOFT: If set, the G(T) of the lines are calculated, and put in
the output structure, instead of the line intensities.
Units are 'photons cm+3 sr-1 s-1' or 'erg cm+3 sr-1 s-1'
KEYWORDS:
ALL: if set, then all lines are included. This means that lines for
which only an approximate wavelength is known,
denoted by a negative wavelength value in the .wgfa file, are
included. These are the lines for which there are no observed
energy levels.
PHOTONS: The output intensities will be in photons instead of
ergs.
VERBOSE: If set, the routine will list each ion it is looking at,
and how many lines from each ion it is including in the
spectrum.
GOFT: If set, the G(T) of the lines are calculated, and put in
the output structure, instead of the line intensities.
Units are 'photons cm+3 sr-1 s-1' or 'erg cm+3 sr-1 s-1'
NOPROT Switch off the inclusion of proton rates in the level
balance (default).
PROGRESS If set, a widget appears, showing the progress of the
calculation and allowing the user to halt the calculation.
NO_SUM_INT Prevents the summing of intensities over temperature.
Only works in conjunction with the LOGT_ISOTHERMAL
option, and is implemented in order to work the
ISOTHERMAL routine. The .INT tag in OUT.LINES becomes
an array with the same number of elements as
LOGT_ISOTHERMAL, corresponding to the intensities at
each temperature.
CALLS: CH_GET_FILE
many CHIANTI standard routines, including:
READ_IONEQ, READ_DEM, READ_MASTERLIST, ION2SPECTROSCOPIC,
ZION2FILENAME, READ_WGFA,READ_ELVLC,READ_SPLUPS,POP_SOLVER,
DESCALE_UPS, CONVERT_TERMS.
CONVERT_TERMS uses some standard SolarSoft routines:
REPSTR, STR_INDEX, DATATYPE,
VALID_NUM, DELVARX, INFO_PROGRESS, SAVEGEN
COMMON BLOCKS:
wgfa, wvl,gf,a_value
upsilon,splstr
elvlc,l1a,term,conf,ss,ll,jj,ecm,eryd,ecmth,erydth,eref
elements,abund,abund_ref,ioneq,ioneq_logt,ioneq_ref
radiative, radt, dilute
proton, pstr
ionrec,rec_rate,ci_rate,temp_ionrec,luprec,lupci,status
RESTRICTIONS:
SIDE EFFECTS:
CATEGORY:
spectral synthesis.
EXAMPLE:
This routine can be called in this way:
IDL> ch_synthetic,5.,10., output=structure, pressure=1.e+15
To make use of the output structure, use MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC or CH_SS
PREV. HIST. :
Based on synthetic.pro, written by Ken Dere
WRITTEN :
Ver.1, 22-Jun-00, Peter Young (PRY) and Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Ver.1, 22-Jun-00, Peter Young and Giulio Del Zanna
Ver.2, 25-Jul-00, PRY
Removed /all keyword; make_chianti_spec can be
used to filter out negative wavelengths.
Added flabel tag to output in order to pick out
dielectronic recombination lines.
Ver.3, 4-Oct-00, PRY
Replaced /all keyword.
Corrected bug when .wgfa files contain two A-values
for the same transition.
Ver.4, 5-Oct-00, PRY
Corrected bug that gave rise to lines from the same
transition when the dielectronic file existed.
V.5, 11-Oct-2000, GDZ
eliminate the abundance call; reinstate the /masterlist keyword;
added the tag ident_latex to have the identification in
late-style format; added a tag flag=-1 for the unobserved lines,
and =0 otherwise; reinstated all wavelengths > 0. ;
added the calculation of the G(T);
added a few other tags in the output, and various checks and
comments.
V.6 15-Oct-2000 ,GDZ
Replaced calls to solarsoft routines to standard IDL ones.
Corrected an error in the output creation, in relation to the
isothermal case. Added isothermal in the output. added checks to
the wavelengths. Default output name is TRANSITIONS. changed
const_net and added const_net_value + a few other things.
v.7, 27-Nov-2000, GDZ. Corrected an error in the calculation of the
G(T).
Version 8, 5-Dec-2000, GDZ, DAMTP. Fixed a bug when checking the
values in the .splups files.
V. 9, GDZ, 10-Apr-2001, corrected another error in the G(T) calc.
V. 10, GDZ, 30-Oct-2001 added CHIANTI Version number, changed isothermal
to logt_isothermal and added logem_isothermal to the output.
Removed the use of log T values, and the calculation.
Added err_msg, a text string with an error message.
Version 11, 8-Nov-01, GDZ
Changed the MASTERLIST keyword. Allowed double use, as a keyword
and as a string.
Version 12, 18-Nov-01, Peter Young
Added /NOPROT, RPHOT and RADTEMP keywords; changed upsilon
common block.
Version 13, 29-Apr-02, GDZ
Added no_protons, photoexcitation, rphot, radtemp
tags into the output structure.
Revised Header. Added the PROGRESS widget.
Added a check if the ion is present in the Ion. Frac. file.
Added informative MSG keyword.
Now uses savegen.pro to save the structure.
V. 14, 28-May-2002, GDZ:
generalize directory concatenation to work for Unix, Windows
and VMS.
modified tags:
limits -> wvl_limits
ioneq_t -> ioneq_logt
wvlunits -> wvl_units
intunits -> int_units
time --> date
no_protons -> add_protons
dem_t -> dem_logt
const_nte -> model_name
const_nte_value -> model_ne, model_pe, model_te
removed from the main STR: .ioneq ctemp
removed from the LINES STR: fwhm flabel
Added model_file input for model Ne(T). Had to considerably
modify the routine.
V. 15, 16-Jul-2002, Peter Young
Added keyword /NO_SUM_INT.
V. 16, 22-Jul-2002, Peter Young
Corrected a bug related to /NO_SUM_INT; logt_isothermal
can now be specified without logem_isothermal.
V. 17, 23-July-2002, GDZ
Modified a few checks on the input. Also, now it prints the
error message whenever the program aborts
V.18, 2-Aug-02, GDZ
Replaced all DBLARR and DOUBLE calls with floats.
Added a comment at the end of the routine when it finishes.
V.19, 8-Aug-02, GDZ
Added more error info. Changed the use of the DENSITY
keyword. It is possible to input an array of values if
LOGT_ISOTHERMAL is defined.
V. 20, 17-Sep-02, GDZ
Corrected a bug: the functional (T,N) form
is now only accepted if DENSITY is an array with at least two
values.
V. 21, 19-Sep-02, GDZ
Corrected the definition of the UNITS in case LOGT_ISOTHERMAL
is defined.
V. 22, 19-Aug-03, Peter Young
when logem_isothermal is input, the derived EM is now a
DOUBLE array rather than FLOAT, preventing infinities when
logem_isothermal values are large.
V. 23, 4-Oct-2003, GDZ
modified the input to POP_SOLVER, now it is dealt with an
input structure.
V.24, 10-Oct-2003, K.Dere
added modifications from K.Dere, regarding the satellite
lines.
V 25, 3-Nov-2003, GDZ
Added GROUP keyword, and modified so the progress widget can
be stopped within IDL Windows.
V 26, 17-Apr-2004, Enrico Landi (EL)
Added the recombination/ionization population processes.
V.27, 13-Apr-2005, EL
Replaced the main loop to calculate individual line intensities
with operations among arrays, to speed the whole program in case
of large numbers of lines.
VERSION : 27, 13-Apr-2004
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
SYNTHETIC
PURPOSE:
calculates a synthetic spectrum
PROCEDURE:
Calculations are done assuming either constant density or
constant pressure. See CH_SYNTHETIC for details.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
SYNTHETIC,Wmin, Wmax, Fwhm, Pressure= , Lambda, Spectrum ,List_wvl, List_ident
,[/all, density=, /cont, min_abund=]
INPUTS:
Wmin: lower limit of the wavelength/energy range of interest (Angstroms)
Wmax: upper limit of the wavelength/energy range of interest (Angstroms)
Pressure: pressure in emitting region (cm^-3 K), or
Density: density in emitting region (cm^-3).
Fwhm: gaussian full width at half maximum of the resolution of the output
spectrum, for example, to correspond to an observed spectrum
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
SNGL_ION: specifies a single ion (e.g. SNGL_ION='Fe_10' to include
only Fe X lines) or an array (e.g. SNGL_ION=['Fe_10','Fe_11']
to include only Fe X and Fe XI lines) of ions to be used
instead of the complete set of ions specified in
!xuvtop/masterlist/masterlist.ions
MASTERLIST: string of a specific masterlist file (full path).
If defined as a keyword (i.e. MASTERLIST=1 or /MASTERLIST)
then a widget allows the user to select a user-defined
masterlist file. Shortcut for SNGL_ION.
MIN_ABUND: If set, calculates the continuum only from those elements which
have an abundance greater than min_abund.
DEM_NAME: Name of the DEM file to used. If not passed, then the user
is prompted for it.
ABUND_NAME: Name of the abundance file to use. If not passed, then
the user is prompted for it.
IONEQ_NAME: Name of the ionization equilization name to use. If not
passed, then the user is prompted for it.
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
RADTEMP The blackbody radiation field temperature (default 6000 K).
OUTPUTS:
Lambda: wavelength array of calculated synthetic spectrum
Spectrum: intensity array (erg cm^-2 s^-1 str^-1 Ang^-1),
unless keyword photons is set then output is is
photons cm^-2 s^-1 str^-1 Ang^-1
List_wvl: a list of wavelengths for use with synthetic_plot.pro
List_ident: a list of line identifications for use with
synthetic_plot.pro
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
ALL: if set, then all lines are included. This means that lines for which
only an approximate wavelength is known (only theoretical energy
levels are known) are included.
SNGL_ION: specifies a single ion (e.g. SNGL_ION='Fe_10' to include
only Fe X lines) or an array (e.g. SNGL_ION=['Fe_10','Fe_11']
to include only Fe X and Fe XI lines) of ions to be used
instead of the complete set of ions specified in
!xuvtop/masterlist/masterlist.ions
MASTERLIST: string of a specific masterlist file (full path).
If defined as a keyword (i.e. MASTERLIST=1 or /MASTERLIST)
then a widget allows the user to select a user-defined
masterlist file. Shortcut for SNGL_ION.
CONTINUUM: if set, then the continuum (free-free, free-bound and
two-photon) are included
MIN_ABUND: If set, calculates the continuum only from those elements which
have an abundance greater than min_abund. Can speed up the
calculations. For example, from Allen (1973):
abundance (H) = 1.
abundance (He) = 0.085
abundance (C) = 3.3e-4
abundance (O) = 6.6e-4
abundance (Si) = 3.3e-5
abundance (Fe) = 3.9e-5
PHOTONS: if set, intensities are in photons cm^-2 s^-1 sr^-1 Ang^-1
DEM_NAME: Name of the DEM file to used. If not passed, then the user
is prompted for it.
ABUND_NAME: Name of the abundance file to use. If not passed, then
the user is prompted for it.
IONEQ_NAME: Name of the ionization equilization name to use. If not
passed, then the user is prompted for it.
NOPROT If set, then proton rates are not included.
RADTEMP Specify background radiation temperature (default: 6000 K)
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
CALLS:
CH_SYNTHETIC, MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC, READ_ABUND, STRPAD
COMMON BLOCKS: None
RESTRICTIONS:
SIDE EFFECTS:
EXAMPLE:
> synthetic,100.,200.,.1, pressure=1.e+16,lambda,spectrum,list_wvl,list_ident
CATEGORY:
spectral synthesis.
WRITTEN :
Version 1, 8-Nov-01, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ).
Rewritten as a wrapper routine using the new procedures.
Compared to the previous SYNTHETIC, these are the main changes:
1-Now the PRESSURE value is a keyword as the DENSITY value
2-The keyword CONT is now renamed CONTINUUM
3-Added keywords PHOTONS, DEM_NAME, ABUND_NAME, IONEQ_NAME
4-MASTERLIST can now be used both as an input string or as a keyword.
5-The description of the line details now has the spectroscopic
designation at the end.
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Version 2, 18-Nov-01, Peter Young
Added /noprot, rphot and radtemp keywords.
Version 3, 11-Dec-01, Peter Young
Changed call to ch_strpad to strpad.
Version 4, 28-Apr-02, GDZ, changed the call to make_chianti_spec and the
continuum keyword.
V. 5, 22-May-2002 GDZ. Removed const_net definitions.
V.6, 14-Feb-2003 GDZ.
Fixed a bug (keyword PHOTONS was not active).
VERSION : 6, 14-Feb-2003
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
synthetic_plot
PURPOSE:
to plot out synthetic spectra calculated with Synthetic
and interactively identify spectral lines
CATEGORY:
spectroscopy
CALLING SEQUENCE:
SYNTHETIC_PLOT,Wvl,Spectrum,List_wvl,List_ident,fwhm
INPUTS:
Wvl: wavelength array from synthetic
Spectrum: spectrum intensity array from synthetic
List_wvl: string array of spectral line wavelengths
List_ident: string array of spectral line identifications
Fwhm: when the cursor is clicked, spectral lines with fwhm
(Angstroms) of the cursor are printed out
KEYWORDS
xrange: similar to IDL keyword to determine wavelength range of plot
OUTPUTS:
None
PROCEDURE:
Click the left mouse button to select a wavelength
Click the right mouse button to exit
EXAMPLE:
> synthetic,100.,200.,.1,1.e+15,wvl,spectrum,list_wvl,list_ident
> synthetic_plot,wvl,spectrum,list_wvl,list_ident,0.1
note: it is not necessary for the two fwhm values to be the same
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
May 1996: Version 2.0
Dec. 1998: revised by Ken Dere
V.4, 23 Oct 2000 GDZ, added the log keyword, and changed a few things
in the plot.
Ver.5, 12-Dec-2001, Peter Young
Changed style of printing, and made method of extracting the
intensity from list_ident compatible with the new version of
isothermal.pro.
VERSION 5 12 Dec 2001 Peter Young
NAME
ISOTHERMAL
PURPOSE:
Computes spectra from isothermal plasmas. A number of isothermal
plasmas can be included.
Note that this routine has a number of unique features that
distinguish it from the other CHIANTI synthetic spectra routines.
See the Programming Notes section.
INPUTS:
WMIN Minimum of desired wavelength range in Angstroms.
WMAX Maximum of desired wavelength range in Angstroms.
WAVESTEP Bin size of spectrum (in Angstroms)
TEMP Electron temperature (or array).
OPTIONAL INPUTS
PRESSURE Electron pressure in units of cm^-3 K.
EDENSITY Electron density in units of cm^-3.
EM Emission measure. The units of EM govern the intensity
units of the emission lines (i.e., column or volume
emission measure units). If EM is not specified, then the
emission measure is set to (N_e * N_H) where N_e is
derived from the user-specified PRESSURE or EDENSITY,
and N_H is derived from the routine PROTON_DENS.PRO.
SNGL_ION Rather than include the entire list of CHIANTI ions in
the calculation, this input can be used to select a
single ion, or a number of different ions. E.g.,
SNGL_ION='s_2' or SNGL_ION=['s_2','s_3','s_4'].
RADTEMP The blackbody radiation field temperature (default 6000 K).
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
MASTERLIST The list of ions that will be considered for the
spectrum is contained in the masterlist file in the
CHIANTI directories. The user can specify his own file
through this keyword. E.g.,
masterlist='/user/home/masterlist.ions'
ABUND_NAME: Name of the abundance file to use. If not passed, then
the user is prompted for it.
IONEQ_NAME: Name of the ionization equilization name to use. If not
passed, then the user is prompted for it.
KEYWORDS
NOPROT Switch off the inclusion of proton rates in the level
balance.
ERGS The units of the output spectrum are by default in photons.
Setting /ERGS switches to erg units.
CONT Adds continuum (free-free, free-bound, two-photon) to
spectrum.
OUTPUTS:
LAMBDA Wavelength array of calculated synthetic spectrum.
SPECTRUM Intensity array. The units depend on the user inputs to
ISOTHERMAL -- see note below.
LIST_WVL A list of wavelengths for use with synthetic_plot.pro
LIST_IDENT A list of line identifications for use with
synthetic_plot.pro
PROGRAMMING NOTES
Intensity Units
---------------
The units are of the form photons cm^3 s^-1 sr^-1 * (units of EM),
changing to ergs if the /ergs keyword is set.
The volume emission measure (N_e*N_H*V) has units cm^-3.
The column emission measure (N_e*N_H*h) has units cm^-5.
Unique features
---------------
The emission lines in the final spectrum have no width and thus
each occupies a single pixel of the spectrum. The size of the
pixels are set by WAVESTEP.
As stated above, the units of the output spectrum are
photons cm^3 s^-1 sr^-1, i.e., there is no "per angstrom" term.
This means that (i) the height of the emission lines in the
spectrum does not change with varying WAVESTEP, and (ii) the height
of continuum does change with WAVESTEP.
COMMON BLOCKS
ELEMENTS
CALLS
CH_SYNTHETIC, READ_ABUND, CH_GET_FILE, CONCAT_DIR, FREEFREE,
FREEBOUND, TWO_PHOTON
HISTORY
Ver.1, 8-Apr-02, Peter Young Rutherford Appleton Laboratory,
p.r.young@rl.ac.uk
Tries to replicate the behaviour of the original ISOTHERMAL which
was found in earlier versions of CHIANTI (v.3 and earlier).
MODIFICATION HISTORY
Ver. 2, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ), 28-Apr-02
Added abund_name,ioneq_name keywords.
Also, added photons keyword in call to MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC.
Ver. 3, Peter Young, 24-May-02
Modified to produce arrays of spectra when an array of
temperatures is given
V.4, GDZ, 28-May-02
Added a couple of checks on file existence and modified the call
to ch_synthetic and make_chianti_spec due to change of keyword
names.
V.5, Peter Young, 16-Jul-02
Restructured routine to avoid crashes when a large number of
temperatures is input.
V.6, 8-Aug-02 GDZ
Added one error checking
V.7, 18-Aug-03, Peter Young
Added EM= keyword.
VERSION :
Version 6, 8-Aug-02
PROJECT : CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME : MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC
PURPOSE :
To create a CHIANTI synthetic spectrum
CALLING SEQUENCE:
IDL> make_chianti_spec, TRANSITIONS, LAMBDA, SPECTRUM,$
[BIN_SIZE= , ,INSTR_FWHM= , PIXEL=PIXEL, BINSIZE = BINSIZE, $
WRANGE= , ALL=ALL, continuum=continuum, $
ABUND_NAME= , MIN_ABUND=, photons=photons, effarea=effarea
PROCEDURE :
From information contained in the structure TRANSITIONS, constructs
a synthetic spectrum
By default, routine assumes thermal widths for lines.
PROGRAMMING NOTES
The line profile is constructed using the IDL gaussint routine.
For a wavelength pixel centred at l and with width dl, gaussint
is used to integrate the Gaussian up to l-dl/2 and up to l+dl/2.
The difference between the two is the intensity in this pixel.
INPUTS :
TRANSITIONS, the structure created by ch_synthetic.pro.
OPT. INPUTS :
LAMBDA Array of wavelengths (X-values). If not defined as input, it is
calculated on the basis of BIN_SIZE, and returned as an output.
If defined as input, the routine checks that there are at least
10 points in the wavelength range defined by WRANGE. If there
are, the corresponding subset of LAMBDA is returned, otherwise
the routine exits with an error.
BIN_SIZE Bin size in Angstroms of the spectrum to be created. A linear
spectrum is assumed. In case an effective area file is used, the
wavelenghts in the file (that might not be linear) are used to
create the spectrum, and this bin size looses any meaning.
WRANGE Allows a subset of the wavelength range to be turned into
a spectrum. When using syn_plot, this speeds up the routine
a lot if you've elected to zoom in on a region.
INSTR_FWHM Instrumental FWHM (Angstroms).
In case an effective area file is used, The line intensities
contributing to each bin are summed, and subsequently convolved
with a gaussian of full-width-half-maximum FWHM if FWHM is not
set = 0 . Please make sure that the FWHM value (if not set to
zero) is larger than the bin size.
ABUND_NAME A CHIANTI abundance file name can be set.
It allows the abundance file given in transitions.abund_name
(if present) to be over-ridden. Note that it also used for
the continuum calculation.
MIN_ABUND: If set, calculates line intensities only from those elements
which have an abundance greater than min_abund.
Can speed up the calculations. For example, from Allen
(1973):
abundance (H) = 1.
abundance (He) = 0.085
abundance (C) = 3.3e-4
abundance (O) = 6.6e-4
abundance (Si) = 3.3e-5
abundance (Fe) = 3.9e-5
FILE_EFFAREA
The Effective Area File (TWO COLUMNS - wavelengths in
Angstroms and cm^2 values) If defined, then the spectrum is
multiplied with these values. Any input LAMBDA value is
over-written by the wavelenghts in the file (that might not
be linear) and are used to create the spectrum.
Note that this option only works well if a sufficient number
of bins is given. The line intensities contributing to each
bin are summed, and subsequently convolved with a gaussian
of full-width-half-maximum FWHM, if FWHM is not set = 0.
Please note that the convolution might not work if a small
number of bins is defined.
OUTPUTS :
LAMBDA Array of wavelengths (X-values).
If not defined as input, it is
calculated on the basis of BIN_SIZE, and returned as an output.
If defined as input, the routine checks that there are at least
10 points in the wavelength range defined by WRANGE. If there
are, the corresponding subset of LAMBDA is returned, otherwise
the routine exits with an error.
SPECTRUM A structure containing all the information:
LAMBDA The array of X-values
SPECTRUM The array of Y-values
UNITS The units of LAMBDA, SPECTRUM
INSTR_FWHM The Instrumental FWHM
BIN_SIZE Width of the Bins (fixed) in angstroms
ABUND_NAME The CHIANTI abundance file name
ABUND The abundance values
MIN_ABUND The minimum abundance value used
ABUND_REF The references
CONTINUUM The values of the continuum (if calculated)
FILE_EFFAREA The Effective Area File used (optional)
EFFAREA The array of effective area values
(optional - same size of LAMBDA)
.LINES An array of structures, for all the lines used
to calculate the SPECTRUM.
The tags are the same as those created by
CH_SYNTHETIC, plus
.PEAK The peak intensity of the line in the spectrum
(approx. value)
OPT. OUTPUTS:
BINSIZE If BIN_SIZE is not specified, then the spectrum
bin-sizes are computed automatically, and the size of the
bin returned in BINSIZE.
KEYWORDS :
PIXEL The spectrum is given in /pixel units rather /ang
(DISABLED)
ALL Add lines that originally had negative wavelengths
PHOTONS If set=1, the output intensities will be in photons instead of
ergs.
CONTINUUM
If set, then the continuum is added to the
spectrum.
verbose
CALLS :
PRY: GET_ATOMIC_WEIGHTS
Chianti: FREEBOUND, FREEFREE
COMMON (with freefree freebound and two_photon):
elements,abund,abund_ref,ioneq,ioneq_logt,ioneq_ref
RESTRICTIONS: The input structure has to be of the type created by ch_synthetic.
The LAMBDA, EFFAREA values must be ordered in wavelength and the
LAMBDA values must be in Angstroms.
SIDE EFFECTS: None known yet.
EXAMPLES :
make_chianti_spec, output_struct, LAMBDA, SPECTRUM,$
bin_size=0.01, instr=0.1
CATEGORY :
spectral synthesis.
PREV. HIST. :
WRITTEN :
Peter Young , CfA, pyoung@cfa.harvard.edu 1-Sept-2000
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Version 1, PRY 1-Sept-2000
Version 2, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ) 10-Oct-2000
put ALL keyword, removed the FWHM obsolete and
confusing call. Reorganised various minor things.
Version 3, PRY 19-Oct-2000
Corrected the way continuum is treated for an isothermal
spectrum.
V. 4, 2-Nov-2001 GDZ. Now MIN_ABUND is effective not only in the
continuum calculation but also in the line spectrum.
Modified for the use of logt_isothermal
V.5, GDZ, added EFFAREA keyword: an ascii file with lambdas and
effective areas can be read
in. The line intensities are
calculated in a different way.
Also, changed the output.
V.6, GDZ, 28-Apr-02 redefined completely the OUTPUT structure.
Major revision (added two_photon verbose).
V.7, GDZ, 3-May-2002
fixed a bug, when negative angpix values occur.
V.8, GDZ, 22 May 2002, changed some tags of the output, and
added min_abund in the continuum call.
V.9, GDZ, 30-May-02 replaced fix() with round()
V. 10, 15-July-2002 , GDZ
changed the location of Effective area files.
V.11 14-Aug-02, GDZ
speeded up the routine, by changing the way the PEAK tag is
added to the structure. The drawback is that only the
'standard v.4 tags' are allowed, and future additions will
have to be dealt properly.
v.12 2-Dec-2002, GDZ.
Fixed a bug: Removed the plotting of the window with the effective areas.
v.13 26-Apr-2005, Enrico Landi (EL)
Fixed a minor bug: if the lines were more than 32768 (2^15), the main
loop crashed.
v.14 22-Jul-2005 GDZ
-fixed a bug. When the routine was run once without
defining the lambdas, and then with the lambdas
defined (the units were switched to photons)
-fixed a bug. When the effective areas were used,
all lines were used to create the spectrum.
-added hard-wired switch to photons when using
effective area files.
-added the keV option
-now can output a spectrum only with the continuum
(i.e. even if no emission lines are present).
15, 2-Aug-2005, GDZ
Added a check on the input structure. If it was
calculated with ch_synthetic and the keyword
/no_sum_int, it cannot be used here.
VERSION : 15, 2-Aug-2005
STILL TO DO:
-speed up the routine with the use of arrays.
-add the option to select only a list of ions, also in the
continuum procedures.
-Allow the use of user-defined line profiles.
-Enable PIXEL keyword
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
ASCII_WVL_DEM
PURPOSE:
create an ascii file of predicted spectral line intensities and
wavelengths corresponding to a selected abundance and differential
emission measure (DEM).
PROCEDURE:
Calculations are done assuming either constant density or
constant pressure. See CH_SYNTHETIC for details.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
ASCII_WVL_DEM, Wmin, Wmax, Pressure= , [density= ], $
[outfile= , mini= , sngl_ion=, /photons, /all, /masterlist], $
[/noprot, radtemp=, rphot=]
INPUTS:
Wmin: lower limit of the wavelength range of interest (Angstroms)
if kev keyword set, then wmin is in kev
Wmax: upper limit of the wavelength range of interest (Angstroms)
if kev keyword set, then wmax is in kev
Pressure: pressure in emitting region (cm^-3 K), or
Density: density in emitting region (cm^-3).
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
OUTFILE: the name of the output ascii file to be written.
MINI: Minimum intensity for a line to be included in the output.
SNGL_ION: specifies a single ion (e.g. SNGL_ION='Fe_10' to include
only Fe X lines) or an array (e.g. SNGL_ION=['Fe_10','Fe_11']
to include only Fe X and Fe XI lines) of ions to be used
instead of the complete set of ions specified in
!xuvtop/masterlist/masterlist.ions
MASTERLIST: string of a specific masterlist file (full path).
If defined as a keyword (i.e. MASTERLIST=1 or /MASTERLIST)
then a widget allows the user to select a user-defined
masterlist file. Shortcut for SNGL_ION.
OUTPUTS:
an ascii file: linelist.txt in the working directory by default
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
MINI: Minimum intensity for a line to be included in the output
SNGL_ION: specifies a single ion (e.g. SNGL_ION='Fe_10' to include
only Fe X lines) or an array (e.g. SNGL_ION=['Fe_10','Fe_11']
to include only Fe X and Fe XI lines) of ions to be used
instead of the complete set of ions specified in
!xuvtop/masterlist/masterlist.ions
MASTERLIST: string of a specific masterlist file (full path).
If defined as a keyword (i.e. MASTERLIST=1 or /MASTERLIST)
then a widget allows the user to select a user-defined
masterlist file. Shortcut for SNGL_ION.
PHOTONS: units will be in photons rather than ergs
KEV: wavelengths will be given in kev rather than Angstroms
ALL: if set, then all lines are included. This means that lines
for which
only an approximate wavelength is known (only theoretical energy
levels are known) are included.
OUTFILE: the name of the output ascii file to be written. By
default a
file 'linelist.txt' in the user's working directory will be
created.
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
RADTEMP Specify background radiation temperature (default: 6000 K)
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
CALLS:
CH_SYNTHETIC, CH_LINE_LIST
COMMON BLOCKS: None
RESTRICTIONS:
SIDE EFFECTS:
EXAMPLE:
IDL> ascii_wvl_dem,400.,800., out='linelist',$
pressure=1.e+15,mini=1.,sngl_ion='o_4'
CATEGORY:
spectral synthesis.
WRITTEN :
Version 1, 8-Nov-01, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ).
Compared to the previous ASCII_WVL_DEM, these are the main changes:
1-Rewritten as a wrapper routine using the new procedures.
2-Now the PRESSURE value is a keyword.
3-The calculations can be done at constant DENSITY.
4-Energies (keV) can be output instead of wavelengths in Angstroms
5-MASTERLIST can now be used both as an input string or as a keyword.
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
18-Nov-01, Peter Young
Added /noprot, rphot and radtemp keywords
V. 2, 22-May-2002 GDZ. Removed const_net definitions.
VERSION : 2, 22-May-2002
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
LATEX_WVL_DEM
PURPOSE:
create a latex file of predicted spectral line intensities and
wavelengths corresponding to a selected abundance and differential
emission measure (DEM)
PROCEDURE:
Calculations are done assuming either constant density or
constant pressure. See CH_SYNTHETIC for details.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
LATEX_WVL_DEM, Wmin, Wmax, Pressure= , [density= ], $
[outfile= , mini= , sngl_ion=, /photons, /all, /masterlist]
INPUTS:
Wmin: lower limit of the wavelength/energy range of interest (Angstroms)
if kev keyword set, then wmin is in kev
Wmax: upper limit of the wavelength/energy range of interest (Angstroms)
if kev keyword set, then wmax is in kev
Pressure: pressure in emitting region (cm^-3 K), or
Density: density in emitting region (cm^-3).
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
OUTFILE: the name of the output latex file to be written.
MINI: Minimum intensity for a line to be included in the output.
SNGL_ION: specifies a single ion (e.g. SNGL_ION='Fe_10' to include
only Fe X lines) or an array (e.g. SNGL_ION=['Fe_10','Fe_11']
to include only Fe X and Fe XI lines) of ions to be used
instead of the complete set of ions specified in
!xuvtop/masterlist/masterlist.ions
MASTERLIST: string of a specific masterlist file (full path).
If defined as a keyword (i.e. MASTERLIST=1 or /MASTERLIST)
then a widget allows the user to select a user-defined
masterlist file. Shortcut for SNGL_ION.
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
RADTEMP The blackbody radiation field temperature (default 6000 K).
OUTPUTS:
a latex file: 'linelist.tex' in the working directory by default
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
MINI: Minimum intensity for a line to be included in the output
SNGL_ION: specifies a single ion (e.g. SNGL_ION='Fe_10' to include
only Fe X lines) or an array (e.g. SNGL_ION=['Fe_10','Fe_11']
to include only Fe X and Fe XI lines) of ions to be used
instead of the complete set of ions specified in
!xuvtop/masterlist/masterlist.ions
MASTERLIST: string of a specific masterlist file (full path).
If defined as a keyword (i.e. MASTERLIST=1 or /MASTERLIST)
then a widget allows the user to select a user-defined
masterlist file. Shortcut for SNGL_ION.
PHOTONS: units will be in photons rather than ergs
KEV: wavelengths will be given in kev rather than Angstroms
ALL: if set, then all lines are included. This means that lines for which
only an approximate wavelength is known (only theoretical energy
levels are known) are included.
OUTFILE: the name of the output latex file to be written. By default a
file 'linelist.tex' in the user's working directory will be
created.
NOPROT If set, then proton rates are not included.
CALLS:
CH_SYNTHETIC, CH_LINE_LIST
COMMON BLOCKS: None
RESTRICTIONS:
SIDE EFFECTS:
EXAMPLE:
> latex_wvl_dem, 400.,800., mini=1, pressure=1.e+15,sngl_ion='o_4'
CATEGORY:
spectral synthesis.
WRITTEN :
Version 1, 8-Nov-01, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ).
Compared to the previous LATEX_WVL_DEM, these are the main changes:
1-Rewritten as a wrapper routine using the new procedures.
2-Now the PRESSURE value is a keyword.
3-The calculations can be done at constant DENSITY.
4-MASTERLIST can now be used both as an input string or as a keyword.
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Version 2, 18-Nov-01, Peter Young
Added /noprot, rphot and radtemp keywords.
V. 3, 22-May-2002 GDZ. Removed const_net definitions.
VERSION : Version 3, 22-May-2002
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
CH_LINE_LIST
PURPOSE:
Create a latex or an ascii file of predicted spectral line intensities and
wavelengths corresponding to selected parameters, as calculated by
CH_SYNTHETIC. Needs as input the line intensity structure calculated by
CH_SYNTHETIC (default) or the SPECTRUM structure output of
MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
IDL> ch_line_list, transitions, outname, latex=latex, ascii=ascii, $
abundfile=abundfile, min_abund=min_abund, $
wmin=wmin,wmax=wmax,$
SPECTRUM=SPECTRUM, minI=minI,photons=photons,kev=kev, $
all=all,no_sort=no_sort, sngl_ion=sngl_ion
PROCEDURE:
INPUTS:
The structure created by CH_SYNTHETIC
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
Wmin: lower limit of the wavelength/energy range of interest (Angstroms)
if kev keyword set, then wmin is in kev
Wmax: upper limit of the wavelength/energy range of interest (Angstroms)
if kev keyword set, then wmax is in kev
Mini: Minimum intensity for line to be included in output
SNGL_ION: specifies a single ion (or a list of ions) to be used instead
of the complete set of ions specified in the structure.
MIN_ABUND: If set, outputs only those elements which
have an abundance greater than min_abund.
For example, from Allen (1973):
abundance (H) = 1.
abundance (He) = 0.085
abundance (C) = 3.3e-4
abundance (O) = 6.6e-4
abundance (Si) = 3.3e-5
abundance (Fe) = 3.9e-5
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
LATEX: Create a latex file (default, exclusive with /ASCII)
ASCII: Create an ascii file (exclusive with /LATEX)
MINI: Minimum intensity for line to be included in output
PHOTONS: units will be in photons rather than ergs
KEV: wavelengths will be given in kev rather than Angstroms
ALL: if set, then all lines are included. This means that lines for which
only an approximate wavelength is known, denoted by a negative
wavelength value in the .wgfa file, are included.
These lines are listed in the file with a * preceding the wavelength.
NO_SORT:
If set, then the lines are *not* sorted in wavelength (or energy).
SPECTRUM
If set, IT IS ASSUMED that the input structure is the SPECTRUM
structure output of MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC, where the line
intensities have already been multiplied by the abundance factor!!
OUTPUTS:
A latex (default) or an ascii file with the line list
CALLS: Many SolarSoft routines.
COMMON BLOCKS:
none.
SIDE EFFECTS:
EXAMPLE:
> ch_line_list, trans,'linelist.tex',/latex, wmin=100.,wmax=200.,/all
CATEGORY:
spectral synthesis.
WRITTEN :
Version 1, Written by: Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ) Oct 31 2001.
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
V.2, 9-Nov-2001 GDZ.
Now correctly handles the case when no
abundances are passed to the routine.
v.3, 11-Dec-2001, PRY.
Removed calls to get_utc and anytim2cal. Replaced with
call to systime()
v.4, 29-Apr-02, GDZ
Fixed a few small bugs, some caused by a change in the
database file format for V4.
Added only_mini, file_effarea keywords to be able to use as
input the structure created by MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC.
V.5, 22-May-2002, GDZ
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS. changed tags.
Changed and added various things, including flabel
V.6, 12-Aug-02, GDZ
Modified the output labeling, and fixed two bugs: 1) when /all was used
the keyword /mini was not working. 2) min_abund was not working
properly when /spectrum was used. Reduced size of latex output (was
12pt)
Changed output in isothermal case (no Tmax given). Better info printed (GDZ)
V.7, 3-Nov-03 GDZ
Modified format e8.2 to e9.2 for Windows compatibility.
v.8, 18-Jul-2005 GDZ
Modified the use of the /kev keyword. Also, now the
routine accepts input structure with the units in keV.
v.9, 4-Aug-2005 GDZ
Corrected a bug introduced in the previous version.
Also switched to \documentclass when making the latex file.
VERSION : 9, 4-Aug-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME: EMISS_CALC()
PURPOSE:
To compute the emissivities of all lines of a specified ion over
given ranges of temperature and density.
CATEGORY:
Scientific analysis
EXPLANATION:
This routine calculates:
hc
-- * N_j * A_ji
lamb
where hc = 1.986 * 10^-8 erg AA, lamb is in angstroms, N_j is the
fraction of ions in the upper emitting level j, and A_ji is the
radiative decay rate for the transition.
The emissivities are stored in a structure called EMISS that also
holds the wavelength of the transition, the level numbers i and j
and also a 'flag', which is set to -1 if the wavelength is negative.
The temperature and density ranges can be specified directly using
the TEMP and DENS keywords. Setting TMAX to the log T_max of the
ion, gives emissivities for 3 temperatures: log T_max +- 0.15.
If DENS is not set, then it is set to 8 to 12 in 0.5 dex intervals.
STDENS allows the start density (of 8) to be changed to some other
value; ND allows the number of densities to be varied (default 9);
DINT allows the density interval to be varied (default 0.5).
CALLING SEQUENCE:
EMISS=EMISS_CALC (IZ, ION, [ TEMP=TEMP, DENS=DENS, RADT=RADT, $
DIL=DIL, PATH=PATH, /NO_DE, /PROTON, $
QUIET, PRESSURE=PRESSURE)
EXAMPLES:
EMISS=EMISS_CALC(26,13)
EMISS=EMISS_CALC(26,13,temp=[6.2],dens=findgen(5)+8)
EMISS=EMISS_CALC(26,13,temp=findgen(11)/100.+5.5,press=10.^15)
INPUTS:
IZ The atomic number of the ion
ION The spectroscopic number of the ion (e.g., 12 = XII)
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
TEMP Direct specification of the temperature range (log T)
DENS Direct specification of the density range (log Ne)
RADTEMP Specify background radiation temperature (default: 6000 K)
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
PATH If specified, the routine will look for the atomic data in
the PATH directory, rather than in the CHIANTI database
PRESSURE If a temperature array is given, and PRESSURE set,
then the emissivities will be evaluated at the
specified temperatures, but for densities =
pressure/temperature. If DENS is set, then it will
be ignored. The pressure is assumed to be in units
K * cm^-3.
ABUND_FILE The name of a CHIANTI abundance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio. Default is
!abund_file.
IONEQ_FILE The name of a CHIANTI ion balance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio and evaluating
the T_max of the ion. Default is !ioneq_file.
SUM_MWL_COEFFS An array of coefficients of the same length as
the array of temperatures. Electron and proton rate
coefficients will be calculated at each temperature
and then a weighted sum of the coefficients is
performed using SUM_MWL_COEFFS. This allows
non-Maxwellian energy distributions to be
incorporated into the level balance equations.
This keyword is not compatible with the PRESSURE
keyword.
RADFUNC The name of a user-defined function that will generate
a radiation spectrum as a function of temperature.
This radiation field will replace the black-body that
is assumed when using the RADTEMP keyword in the call
to pop_solver.
KEYWORDS:
NO_DE Drops the hc/lambda factor in the computation of the
emissivities. Useful for emission measure analyses involving
photon fluxes
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
QUIET If set, don't list the temperatures and densities at which
the emissivities are caculated.
DIEL If the dielectronic recombination files exist for the ion,
then these are used to derive the emissivities.
NO_SETUP If emiss_calc is called from a routine where the ELEMENTS
common block has already been set up, then this keyword
stops emiss_calc loading up the common block
OUTPUT:
The structure that is output has the following tags:
.ion_name string; contains ion name, e.g., 'Fe XIII'
.lambda float; contains wavelength
.level1 integer; contains lower level of transition
.lvl1_desc string; gives config. and term of lower level
.level2 integer; contains upper level of transition
.lvl2_desc string; gives config. and term of upper level
.flag integer; a flag to mark particular transitions
.em fltarr(nt,nd); contains emissivities at particular
temperatures and densities.
PROGRAMMING NOTES:
Transitions where only theoretical energies are available for at
least one of the two levels are assigned negative wavelengths in
the .wgfa file. With emiss_calc, the wavelength is set to be
positive, but emiss.flag is set to -1 for that transition, so
that other routines can keep track of the theoretical wavelengths.
COMMON BLOCKS:
ELVLC, WGFA, UPSILON, RADIATIVE, PROTON, ELEMENTS, IONREC
CALLS:
SETUP_ION, POP_SOLVER
ZION2FILENAME, ZION2SPECTROSCOPIC
READ_PROT, PROTON_DENS
HISTORY:
Ver 1, PRY 28-Jun-97
Ver 2, PRY 26-Jul-97 - corrected problem with size of emiss
Ver 3, PRY 22-Sep-97 - allowed photo-excitation to be included
Ver 4, PRY 6-Jul-98 - added PATH
Ver 5, PRY 5-Sep-98 - added call to choose_ioneq
Ver 6, PRY 3-Dec-98 - dosen't crash if no params given
Ver 7, PRY 9-Jan-99 - allowed proton rates to be added through
/PROTON keyword.
Ver 8, PRY 10-Feb-99 - added /QUIET keyword
Ver 9, PRY 8-Oct-99 - for H-like ions, there's a 2-photon
transition with a non-zero A-value that is
assigned a zero wavelength (as it does not
produce an emission line). This caused
problems for dens_plotter, so emiss_calc
now removes this transition from the emiss
structure.
Ver 10, PRY 15-Dec-99 - added deu to the upsilon common block in
order to be consistent with the main Chianti
routines.
Ver 11, PRY 8-May-00 - added PRESSURE
Ver 12, PRY 17-Aug-00 - changed elvlc common block to match new
version of pop_solver
Ver 13, PRY 10-Oct-00 - now calls setup_ion to read ion data
Ver 14, PRY 1-Jun-00 - removed call to choose_ioneq; now makes use
of the !ioneq_file system variable.
Ver 15, PRY 25-Sep-01 - modified for 9-point splines and proton rates
Ver 16, PRY 9-Dec-01 - completed changes for v.4
V. 17, 29-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
Now we only call zion2filename, corrected the call to
zion2spectroscopic (dielectronic cases were not handled
correctly).
V.18, 6-Aug-2002, Peter Young
Theoretical wavelengths weren't being flagged so this
has now been corrected.
V.19, 7-Aug-2002, Peter Young
Stopped "lines" with zero wavelength being included in
the structure.
Changed the use of CHIANTI system variables.
V.20 14-Aug-2002, GDZ
Modified the use of Version, to make it compatible with the
other CHIANTI v.4 routines.
V.21 10-Sep-2002, Peter Young
Allowed a density of 1 cm-3 to be input.
V.22 7-Aug-2003, Peter Young
Added keyword /NO_SETUP
V.23 4-Oct-2003, GDZ
modified the input to POP_SOLVER, now it is dealt with an
input structure.
V.24 5-Mar-2004, Enrico Landi (EL)
included ionization and recombination as level population
processes
V.25 6-May-2005, EL
corrected a minor incompatibility with IDL 5.6
V.26 5-Jul-2005, Peter Young
added RADFUNC= and SUM_MWL_COEFFS= keywords
V.27 1-Aug-2005, Peter Young
re-ordered code for setup to prevent crash
V.28 3-Aug-2005,GDZ
fixed bug, only define ioneq_ionrec when files are
there (it was failing with neutrals)
VERSION : 28 3-Aug-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
GOFNT
PURPOSE:
calculate G(n,T) function (line intensity per unit emission measure)
PROCEDURE:
Must specify line to form numerator and denominator
Multiple lines can be selected and summed
This can now be done interactively or not.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
GOFNT,Ion,Wmin,Wmax,Temperature,G,Desc,density=
INPUTS:
Ion: the CHIANTI style name of the ion, i.e., 'c_5' for C V
Wmin: minimum of wavelength wavelength range of interest in Angstroms
Wmax: maximum of wavelength wavelength range of interest
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
Many - see the keywords below.
OUTPUTS:
Temperature: an array of temperatures
G: Intensity per unit emission measure N_e*N_H*dh [cm^-5].
The resulting units are therefore erg cm^+3 s^-1 sr-1
C(T)= 1/(4*!pi)* A_ji*(N_j(X^+m)/N(X^+m))*(N(X^+m)/N(X))*(N(X)/N(H))/N_e
unless /NOABUND is set, in which case
C(T)= 1/(4*!pi)* A_ji*(N_j(X^+m)/N(X^+m))*(N(X^+m)/N(X))/N_e
G(T)=(hc/lambda_ij)*C(T)
G(T)= C(T) if /PHOTONS is set
Desc: a short string description of the selected line
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
Postscript file withthe plot of G(T).
Ascii file with the values of G(T).
VALUE The array of G(T) values corresponding to logt0.
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
PRESSURE: specifies the pressure in units of NeT (cm^-3 K). G is then
calculated at that constant pressure
DENSITY: specifies the electron density in units of cm^-3. G is then
calculated at that value of the electron density. If neither the
density or pressure keywords are specified, a constant
density of 1.e+10 cm^-3 is assumed
PHOTONS: sets output in photons/s
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
RADTEMP The blackbody radiation field temperature (default 6000 K).
OUTFILE: the (optional) name of the output ascii file where a
listing of the line ratio intensity as a function of
temperature is saved.
PSFILE: the (optional) name of the output postscript file
where a plot of the chosen G(T) is saved.
NOABUND: If set, the G(T)'s are not multiplied by the abundance
factor.
NOPROT If set, then proton rates are not included.
ABUND_NAME: Name of the abundance file to use. If not passed, then
the user is prompted for it.
IONEQ_NAME: Name of the ionization equilization name to use. If not
passed, then the user is prompted for it.
ALL If set, all lines are calculated, including
the 'unobserved' ones.
LOWER_LEVELS
UPPER_LEVELS
Arrays with the indices of the lower and upper levels
pertaining to the transitions you want to get.
If more than one couple is given, the G(T) of the
lines are summed.
Obviously, the given indices must correspond to transitions
that are present in the database.
ARCSECS
If set, units are photons (ergs) cm^+3 s^-1 arcsecs^-2
VERBOSE
LOGT0 An array of log T values for which the G(T) are wanted.
VALUE The array of G(T) values corresponding to logt0.
If logt0 is defined, and within the limits of the
temperatures for which G(T) NE 0, the array VALUE
is returned with a simple spline interpolation.
CALLS:
CH_SYNTHETIC, CH_XMENU_SEL
COMMON BLOCKS: None
RESTRICTIONS:
SIDE EFFECTS:
EXAMPLE:
IDL> gofnt,'o_5',1000.,1500.,temp,goft,desc,density=1.e+16
CATEGORY:
spectral diagnostics
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
October 4, 1996: Version 1
14-Jul-2000 Peter Young, now calls pop_solver
26-Oct-2000 GDZ, added keyword NOABUND to not multiply for the abundence
factor. Corrected header for a wrong description.
Version 4, 21-Dec-2000, William Thompson, GSFC
Modified for better cross-platform graphics capability
Version 5, 8-Nov-01, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ).
Rewritten as a wrapper routine using the new procedures.
Corrected a few inconsistencies in the plots.
Version 6, 18-Nov-01, Peter Young
Added /noprot, rphot and radtemp keywords.
Version 7, 11-Dec-01, Peter Young
Changed call to ch_strpad to strpad.
V. 8, GDZ, 28-Apr-02 Added abund_name,ioneq_name keywords.
v. 9 21-May-2002, GDZ
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V.10, 15-Aug-02, GDZ
Major revision:
-Removed the call to ch_xselect_s, that did not work for long lists.
-Added a '*' in the line lists, to identify 'unobserved' lines.
-Replaced the commands to create PS file, to make it
cross-platform compatible.
-Added a large number of cosmetics, mainly lables to the axes and
titles.
-Added keyword ALL. If set, all lines are calculated, including
the 'unobserved' ones.
-Added the CHIANTI version number in the outputs.
V. 11, 19-Sep-02, GDZ
Clarified output units.
V.12, 25-Jun-03, GDZ,
Added many new keywords. Now is possible to use the routine
with background jobs, in not-interactive mode.
Rounded the wavelengths.
V.13, 24-Sept-2003, GDZ
Corrected a bug when logt0 is not defined.
V.14, 3-Nov-03 GDZ
Modified format e8.2 to e9.2 for Windows compatibility.
VERSION : 14, 3-Nov-03
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME: G_OF_T()
PURPOSE:
To compute DE * F(T) * n_j * A_ji / N_e for selected emission lines.
Option to also multiply by abundance.
CATEGORY:
Atomic data analysis
EXPLANATION:
The G-of-T function has a number of different definitions in the
literature. In the most basic form it contains only the temperature
dependent parts (i.e., 0.83*n_j*A_ji*F(T)/N_e), but often a Delta-E
and Ab(X) are added as well. Here, the _default_ form is:
Delta-E * 0.83 * n_j * A_ji * F(T) / N_e
By using the NO_DE keyword, the Delta-E can be omitted, while the
ABUND keyword allows the abundance to be added.
The function that is output is tabulated over 4.0 <= logT <= 8.0
in 0.1 dex intervals. If you want the function tabulated over
smaller intervals, run the ION_INTERP routine afterwards.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
EXAMPLES:
RESULT=G_OF_T(26,13)
RESULT=G_OF_T(26,13,DENS=7)
RESULT=G_OF_T(26,13,GOFTFILE='my_gofts.dat')
RESULT=G_OF_T(26,13,/ABUND)
RESULT=G_OF_T(26,13,ABUND_FILE=ABUND_FILE, IONEQ_FILE=IONEQ_FILE)
INPUTS:
IZ: The atomic number of the ion (e.g., 26 = Fe)
ION: The spectroscopic number of the ion (e.g., 12 = XII)
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
DENS: The logarithm (to base 10) of the density at which the
emissivities are calculated (default=10.)
WRANGE: Wavelength range from which lines are required. If not
specified, then the 10 strongest lines are displayed.
PATH: If specified, the routine will look for the atomic data in
the PATH directory, rather than in the CHIANTI database
GOFTFILE: By specifying GOFTFILE as a filename, the G-of-T
function can be stored in this file. It is stored
in the form a structure (called goft_list) with the following
labels:
goft_list.label: user-specified string, e.g., 'Si XII 520.7'
goft_list.func: fltarr(41), the G-of-T function
If the same GOFTFILE is specified for another ion, then the
G-of-T function is added to the existing structure. The GOFTFILE
option only works when the ABUND keyword is set. The GOFTFILE is
meant to be read by another routine called GOFT_PLOTTER.
INDEX: Allows the direct specification of indices within the
emiss structure. This allows the g_of_t routine to be
run without the menu widget appearing. If the /quiet
keyword is also used, then the routine will run "silently".
RADTEMP Specify background radiation temperature (default: 6000 K)
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
IONEQ_FILE Directly specify the name of the ion balance file
(including directory path). If not set, then a widget will
pop up allowing you to select a file.
ABUND_FILE Directly specify the name of the abundance file
(including directory path). One can also use /ABUND_FILE
to include the abundances in the G(T) function, but allow
the abundance file to be picked through a widget.
KEYWORDS:
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
NO_DE: If set, then the output function will *not* contain the
Delta-E. Be careful using this if you are using blends
(as Delta-E is different for different wavelengths).
QUIET If set, then don't plot the G(T) function or print out
information to the screen.
CALLS:
EMISS_CALC, READ_IONEQ, READ_ABUND, EMISS_SELECT, CH_GET_FILE
RESTRICTIONS:
HISTORY:
Ver.1, PRY 28-Jul-97.
Ver.2, PRY 22-Jun-98, added CHOOSE keyword and removed RAY
Ver.3, PRY 4-Aug-98, cosmetic changes following comments of Giulio
Del Zanna
Ver.4, PRY 5-Sep-98, added call to choose_ioneq
Ver.5, PRY 23-Sep-98, added GOFTFILE input
Ver.6, PRY 3-Mar-99, now calls EMISS_SELECT
Ver.7, PRY 6-Nov-00, removed the /CHOOSE keyword; also changed
PICKFILE call to DIALOG_PICKFILE and removed call
to the CHIANTI routine ADD\_SUBDIR
Ver.8, PRY 18-Oct-01, adjusted for proton rates, and
photoexcitation.
Ver.9, PRY 9-Dec-01, completed modifications for v.4 of CHIANTI.
V. 10, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
Ver. 11, 9-Feb-2005, Peter Young
changed keyword_set(abund) to keyword_set(abund_file)
VERSION : 11, 9-Feb-2005
PROJECT
CHIANTI http://wwwsolar.nrl.navy.mil/chianti.html
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME
dens_plotter
PURPOSE:
A widget-based routine to allow the analysis of density sensitive
ratios. **** See RATIO_PLOTTER for details. *****
CALLING SEQUENCE:
IDL> dens_plotter, name,$
EM, PATH=PATH, NOPROT=NOPROT, $
IONEQ_FILE=IONEQ_FILE, ABUND_FILE=ABUND_FILE
INPUTS:
The ion name (e.g. 'si_3' for Si III)
OPTIONAL INPUTS : none
OUTPUTS:
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
EM: Save the displayed emissivities to structure EM.
**** See RATIO_PLOTTER for details. *****
KEYWORDS:
PATH: Data in the CHIANTI format that is not in the CHIANTI
database can be read by specifying the directory in which
it lies through PATH.
ABUND_FILE The name of a CHIANTI abundance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio. Default is
!abund_file.
IONEQ_FILE The name of a CHIANTI ion balance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio and evaluating
the T_max of the ion. Default is !ioneq_file.
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
CALLS: CONVERTNAME RATIO_PLOTTER
COMMON BLOCKS: none
RESTRICTIONS:
SIDE EFFECTS:
CATEGORY:
spectral synthesis.
EXAMPLE:
IDL> dens_plotter, 'si_9'
WRITTEN :
Ver.1, 18-Apr-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ) written as a wrapper
routine to call RATIO_PLOTTER.
MODIFIED: V.2, 2-Aug-2005, GDZ
Now the routine handles the dielectronic case
VERSION : 2, 2-Aug-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
DENSITY_RATIOS
PURPOSE:
to calculate line intensity ratios as a function of electron density
CATEGORY:
scientific analysis
CALLING SEQUENCE:
DENSITY_RATIOS,Ion,Wmin,Wmax,Dmin,Dmax,Density,Ratio,Description
INPUTS:
Ion: the CHIANTI style name of the ion, i.e., 'c_5' for C V
wmin: minimum of the wavelength range of interest in Angstroms
wmax: maximum of the wavelength range of interest in Angstroms
dmin: log10 of the minimum desired density (8. = 10^8 cm^(-3) )
dmax: log10 of the maximum desired density range
INTERACTIVE INPUTS:
Must select the line for the numerator and denominator
It is possible to select multiple lines to be summed
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
OUTFILE: the (optional) name of the output ascii file where a
listing of the line ratio intensity as a function of
density is saved. For example, outfile='den_rat.lis'
PSFILE: the (optional) name of the output postscript file
where a plot of the choses density sensitive line
ratio is saved. For example, psfile='den_rat.ps'
TEMP: to specify the temperature, otherwise the temperature at
the peak
of the ionization equilibrium is used. For example,
temp=1.e+6
/PHOTONS: if set, the ratio will be in photon units, as opposed
to ergs
RADTEMP Specify background radiation temperature (default: 6000 K)
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
VERBOSE To print out information about the lines.
OUTPUTS:
Density: an array of the density values for which the selected
intensity ratio calculated
Ratio: an array of line intensity ratios
Description: a string describing the transitions selected
Plots the intensity ratio of the selected line as a function of density
COMMON BLOCKS:
None.
CALLS
EMISS_CALC, ION2SPECTROSCOPIC, CONVERTNAME, READ_IONEQ,
CH_XMENU_SEL
EXAMPLE:
density_ratios,'o_5',1000.,1500.,8.,13.,den,rat,desc
choose the ratio of 1371.294 to 1218.393
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1996: Version 2.0
May 28, 1996: Ken Dere added psfile keyword/option
Sept 1996: modified to work with VMS
and added keyword TEMP, Ken Dere
Feb. 2000: Modified for Version 3, K. Dere
14-Jul-2000 Peter Young, now calls pop_solver
26-Sep-2001 Modified for 9-point splines and proton rates;
added radtemp and rphot keywords for photoexcitation.
20-Nov-2001 Routine now calls emiss_calc to get emissivities.
V.9, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V.10, 1-Aug-02 GDZ
Changed all the formats.
V.11, 06-Aug-02 GDZ
Changed the use of CHIANTI system variables.
V.12, 15-Aug-02, GDZ
Major revision:
-Added the keyword VERBOSE, to avoid printing out long lists of lines.
-Removed the call to ch_xselect_s, that did not work for long lists.
-Added a '*' in the line lists, to identify 'unobserved' lines.
-Replaced the commands to create PS file, to make it
cross-platform compatible.
-Added a large number of cosmetics, mainly lables to the axes and
titles, that were missing.
-Removed plotting in windows already present.
-Added the CHIANTI version number in the outputs.
V.13, 3-Nov-03 GDZ
Modified format e8.2 to e9.2 for Windows compatibility.
VERSION : 13, 3-Nov-03
Project : SOHO - CDS
Name : CHIANTI_NE
Purpose : Calculate and plot CHIANTI density sensitive line ratios.
Explanation : CHIANTI_NE (density ratios)
calculates and plots density sensitive line ratios based on
the CHIANTI atomic database of Dere et. al.
Use : IDL> chianti_ne
Inputs : None
Opt. Inputs : None
Outputs : None
Opt. Outputs: None.
Keywords : None
Calls : CALC_DMM_DR, plot_dmm_dr_fig , make_ion_list
Common : dmm_dr_com dmm_lines(with plot_dmm_dr_fig),
Restrictions: None
Side effects: None
Category : Spectral
Prev. Hist. : Started life as 'density_ratios' by Ken Dere
Written : C D Pike, RAL, 13-Jan-96
Modified : Added selection of els/ions from master file. CDP, 21-Jan-96
Added hardcopy of line list, refs etc. CDP, 22-Jan-96
Include multiple lines in ratio. CDP, 27-Jan-96
General upgrade and added temp/unit selections. CDP, 6-Jun-97
Added intensity ratio selection. CDP, 17-Jul-97
Added wavelength ranges. CDP, 18-Jul-97
Fixed typos introduced in version 7. CDP, 22-Jul-97
Float the user-supplied Log Temperature. CDP, 1-Aug-97
Update for IDL v5.2. CDP, 20-Apr-99
v. 11 Update list of elements. CDP, 18-Jun-99
V.12. Added ratio plots and hardcopies in linear scale, added various
checks and minor things. Added a few tags to the
ratio output structure (temperature, units, comment).
Removed optional output structure.
Updated to be CHIANTI v.3-compatible.
Giulio Del Zanna, DAMTP, 7-Oct-2000
Version 13, 21-Dec-2000, William Thompson, GSFC
Modified for better cross-platform graphics capability
V. 14, 1-May-02, GDZ, commented out a few refs.
V. 15, 21-May-2002, GDZ, changed the way to deal with fonts.
V.16, 17-Sep-2002 (GDZ)
added !p.multi = 0 upon exit and added X-label.
Version : Version 16, 17-Sep-2002
Project : SOHO - CDS
Name : PLOT_CHIANTI_NE
Purpose : Plots a density sensitive ration saved from CHIANTI_NE
Explanation : The routine CHIANTI_NE allows the calculated ratio to be
saved in an IDL save file. This routine retrieves and
plots the ratio.
Use : IDL> plot_chianti_ne, file, data
Inputs : file - save file name (an extension of .CH_NE will have
been added, specifying this is optional)
Opt. Inputs : None
Outputs : None
Opt. Outputs: data - returns the retrieved ratio structure
Keywords : log. If set, a log-log plot is produced.
Calls : print2d_plot
Common : None
Restrictions: None
Side effects: None
Category : Synthetic spectra
Prev. Hist. : None
Written : C D Pike, RAL, 7-Oct-96
Modified : v.2 Added a few extra things, including possibility to create a
postscript file.
Giulio Del Zanna (DAMTP), 10-Oct-2000
Version : Version 2, GDZ 10-Oct-2000
PROJECT
CHIANTI http://wwwsolar.nrl.navy.mil/chianti.html
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME
temp_plotter
PURPOSE:
A widget-based routine to allow the analysis of temperature sensitive
ratios. **** See RATIO_PLOTTER for details. *****
CALLING SEQUENCE:
IDL> temp_plotter, name,$
EM, PATH=PATH, NOPROT=NOPROT, $
IONEQ_FILE=IONEQ_FILE, ABUND_FILE=ABUND_FILE
INPUTS:
The ion name (e.g. 'si_3' for Si III)
OPTIONAL INPUTS : none
OUTPUTS:
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
EM: Save the displayed emissivities to structure EM.
**** See RATIO_PLOTTER for details. *****
KEYWORDS:
PATH: Data in the CHIANTI format that is not in the CHIANTI
database can be read by specifying the directory in which
it lies through PATH.
ABUND_FILE The name of a CHIANTI abundance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio. Default is
!abund_file.
IONEQ_FILE The name of a CHIANTI ion balance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio and evaluating
the T_max of the ion. Default is !ioneq_file.
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
CALLS: CONVERTNAME RATIO_PLOTTER
COMMON BLOCKS: none
RESTRICTIONS:
SIDE EFFECTS:
CATEGORY:
spectral synthesis.
EXAMPLE:
IDL> temp_plotter, 'fe_13'
WRITTEN :
Ver.1, 18-Apr-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ) written as a wrapper
routine to call RATIO_PLOTTER (written by P. Young).
MODIFIED: V.2, 2-Aug-2005, GDZ
Now the routine handles the dielectronic case
VERSION : 2, 2-Aug-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
TEMPERATURE_RATIOS
PURPOSE:
calculate and display temperature sensitivity of line intensity ratios
CATEGORY:
spectral diagnostics
PROCEDURE :
The intensities (Population of the upper level * A) of the lines within
the selected ion are first calculated, either at constant pressure or
at constant density (however specified in the input). They are plotted
in window 0. The intensities relative to the brightest reference line
are then plotted in window 1. A widget allows the user to select a
number of lines (at least one!) for the numerator of the ratio, and a
number of lines for the denominator. In case of multiple selections, the
line intensities are summed. The ratio values are plotted in window 2, and
optionally also saved in a text file. A postscript file can also be
created. The ratio values, calculated at twice and half the prescribed
density are also calculated and overplotted, to show how the
temperature ratio also depends on the density.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
> temperature_ratios,ion,wmin,wmax,Log10(tempmin),Log10(tempmax),temperature,ratio,description,$
[pressure= ,density= , psfile= , outfile= ]
EXAMPLE:
> temperature_ratios,'c_4',100.,1600.,4.,6.,temp,ratio,desc,density=1.e+10,$
psfile='test.ps', outfile='test.txt'
then select the ratio of (384.17 + 384.19) to 1550.772
INPUTS:
Ion: the CHIANTI style name of the ion, i.e., 'c_5' for C V
Wmin: minimum wavelength limit in Angstroms
Wmax: maximum wavelength limit in Angstroms
Tempmin: log10 of lowest temperature of interest, i.e. 4 for 10.^4 K
Tempmax: log10 of highest temperature of interest
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
Must specify indices of lines which are to form the ratio
RADTEMP The blackbody radiation field temperature (default
6000 K).
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius
units. I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface.
(Default is infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
ABUND_FILE The name of a CHIANTI abundance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio. Default is
!abund_file.
IONEQ_FILE The name of a CHIANTI ion balance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio and evaluating
the T_max of the ion. Default is !ioneq_file.
OUTPUTS:
Temperature: an array of temperatures spanning Tempmin to Tempmax
Ratio: an array of the intensity ratio of the selected lines
Desc: a short string description of the selected line ratio
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
Ps and/or text file with the intensity ratio.
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
DENSITY: calculates the intensity ratios for constant density.
If neither density or pressure are specified, a constant
density of 1.e+10 cm^-3 is assumed as default.
OUTFILE: the (optional) name of the output ascii file where a
listing of the line ratio intensities as a function of
temperature is saved.
PSFILE: the (optional) name of the output postscript file
where a plot of the chosen temperature sensitive line
ratio is saved.
NOPROT Switches off inclusion of proton rates.
VERBOSE prints out information
CALLS:
read_ioneq, convertname, ion2spectroscopic,ion2filename,
ch_xmenu_sel, emiss_calc
COMMON:
elvlc,l1a,term,conf,ss,ll,jj,ecm,eryd,ecmth,erydth,eref
wgfa, wvl,gf,a_value
upsilon,t_type,deu,c_ups,splups
proton, pstr, pe_ratio
radiative, radt, dilute
RESTRICTIONS:
SIDE EFFECTS: None known yet.
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
May 1996: Version 2.0, Ken Dere
April 2000: V. 3 Ken Dere modified for V3
14-Jul-2000 V. 4 Peter Young, now calls pop_solver
2-Oct-2000 V. 5 Giulio Del Zanna, corrected an error in the
creation of the string list of the lines in the ratio.
Also corrected a few minor errors.
Removed the device,window_state call, and added a few
other 'cosmetic' adjustments.
Version 6, 21-Dec-2000, William Thompson
Modified for better cross-platform capability.
Ver.7, 6-Dec-2001, Peter Young
Revised to call emiss_calc for the emissivities.
V.8, 21-May-2002, GDZ
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V.9, 1-Aug-02 GDZ
Fixed label mistake, and changed all the formats.
V.10, 06-Aug-02 GDZ
Changed the use of CHIANTI system variables.
V.11, 15-Aug-02, GDZ
Major revision:
-Added the keyword VERBOSE, to avoid printing out long lists of lines.
-Removed the call to ch_xselect_s, that did not work for long lists.
-Added a '*' in the line lists, to identify 'unobserved' lines.
-Replaced the commands to create PS file, to make it
cross-platform compatible.
-Added a large number of cosmetics, mainly lables to the axes and
titles, that were missing.
-Removed plotting in windows already present.
-Removed the pressure keyword.
-Added the CHIANTI version number in the outputs.
V.12, 3-Nov-03 GDZ
Modified format e8.2 to e9.2 for Windows compatibility.
VERSION : 12, 3-Nov-03
Project : SOHO - CDS
Name : CHIANTI_TE
Purpose : Calculate and plot CHIANTI temperature sensitive line ratios.
Explanation : CHIANTI_TE (temperature ratios)
calculates and plots temp. sensitive line ratios based on
the CHIANTI atomic database of Dere et. al.
Use : IDL> chianti_te
Inputs : None
Opt. Inputs : None
Outputs : None
Opt. Outputs: none.
Keywords : None
Calls : CALC_DMM_TR, make_ion_list
Common : dmm_tr_com
Restrictions: None
Side effects: None
Category : Spectral
Prev. Hist. : Started life as 'temperature_ratios' by Ken Dere
Written : H.E. Mason, 3 Oct 1996
Modified : Update for IDL v5.2. CDP, 20-Apr-99
V.3. Update list of elements. CDP, 18-Jun-99
V.4 , Giulio Del Zanna (DAMTP), 10 Oct-2000
Rewritten completely, adding possibility to select the density
at which the intensities are calculated, making this routine
compatible ith CHIANTI v.3, and with the same characteristics as
CHIANTI_TE. Added ratio plots and hardcopies in linear scale, added various
checks and minor things. Added a few tags to the
ratio output structure (density, units, comment).
Removed optional output structure.
Version 5, 21-Dec-2000, William Thompson, GSFC
Modified for better cross-platform graphics capability
V. 6, 1-May-02, GDZ, commented out a few refs.
V.7, 21-May-2002, GDZ, fixed a bug with the fonts.
V.8, 17-Sep-2002 (GDZ)
added !p.multi = 0 upon exit and added X-label
Version : Version 8, 17-Sep-2002
Project : SOHO - CDS
Name : PLOT_CHIANTI_TE
Purpose : Plots a temperature sensitive ratio saved from CHIANTI_TE
Explanation : The routine CHIANTI_TE allows the calculated ratio to be
saved in an IDL save file. This routine retrieves and
plots the ratio.
Use : IDL> plot_chianti_te, file, data
Inputs : file - save file name (an extension of .CH_TE will have
been added, specifying this is optional)
Opt. Inputs : None
Outputs : None
Opt. Outputs: data - returns the retrieved ratio structure
Keywords : log. If set, a log-log plot is produced.
Calls : None
Common : None
Restrictions: None
Side effects: None
Category : Synthetic spectra
Prev. Hist. : None
Written : C D Pike, RAL, 7-Oct-96
Modified : v.2 Added a few extra things, including possibility to create a
postscript file.
Giulio Del Zanna (DAMTP), 10-Oct-2000
Version : Version 2, GDZ 10-Oct-2000
PROJECT : CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME
FREEFREE
PURPOSE:
This routine computes the free-free continuum (bremsstrahlung)
using the fitting formulae of Itoh et al. (ApJS 128, 125, 2000)
and Sutherland (MNRAS 300, 321, 1998).
The Itoh et al. data are valid for smaller ranges for temperature
and wavelength than Sutherland and so for points outside of their
ranges we use the data of Sutherland.
INPUTS
TEMP Temperature (in K).
WVL Wavelengths in angstroms. Can be a scalar or vector.
OUTPUTS
INT Free-free continuum intensity in units of
10^-40 erg cm^3/s/sr/Angstrom
[ integral(N_H N_e dh) in cm^-5 ] if a DEM is not defined.
If DEM values are defined, it is assumed that they are given
as N_H N_e dh/dT. The units are 10^-40 erg/cm^2/s/sr/Angstrom.
If T is given as a 1-D array, then the output will be a 2-D array,
with one element for each temperature and wavelength
(but also see SUMT).
OPTIONAL INPUTS
DEM_INT An array of same length as TEMP which contains the
differential emission measure values at each temperature.
The emissivity at each temperature is multiplied by the
DEM value and the d(logT) value.
MIN_ABUND This keyword allows the specification of a minimum abundance,
such that any elements with an abundance (relative to
hydrogen) less than MIN_ABUND will not be included in the
calculation. E.g., MIN_ABUND=1e-5.
KEYWORDS
NO_SETUP By default the routine asks the user which ion balance
and abundance files to use via pop-up widgets. If
/no_setup is used then this data is taken from the common
block.
SUMT The default is to output the intensity array as an array
of size (nwvl x nT). Setting this keyword performs a sum
over the temperatures to yield a vector of same size as
the input wavelengths, thus producing the complete
free-free spectrum.
PHOTONS Gives output emissivity in photon units rather than ergs.
CALLS
SUTHERLAND, ITOH
COMMON BLOCKS
ELEMENTS
PROGRAMMING NOTES
The Itoh fitting formula is only valid for (6.0 LE logT LE 8.5).
For temperatures below this, we thus switch to the Sutherland
fitting formula. There is very little (<1%) between the two at
logT=6.
Itoh also has a constraint on the quantity u=hc/kTl (l=wavelength),
such that (-4 LE log u LE 1.0). The upper limit corresponds to the
continuum being cut-off prematurely at low wavelengths. E.g., for
T=10^6 the cutoff is at 14.39 angstroms. For these low wavelengths
we also use the Sutherland data to complete the continuum. Note that
the continuum at these wavelengths is very weak
MODIFICATION HISTORY
Ver.1, 5-Dec-2001, Peter Young
Completely revised to call the separate itoh.pro and
sutherland.pro routines.
V. 2, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ),
Corrected the description of the units.
Added verbose keyword and a printout.
V. 3, 22-May-2002, Peter Young (PRY)
Added MIN_ABUND optional input.
Changed ioneq_t to ioneq_logt (GDZ).
V 4, 25-May-2005, GDZ
corrected routine header.
VERSION : 4, 25-May-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME
FREEBOUND
PURPOSE:
Calculates the free-bound (radiative recombination) continuum.
INPUTS
TEMP Temperature in K (can be an array).
WVL Wavelength in angstroms (can be an array).
OUTPUTS
INT Free-bound continuum intensity in units of
10^-40 erg cm^3/s/sr/Angstrom
( integral(N_H N_e dh) in cm^-5) if a DEM is not defined.
If DEM values are defined, it is assumed that they are given
as N_H N_e dh/dT. The units are 10^-40 erg/cm^2/s/srAngstrom
If T is given as a 1-D array, then the output will be a
2-D array, with one element for each temperature and
wavelength (but also see SUMT).
OPTIONAL INPUTS
DEM_INT The intensity array is multiplied by a DEM number for
each temperature. DEM_INT needs to be of the same size
as TEMPERATURE. It is needed for the synthetic spectrum
routines.
IZ Only calculate continuum for the element with atomic
number IZ
ION (To be used in conjunction with IZ.) Calculated continuum
for a single ion (IZ, ION).
KEYWORDS
NO_SETUP If the procedure setup_elements has already been called
then the keyword /nosetup should be set to avoid
repeating this step
MIN_ABUND If set, calculates the continuum only from those
elements which have an abundance greater than
min_abund. Can speed up the calculations. For
example:
abundance (H) = 1.
abundance (He) = 0.085
abundance (C) = 3.3e-4
abundance (Si) = 3.3e-5
abundance (Fe) = 3.9e-5
PHOTONS The output spectrum is given in photon units rather
than ergs.
SUMT When a set of temperatures is given to FREEBOUND, the
default is to output INTENSITY as an array of size
(nwvl x nT). With this keyword set, a summation over
the temperatures is performed.
VERBOSE Output information from FREEBOUND.
COMMON BLOCKS
ELEMENTS
CALLS
FREEBOUND_ION, SETUP_ELEMENTS, READ_KLGFB, GET_IEQ
HISTORY
Ver.1, 24-Jul-2002, Peter Young
Ver.2, 26-Jul-2002, Peter Young
revised call to freebound_ion; corrected ion fraction problem
V 3, 25-May-2005, GDZ
corrected routine header.
VERSION : 3, 25-May-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
TWO_PHOTON
PURPOSE:
Calculate the 2 photon continuum from a hot, low density plasma.
For the hydrogen isoelectronic sequence, A values
Parpia, F. A., and Johnson, W. R., 1982, Phys. Rev. A, 26, 1142.
and distribution function as a function of Z is taken from:
Goldman, S.P. and Drake, G.W.F., 1981, Phys Rev A, 24, 183
For the helium isoelectronic sequence, A values are from:
Drake, G.W.F., 1986, Phys. Rev. A, 34, 2871
and the distribution function as a function of Z is taken from:
Drake, G.W.F., Victor, G.A., Dalgarno, A., 1969, Phys.
Rev. A, 180, 25.
in this paper the distribution is only given up to Z=10 but
extrapolation to higher Z appears to be OK.
Note that, unlike the freefree and freebound routines, two_photon
requies the electron density to be specified. This is because there
is a call to pop_solver
CALLING SEQUENCE:
TWO_PHOTON,temperature, density, wavelength, intensity
INPUTS:
TEMPERATURE Temperature in degrees Kelvin, can be a 1D array
WAVELENGTH Wavelengths in Angstroms.
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
DENSITY Electron density in cm^-3, can also be a 1D array
of the same size as Temperature. If there are several
temperatures specified but only one density, then
density is assumed the same at all temperatures.
If not specified, then default densities of 10^10
electrons/cm^3 are assumed.
DEM_INT An array of same length as TEMP which contains the
differential emission measure values at each temperature.
The emissivity at each temperature is multiplied by the
DEM value and the d(logT) value.
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
NO_SETUP: If the procedure setup_elements has already been called
then the keyword /no_setup should be set to avoid
repeating this step
MIN_ABUND: If set, calculates the continuum only from those
elements which have an abundance greater than min_abund.
Can speed up the
calculations. For example:
abundance (H) = 1.
abundance (He) = 0.085
abundance (C) = 3.3e-4
abundance (Si) = 3.3e-5
abundance (Fe) = 3.9e-5
SUMT If several temperatures have been specified, then /sumt
will sum the emissivities over the different
temperatures, giving an output INTENSITY that has the
same size as WAVELENGTH.
PHOTONS If set the continuum emissivity is output in photon
units rather than erg units.
VERBOSE
OUTPUTS:
RAD 2 photon continuum intensity in units of
10^-40 erg cm^3/s/sr/Angstrom per unit emission measure
( integral(N_H N_e dh) in cm^-5) if a DEM is not defined.
If DEM values are defined, it is assumed that they are given
as N_H N_e dh/dT. The units are
10^-40 erg/cm^2/s/sr/Angstrom
If T is given as a 1-D array, then the output will be a 2-D array,
with one element for each temperature and wavelength
(but also see SUMT).
CALLS
POP_SOLVER, SETUP_ION, SETUP_ELEMENTS, READ_MASTERLIST,
CONVERTNAME
COMMON BLOCKS:
ELEMENTS, ELVLC, WGFA, UPSILON, PROTON
EXAMPLE:
> two_photon,1.e+6,3.e+10,wvl,int
> two_photon,1.e+6,3.e+10,wvl,int,min_abund=3.e-5
> two_photon,1.e+6,3.e+10,wvl,int,/no_setup
PROGRAMMING NOTES
For He 2-photon decays, the distribution function is from Table II
of Drake et al. (1969), except that the values have been divided by
the A-value from Drake (1986).
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
February 2001: Version 1.0
Ver.2, 19-Dec-2001, Peter Young
Now allows an array of temperatures.
Added /SUMT keyword.
Added DEM_INT= optional input.
Switched to using spl_init & spl_interp for the spline fits.
Corrected a small bug.
Ver.3, 20-Dec-2001, Peter Young
Corrected a bug related to density indices.
Ver.4, 23-Apr-2002, Peter Young
Added /photons keyword.
Ver.5, 28-May-2002, Peter Young
Corrected way in which DEM_INT is handled.
V. 6, 28-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
Corrected the description of the units and various
inaccuracies in the header.
V.7, 14-Aug-02, GDZ
Added keyword VERBOSE
V.8, 4-Oct-2003, GDZ
modified the input to POP_SOLVER, now it is dealt with an
input structure.
V.9, 8-Jun-2004, EL
modified the input to POP_SOLVER, now it includes ion/rec
V.10, 5-Jul-2005
corrected problems with the input structure for pop_solver
v.11 29-Jul-2005, GDZ
fixed bug, only define ioneq_ionrec when files are
there (it was failing with neutrals)
VERSION : 11 29-Jul-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME: SHOW_POPS
PURPOSE:
To display populations of significant levels in a CHIANTI ion
model
CATEGORY:
Scientific analysis
EXPLANATION:
Displays percentage level populations and level IDs for all levels
in the specified ion with populations greater than 0.01%. If the
temperature is not specified, then it is taken to be where the
maximum of the ionisation fraction is.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
SHOW_POPS, IZ, ION [, POPSTR, DENS= , TEMP= , /NOPROT,
RADTEMP= , RPHOT= , /ALL, /DIEL, PATH=,
IONEQ_FILE= , ABUND_FILE= ]
EXAMPLES:
show_pops,26,13,popstr
show_pops,26,13,dens=7.5,temp=6.0,rphot=1.2
INPUTS:
IZ The atomic number of the ion
ION The spectroscopic number of the ion (e.g., 12 = XII)
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
DENS Logarithm of electron density
TEMP Logarithm of electron temperature. If not specified, then
T_max of the ion is used
RADTEMP Specify background radiation temperature (default: 6000 K)
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
PATH Directly specify the path where the ion data is contained,
e.g., path='/home/other_data/fe_13'
N_LEVELS The size of the ion model is automatically determined
from the information in the CHIANTI data files. Setting
this keyword allows the number of levels in the model to
be reduced. E.g., N_LEVELS=14 reduces the model to the
first 14 levels given in the .ELVLC file.
IONEQ_FILE To include proton rates in the level balance equations
requires the number of density of protons to be known,
and this requires an ion balance file and an abundance
file to be specified, which are done through the
IONEQ_FILE and ABUND_FILE keywords. If they are not set
then the default files specified by !ioneq_file and
!abund_file are used.
ABUND_FILE See IONEQ_FILE.
SUM_MWL_COEFFS An array of coefficients of the same length as
the array of temperatures. Electron and proton rate
coefficients will be calculated at each temperature
and then a weighted sum of the coefficients is
performed using SUM_MWL_COEFFS. This allows
non-Maxwellian energy distributions to be
incorporated into the level balance equations.
If this keyword is set for an ion that has ionization
and recombination included in the level balance, then
these processes will be switched off for the
calculation since their rates implicitly assume a
single Maxwellian to describe the ion fractions of
the neighbouring ions.
LEVEL Allows the control of which level populations are displayed
to the screen. If set to a positive scalar or array, then
only those levels are printed. If it is set to a negative
scalar (-n), then all level populations up to level n are
printed. E.g., LEVEL=20 (only level 20); LEVEL=[5,7,20]
(levels 5, 7 and 20); LEVEL=-20 (all levels up to level 20).
RADFUNC The name of a user-defined function that will generate
a radiation spectrum as a function of temperature.
This radiation field will replace the black-body that
is assumed when using the RADTEMP keyword in the call
to pop_solver.
; OPTIONAL OUTPUTS
POPSTR Send level population information to a structure. POPSTR has
the tags:
.dens Density (cm^-3)
.temp Temperature (K). Can be an array if SUM_MWL_COEFFS=
is used.
.radtemp RADTEMP. Set to -1 if RADTEMP not
set.
.rphot RPHOT value. Set to -1 if RPHOT not set.
.proton String set to 'yes' if proton rates included, 'no'
otherwise
.version CHIANTI version used to derive populations.
.date Date and time at which structure created.
.level Structure containing level information. Tags are:
.index CHIANTI level index
.term String containing level identifier.
.pop Population of level
.sumtst Set to 1 if the SUM_MWL_COEFFS keyword has been used.
Set to 0 otherwise.
.sum_mwl_coeffs Contains SUM_MWL_COEFFS. Set to -1 if sumtst=0.
KEYWORDS:
ALL Show populations for all levels.
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
DIEL Use the dielectronic recombination files. E.g., for Fe XXII,
the routine will read in the fe_22d.* files instead of the
fe_22.* files.
COMMON BLOCKS:
ELVLC, WGFA, UPSILON, RADIATIVE, PROTON, ELEMENTS
CALLS:
ZION2FILENAME, POP_SOLVER, SETUP_ION, READ_IONEQ,
READ_ABUND, PROTON_DENS, CONCAT_DIR
HISTORY:
Ver 1, PRY 22-Sep-97
Ver.2, PRY 5-Sep-98 - added call to choose_ioneq
Ver.3, PRY 23-Apr-99 - calls pop_solver now; added DENS keyword
Ver.4, PRY 18-Dec-99 - added deu to upsilon common block to be
consistent with main Chianti routines.
Ver.5, PRY 7-Aug-00 - added /DIEL keyword to allow populations of
the dielectronic recombination files to be studied.
Also changed elvlc common block to match new
version of pop_solver.
Ver 6, PRY 10-Oct-00 - now calls setup_ion to read ion data
Ver 7, PRY 12-Nov-01 - modified for proton rates, photoexcitation,
and 9 pt splines.
Ver 8, PRY 9-Dec-01 - completed modifications for v4 of CHIANTI.
V. 9, 25-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
Now we only call zion2filename
V. 10, 9-Aug-2002, Peter Young
corrected !ioneq_file problem
V. 11, 12-Aug-2002, Peter Young
added POPSTR output, and tidied up header.
V. 12, 4-Oct-2003, GDZ
modified the input to POP_SOLVER, now it is dealt with an
input structure.
V 13, 4-May-2005, Enrico Landi (EL)
Modified in order to include ionization and recombination
data in the input to POP_SOLVER
V.14, 26-May-2005, Peter Young (implemented by GDZ)
added SUM_MWL_COEFFS optional input for allowing
non-Maxwellian distributions to be considered.
added LEVEL= optional input to only print the populations of
a few levels.
V.15, 5-Jul-2005, Peter Young
added RADFUNC= and /QUIET keywords
VERSION : 15, 5-Jul-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
PLOT_POPULATIONS
PURPOSE:
plot the population of a number of the lowest levels as a function of
electron density for a specific temperature
CATEGORY:
science.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
PLOT_POPULATIONS,Ion,T,Nlevels
INPUTS:
Ion: CHIANTI style name for the ion, i.e., 'c_6' for C VI
T: electron temperature (K)
OPTIONAL INPUT:
Nlevels: the number of levels for which populations are plotted
starts from level 1 (the ground level)
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
OUTFILE: the (optional) name of the output file where the listing
is produced
PSFILE: the (optional) name of the output file where a postscript
plot produced
RADTEMP Specify background radiation temperature (default: 6000 K)
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
NOT_INTERACTIVE Avoid interactive use.
OUTPUTS:
COMMON BLOCKS:
common elvlc,l1a,term,conf,ss,ll,jj,ecm,eryd,ecmth,erydth,eref
common wgfa, wvl,gf,a_value
common upsilon,t_type,c_ups,splups
CALLS
POP_SOLVER, ION2SPECTROSCOPIC, ION2FILENAME, READ_IP,
CONVERTNAME, READ_ELVLC, READ_WGFA2, READ_SPLUPS
EXAMPLE:
to plot populations of the 5 ground configuration levels of Fe XIII
and store these values in a file 'Fe_XIII.lis' for a temperature of 1.5 MK
> plot_populations,'fe_13',1.5e+6,5,outfile='Fe_XIII.lis'
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1996: Version 2.0
November 1997: Ken Dere, added psfile keyword
September 1999: Ken Dere, for Version 3,
14-Jul-2000 Peter Young, now calls pop_solver
Version 6, 21-Dec-2000, William Thompson
Modified for better cross-platform capability.
V. 7, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ), modified the plotting bit
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V 8, 15-July-2002, GDZ
Added keyword not_interactive
V 9, 4-Oct-2003, GDZ
modified the input to POP_SOLVER, now it is dealt with an
input structure.
V 10, 4-May-2005, Enrico Landi (EL)
Modified in order to include ionization and recombination
data in the input to POP_SOLVER, now it allows choice of .ioneq
file needed to include ionization and recombination.
V 11, 12-Aug-2005, GDZ
The number of levels is now optional. Also, a check that the
number of levels must be less than the levels in the file is
now enforced.
VERSION : 11, 12-Aug-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME: POP_PLOT
PURPOSE:
To compute n_j A_ji / N_e for a selected transition(s) and plot it
against N_e. If it is insensitive to N_e, then the line(s) is
suitable for emission measure analysis.
CATEGORY:
Atomic data analysis
EXPLANATION:
The routine calls EMISS_CALC to give values of DE*n_j*A_ji at the
temperature TEMP and densities from 10^8 to 10^12. You are then
asked to select which transition(s) you are interested in. (If
more than one line is selected, the lines are blended.)
DE*n_j*A_ji/N_e is then plotted against density.
If TEMP is not specified, then the temperature at which the
ionisation fraction has its maximum is calculated. For the iron
ions, the ion balance calcs of Arnaud & Raymond are used,
otherwise Arnaud & Rothenflug are used. If TEMP is specified,
and the value is less than 20, then it is assumed that the log
of the temperature has been specified.
In emission measure work it is important to isolate lines for
which DE*n_j*A_ji/N_e is insensitive to density. If only such lines
are used, then the derived emission measure curve is independent
of density.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
POP_PLOT, IZ, ION, WRANGE=WRANGE, [TEMP=TEMP, /QUICK, DATA=DATA, $
DENS_RANGE=DENS_RANGE, DILUTE=DILUTE]
EXAMPLES:
POP_PLOT, 26, 14, WRANGE=[330,360]
- 3 lines should appear in the widget. Selecting 334.17 should show
a curve that falls off with density. Choosing 353.83 shows a curve
that rises with density. By selecting a blend of the two lines,
the curve will be insensitive to density, telling us that only a
blend of 334.17 and 353.83 is suitable for emission measure work.
POP_PLOT, 8, 4, WRANGE=[550,560], TEMP=6.0, /QUICK, DENS_RANGE=[6,10]
- O IV is a member of the boron sequence, and so calculations take a
lot longer. Giving the QUICK keyword speeds things up. The
temperature is well away from the T_max of the ion
INPUTS:
IZ The atomic number of the ion
ION The spectroscopic number of the ion (e.g., 12 = XII)
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
DILUTE Used to set radiative dilution factor. (Default: 0.0)
TEMP The temperature at which calculations are required. Usually
this will be the Tmax of the ion.
DENS_RANGE The default density range is log Ne = 8 to 12. By
inputting two integers, a different range can be chosen.
WRANGE Wavelength range from which lines are required. If not
given, then the user is allowed to choose from the complete
set of lines for the ion.
ABUND_FILE The name of a CHIANTI abundance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio. Default is
!abund_file.
IONEQ_FILE The name of a CHIANTI ion balance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio and evaluating
the T_max of the ion. Default is !ioneq_file.
RADTEMP The blackbody radiation field temperature (default
6000 K).
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius
units. I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface.
(Default is infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
DATA: An array that contains the data that is plotted: data(*,0)
contains
the densities, while data(*,1) contains the Y-axis values.
KEYWORDS:
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
QUICK: The density range over which the calculations are done is
8 to 12 in 0.2 intervals. This keyword forces the
calculations to be done at 0.5 intervals.
CALLS:
EMISS_CALC, EMISS_SELECT, READ_IONEQ
HISTORY:
Ver.1, PRY 28-Jul-97.
Ver.2, PRY 23-Sep-97 - added DILUTE keyword for photo-excitation
Ver.3, PRY 30-May-98 - added DENS_RANGE
Ver.4, PRY 5-Sep-98 - added call to choose_ioneq
Ver.5, PRY 7-Apr-99 - tidied up, and introduced call to emiss_select
Ver.6, PRY 7-Dec-01 - modified for v.4 of CHIANTI
V. 7, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V.8, 06-Aug-02 GDZ
added ABUND_FILE to the call to emiss_calc (was missing).
Changed the use of CHIANTI system variables.
VERSION : 8, 06-Aug-02
NAME
POP_PROCESSES
PROJECT
CHIANTI
PURPOSE:
Outputs to the screen the contributions of the different physical
processes to the population of the specified level within the ion.
E.g., for Fe XIII, level 4, the output is:
Population leaving level 4
rad. decay: 1.51e+01 39.17%
e de-exc: 3.56e-01 0.92%
e exc: 2.28e+01 59.12%
p de-exc: 2.63e-01 0.68%
p exc: 4.05e-02 0.11%
stim. emiss: 0.00e+00 0.00%
photoexc: 0.00e+00 0.00%
--------
TOTAL 3.85e+01
Population entering level 4
rad. decay: 3.59e+01 93.19%
e de-exc: 3.81e-02 0.10%
e exc: 1.46e+00 3.79%
p de-exc: 3.18e-03 0.01%
p exc: 1.12e+00 2.91%
stim. emiss: 0.00e+00 0.00%
photoexc: 0.00e+00 0.00%
--------
TOTAL 3.85e+01
which shows that the level population is dominated by electron
excitation and cascading into the level, and by radiative decay
out of the level.
Note that the rates for each physical process are multiplied by the
population of originating level (this results in the totals for
entering and leaving the level to balance).
For some ions, ionization and recombination are additional processes
included when working out the level balance. Because of the way these
processes are included (see the v.5 paper for details), the populations
entering and leaving some levels *will not balance*.
INPUTS
IZ The atomic number of the ion
ION The spectroscopic number of the ion (e.g., 12 = XII)
OPTIONAL INPUTS
LEVEL The ion level for which information is required.
DENS Electron density at which rates calculated (units: cm^-3).
If not specified, a value of 10^10 is assumed.
TEMP Temperature at which rates calculated (units: K). If not set,
then T_max of the ion is used
PATH If the ion data-files are not in the CHIANTI directories,
then PATH allows you to choose an alternative location.
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
RADTEMP Specify background radiation temperature (default: 6000 K)
N_LEVELS Restrict the ion model to this number of levels. E.g., if
the CHIANTI model contains 40 levels for the ion, then
setting N_LEVELS=12 reduces the model to 12 levels.
RADFUNC The name of a user-defined function that will generate
a radiation spectrum as a function of temperature.
This radiation field will replace the black-body that
is assumed when using the RADTEMP keyword in the call
to pop_solver.
KEYWORDS
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
CALLS
R2W, ZION2FILENAME, PROTON_DENS, POP_SOLVER, SETUP_ION
EXAMPLES
One can compare the effect of cascading on a level population by using
the N_LEVELS keyword. Consider the case of Fe XIV:
IDL> pop_processes,'fe_14',lev=5
IDL> pop_processes,'fe_14',lev=5,n_levels=12
With the first call there are two dominant terms to the population
entering level 5: approximately 47% for radiative decays (cascading)
and 53% for electron excitation. Setting n_levels=12, one finds that
the cascading contribution disappears as there are no longer any
high-lying levels that cascade into level 5. The cascading provides
a strong contribution to the population of this level.
HISTORY
Ver.1, 11-Sep-2002, Peter Young
Ver.2, 15-Jan-2004, Peter Young
modified call to pop_solver following recent revision to
pop_solver; changed input from IZ,ION to IONNAME to match other
CHIANTI routines
Ver.3, 26-May-2005, Peter Young
changed TEMP and DENS keywords
Ver.4, 10-Jun-2005, Peter Young
added common block for ionization/recombination data and modified
INPUT structure.
Ver.5, 14-Jun-2005, Peter Young
routine now prints the percentage contribution of each process;
added N_LEVELS= keyword
Ver.6, 1-Jul-2005, Peter Young
added warning for ions with ionization/recombination
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
RAD_LOSS
PURPOSE:
Calculates energy loss rate by free-free (ff), radiative
recombination (fb) and by line (bound-bound) radiation.
CATEGORY:
synthetic spectra
CALLING SEQUENCE:
RAD_LOSS,Temperature,Loss_rate
INPUTS:
None: The user will select an elemental abundance file and a
ionization equilibrium file through widgets.
KEYWORDS:
Pressure: pressure in emitting region (cm^-3 K)
density=pressure/temperature(K)
Density: density (cm^-3), constant for all temperatures
if neither density or pressure is set, then a default
constant density of 10^10 cm^-3 is used.
Psfile: to create a postscript plot of the radiative loss in
the file specified by the name assigned to 'Psfile'
Outfile: name of an ascii file where the radiative loss rate
as a function of temperature is output
RADTEMP Specify background radiation temperature (default: 6000 K)
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
OUTPUTS:
Temperature: array of temperatures (K)
Loss_rate: energy loss rate in erg cm^3 s^-1
PROCEDURE:
if keyword pressure is set then calculations performed at constant pressure
if keyword density is set then calculations performed at constant density
otherwise, density is set to 1.e+10
pressure = density * temperature (cm^-3 K)
the user will be asked to select an abundance file and a
ionization balance file.
EXAMPLE:
> rad_loss,t,r
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
January 1999: version 1, adopted from synthetic.pro
Version 2, 21-Dec-2000, William Thompson
Modified for better cross-platform capability.
Ver.3, 6-Dec-2001, Peter Young
Added /noprot, radtemp and dilute keywords.
Removed elvlc, wgfa and upsilon common blocks.
Removed calls to read_ip and read_masterlist (not needed).
Ver.4, 8-Jul-2003, Peter Young
Updated routine header (no changes to code).
V 5, 25-May-2005, GDZ
corrected routine header.
VERSION : 5, 25-May-2005, GDZ
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
Name : PLOT_IONEQ
Purpose : Plots the ionisation equilibrium values for an element.
Explanation :
Use : IDL> plot_ioneq, element [ ion=ion]
Inputs : element - the element name
Opt. Inputs : Ion (as keyword)
Outputs : None
Opt. Outputs: a postscript file.
Keywords : ION_RANGE - specify range of ions. E.g., ion_range=[5,8]
means V to VIII inclusive.
IONEQ_NAME: Name of the ionization equilization name to use.
If not passed, then the user is prompted for it.
NOT_INTERACTIVE Avoid interactive use.
Calls : Other CHIANTI routines
Common :
Restrictions: None
Side effects: None
Category : Spectral
Prev. Hist. : None
Written : C D Pike, RAL, 9-Jun-97
Modified : V.2. Update element list. modified definition of XUVTOP, and
allowed selection of ionization eq. file and creation of
postscript file.
Giulio Del Zanna (DAMTP) 10-Oct-2000
V.3, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V 4, 15-July-2002, GDZ
Added keywords ioneq_name, not_interactive
V.5, 9-Feb-2005, Peter Young
Changed ion= keyword to ion_range=
VERSION : 5, 9-Feb-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
Name : MAX_TEMP
Purpose : Calculates temperature at max ionisation ratio for an ion
Explanation :
Use : IDL> print,max_temp(ion)
Inputs : ion - the specific ion in the form eg 'Fe_XII' or 'Fe XII'
Opt. Inputs : None
Outputs : Function returns log of max temperature
Opt. Outputs: None
Keywords : ALL - if set produces a plot of all temperatures
Calls : Other CHIANTI routines
Common :
Restrictions: None
Side effects: None
Category : Spectral
Prev. Hist. : None
Written : C D Pike, RAL, 9-Jun-97
Modified : V.2 Update element list. CDP, 18-Jun-99
V.3 modified definition of XUVTOP, and allowed selection of
ionization eq. file. Giulio Del Zanna (DAMTP) 10-Oct-2000
V.4, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
VERSION : 4, 21-May-2002, GDZ
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
Name : CHIANTI_DEM
Purpose : Calculates the Differential Emission Measure DEM(T) using
the CHIANTI database, from a given set of observed lines.
Constant pressure or density can be used.
Category : diagnostic analysis
Explanation : This routine has several options, all in the form of keywords.
First, the input file with the observed fluxes is read.
THE FIRST TIME YOU USE THIS ROUTINE
you'll have to do the calculation of the contribution
functions G(T), so the routine GET_CONTRIBUTIONS will come
into play. You'll have to specify the value of the
pressure or density, and you'll be asked to select an
ionization equilibrium file and an abundance file.
GET_CONTRIBUTIONS searches the CHIANTI database (ion per ion)
for all the theoretical lines corresponding to the observed
lines, i.e. that lie in a OBS_WVL(i) +/- DELTA_LAMBDA_OBS(i)
interval centered on the observed wavelength OBS_WVL(i).
The routine calculates the C(T) values (G(T)=Ab(element)*C(T))
for the temperature interval log(T)= 4.0 - 8.0
with steps of log(T) = 0.1 .
You can either select a constant pressure OR a constant
density for all the lines; if you select a constant pressure,
for each ion the contribution function is calculated at an
electron density N_e equal to the ratio of the pressure
and the temperature of maximum ionization fraction:
C=C( T, N_e= P/T_ion )
The C(T) values are stored by GET_CONTRIBUTIONS in the output
file OUTPUT.CONTRIBUTIONS that can be used later to calculate
the DEM, changing various parameters,
without having to start again and read the CHIANTI database,
which can take long time.
In the case no theoretical lines corresponding to an observed
line are found, the routine writes the wavelength of the line
(to be excluded from the fit) in the array
EXCLU_OBS_WVL_NO_TEO. The lines with no theoretical
counterparts are then automatically excluded from the fit by
CHIANTI_DEM. You might consider the possibility to start again
incrementing the DELTA_LAMBDA_OBS, to see if there are
theoretical lines in the vicinity.
Note: if you want to exclude some of the observed lines from
the fit, you just have to use the keyword EXCLUDE_OBS_WVL,
BUT GET_CONTRIBUTIONS will store anyway the results (if any)
in the C(T) file.
After having excluded the lines in EXCLUDE_OBS_WVL,
any *.abund file present in the CHIANTI database or in
the working directory can be selected, and eventually edited,
if you like to change some abundances.
Then the $G(T)$ are calculated, multiplying each theoretical
line by the abundance factor. Then the
theoretical lines contributing to each blend are sorted by
intensity and then their G(T) can be plotted if the keyword
PLOT_GT is activated. It is recommended to do this the first
time, to check if there are some observed lines terribly
blended with lines of other elements, in which case it is
better to exclude them with a second run (if you are not
sure about the abundances).
Then the G(T) for each blend are summed and plotted.
Then the fit starts calling DEM_FIT.
A series of parameters can change the
result (DEM), especially the number and position of the mesh
points of the spline that represents the DEM. The keyword
MESH_POINTS serves for this purpose.
The other keywords that control the fit are N_ITER, DCHISQ_M.
At the end of the fit, the files OUTPUT.DEM and OUTPUT.GENERAL
are created.
Use : IDL>chianti_dem,output='serts89',file_input='serts89.obs',$
pressure=3.e15
Examples :
Assume you have a file input 'serts89.obs' like this:
243.031 491. 97. 0.1 He II
256.323 1580. 186. 0.1 He II b
315.024 253. 31. 0.1 Mg VIII
335.401 10400. 1650. 0.1 Fe XVI
319.839 113. 14. 0.1 Si VIII
356.027 218. 25. 0.1 Si X
IDL>chianti_dem,output='serts89',file_input='serts89.obs',$
pressure=3.e15,cut_gt=1e-30,/plot_gt
After having selected the ionization file,
the C(T) (with MAX(C(T)) gt 1e-30) are stored in the file
'serts89.contributions'. Then select one of the abundance
files.
Have a look at the plots of the G(T), and annotate
if there is a line you want to exclude, let's say the second.
Have a look at the DEM obtained ('serts89.dem') and at
the details contained in the file 'serts89.general'.
Maybe there is another line you want to exclude, let's say
the last one. Maybe you want to change the mesh points, too.
So run
IDL>chianti_dem,output='serts89_2',file_input='serts89.obs',$
file_gt='serts89.contributions',$
exclude_obs_wvl=[243.031,356.027 ],$
mesh_points= [4.5,5.,5.5,6.2,7.5]
The files 'serts89_2.dem' and 'serts89_2.general' will be
created. They have the essential information about what you
did.
Inputs : various, all in form of keywords. The required ones are
OUTPUT and FILE_GT (or PRESSURE/DENSITY)
Opt. Inputs : various... see the software note.
Outputs : OUTPUT.CONTRIBUTIONS
Created only if the keyword FILE_GT is NOT set.
Is the file where all the contribution functions G(T) are
stored. In the first two lines the ionization equilibrium
file name, and the constant value of pressure or density
adopted are reported. Then for each line you have reported
the observed wavelength, the theoretical one, the element and
ionization stage, then the C(T) values. At the end the
specification for each transition.
OUTPUT.DEM
Is the file where the log T and log DEM values are
written, with a format suitable
as input for the DMM_SS procedure,that calculates the
synthetic spectrum. At the end some info on how it was
calculated are printed.
OUTPUT.GENERAL
Is the file where general information is stored.
The abundance file, the ionization equilibrium file and the
constant value of pressure or density used are reported.
Then there is one line for each
observed line, with the provisional identification, the
observed wavelength, the observed flux, the theoretical one
(corresponding to the DEM), the error on the flux,
the square of the difference between the theoretical and the
observed fluxes divided by the error (this number should be
close to zero if the line is well reproduced), and finally
the ratio of the theoretical flux versus the observed one
(which should be close to 1).
After this line, there is one line per each theoretical line
contributing to the blend, with the identification, the
theoretical wavelength, the configuration and terms, and the
contribution to the total theoretical flux (in percentage)
of each line in the blend.
OUTPUT.OUT
This file , toghether with OUTPUT.DEM ,
can be used to reproduce the results using
user-written software. See the software notes.
The ouput has this format:
format='(a20,1x, 1f10.3,1x, 3e10.3, 1x, f4.2,1x,f6.3)'
Opt. Outputs:
An abundance file with the modifications inserted.
Postscript files of the G(T).
A postscript file with the DEM (OUTPUT.DEM.PS)
A postscript file with other plots too (OUTPUT_4PLOTS.PS)
Keywords :
ARCSEC:
optional. If set, it means that the intensities in the input
file are per arcsec-2 .
These intensities are then converted to
sterad-1 .
CUT_GT:
optional. If set, only the those theoretical lines that
have a MAX(C(T)) greater than the value set, are kept;
it is useful to set this value in order to reduce the number
of lines in the file where the C(T) are stored.;
if not set, a default value of 1e-30 is adopted.
DCHISQ_M:
optional. If not set, a default value of DCHISQ_MIN=1.e-5
is assumed. For each iteration, the CHISQ and it's variation
are calculated. As long as the iteration achieves an
improvement in CHISQ greater than DCHISQ_MIN , another
iteration will be performed.
DEM_FILE:
optional.If set (,/DEM_FILE) you have to choose a DEM file to
be used as a start, instead of the default constant value of
10.^22.
You can either choose one of the files in the CHIANTI database
or any you have in the working directory.
The values in the file are marked as crosses, the mesh points
are marked with triangles.
DENSITY :
the value of the density (Ne). Required if you do NOT have
already the contribution functions G(T).
EXCLUDE_OBS_WVL:
optional.
If set, you can exclude some of the observed lines from
the fit. Note that even if you set this keyword and run
GET_CONTRIBUTIONS all the theoretical lines found corresponding
to all the lines in the input file are written in the C(T)
file. It is only in the fit that the lines are excluded.
FILE_GT:
optional.
If NOT set, the routine GET_CONTRIBUTIONS is called.
If set, it has to specify the name of the file created by
GET_CONTRIBUTIONS, where all the contribution functions G(T)
are stored. In the first two lines the ionization equilibrium
file name, and the value of the pressure or density
adopted is reported. Then for each line you have reported
the observed wavelength, the theoretical one, the element and
ionization stage, then the C(T) values. At the end the
specification for each transition.
FILE_INPUT:
optional.
if set, you are not requested to select the observation file
using a widget-type search.
The input file must contain 5 columns, unformatted:
1)the observed wavelength (A)
2)the observed flux in erg cm-2 s-1 st-1
3)the corresponding error on the flux in erg cm-2 s-1 st-1
4)half the width (A) of the range (centered on the observed
wavelength) where you want to look for the corresponding
theoretical lines. A value of HWHM or more would do.
5)The identification, written as string (max 20 characters)
MESH_POINTS:
optional. It is a vector that specifies the mesh points for the
spline that represent the fitted DEM, in log(T).
If not set, the default values
[4.,4.5,5.,5.5,6.,6.5,7.,7.5,8.0] are assumed.
N_ITER:
optional.It is the number of iterations of the fitting routine.
If not set, a default value of 20 is assumed.
Changing this value alone might not affect the fit, since
also the value of DCHISQ_MIN is checked during the fit.
N_MATCHES:
optional.
In the unlikely event that more than 50 (default value for
N_MATCHES) theoretical lines corresponding to an observed
line are found, the routine stops; in this case, you have to
start again setting N_MATCHES equal to a greater number.
OUTPUT :
required.
It is the output name. Suffixes will be added when creating
the various outputs.
PHOT:
optional.
If set, it means that in the input file the intensities
are in photons instead of ergs.
PLOT_GT:
optional.
If set (,/PLOT_GT), plots of the G(T) for each
observed line not excluded are created.
PRESSURE:
the value of the pressure (Ne T). Required if you do NOT have
already the contribution functions G(T).
QUIET:
optional. Set to avoid various messages and the details of the
result.
Calls : GET_CONTRIBUTIONS
DEM_FIT
ZION2SPECTROSCOPIC
print2d_plot
Common : obs, obs_int,obs_sig,n_obs
obs_o, obs_wvl,obs_id,obs_delta_lambda
dem, d_dem_temp,dem_temp,log_dem_temp,log_t_mesh,log_dem_mesh
contr, ch_tot_contr
ab, abund_name,abund_info,xuvtop,ioneq_name
these are the commons with GET_CONTRIBUTIONS.PRO:
various, exclu_obs_wvl_no_teo,const_net,$
dem_temp_min,dem_temp_max,n_dem_temp,$
ch_wvl,ch_l1,ch_l2,ch_id,ch_z,ch_ion,ch_contr_wa,$
ch_pop,ch_contr_list, ch_term,ch_n_contr
Restrictions:
In the unlikely event that more than 50 (default value for
N_MATCHES) theoretical lines corresponding to an observed
line are found, the routine stops; in this case, you have to
start again setting N_MATCHES equal to a greater number.
Also, if the starting DEM values are not proper, or you
don't have enough constraints at lower and higher temperatures,
you might get "strange" results, and should consider using
different starting values.
Of course you need to have the enviroment variable CDS_SS_DERE
pointing to the CHIANTI database top directory.
Side effects: None known yet.
Category : spectrum
Prev. Hist. :
Written by Ken Dere (NRL) as part of the CHIANTI package
in collaboration with Brunella Monsignori Fossi, Enrico Landi
(Arcetri Observatory, Florence), Helen Mason and Peter Young
(DAMTP, Cambridge Univ.). Incorporated into the CDS software.
Written :
V. 1.0 5 November 1997 Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ),
UCLAN (University of Central Lancashire, UK)
Modified : Removed the print2d_plot subroutine. Increased the default value
of N_MATCHES from 20 to 50. Changed way to deal with xuvtop.
GDZ, 31-Oct-2000
Version : 2.0 GDZ, DAMTP, 31-Oct-2000
V.3, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
VERSION : 3, 21-May-2002, GDZ
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
PLOT_DEM
PURPOSE:
To plot differential emission measure (DEM) values
CATEGORY:
Widgets.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
PLOT_DEM,filename
INPUTS:
filename: the name of the DEM file to be plotted. The file must b
in the standard CHIANTI format for DEM files. If filename
is a blank string ('') then an interactive window will come
up to allow the user to select a DEM file from the CHIANTI
DEM directory or some other directory.
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
PSFILE: If set, the a postscript plot will be place in the
file 'psfile' specified by the user
OUTPUTS:
None, other than a plot
EXAMPLE:
> plot_dem,'ademfile.dem'
or
> plot_dem,''
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
June 1998: Version 1.0
Version 2, 21-Dec-2000, William Thompson, GSFC
Modified for better cross-platform graphics capability
V. 3, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
VERSION : 3, 21-May-2002
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME: INTEGRAL_CALC
PURPOSE:
To compute the atomic data integral for use in column or volume
emission measure work.
CATEGORY:
Scientific analysis
EXPLANATION:
Defining
G(T) = 0.83 * Fr(T) * N_j * A_ji / N_e
where Fr(T) is the ionisation fraction (e.g., from Arnaud &
Rothenflug), N_j the relative population of level j, A_ji the
A-value for the j->i transition and N_e the electron density. The
0.83 is the ratio of hydrogen to free electrons, which is constant
above around 10^4 K. This function is sharply-peaked at a
temperature T_mem (the temperature of maximum emission, which can
be different from the temperature of maximum ionisation, T_max)
and so an oft-used approximation is to take G(T) constant in the
range log T_mem - 0.15 to log T_mem + 0.15 and zero outside. The
value of the constant, which we call C_lambda here, is then given
by
C_lambda = integral { G(T) dT }
--------------------
T_mem * (10^0.15 - 10^-0.15)
If EM(s) is the column emission measure, F the flux (erg cm-2 s-1)
in a line lambda, Ab the abundance of the element and DE (erg) the
energy for the transition, then:
F = DE * Ab * C_lambda * EM(s)
If we are dealing with intensities I (erg cm-2 s-1 sr-1) then:
4pi * I = DE * Ab * C_lambda * EM(s)
This program extracts the ionisation balance and emissivities from
the CHIANTI database and calculates C_lambda for all lines in the
specified wavelength interval WRANGE by integrating over
0.02 dex temperature intervals, using the IDL INT_TABULATED function.
The C_lambda functions for all the lines in the selected wavelength
range WRANGE are displayed as well as the temperature of maximum
emission (T_mem), DE*C_lambda and 4pi/(DE*C_lambda). These latter
two quantities are useful for the emission measure analysis.
Any combination of the displayed lines can then be blended and the
corresponding quantities for the blend will be displayed.
The function Fr(T) * N_j * A_ji can also be plotted at this stage.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
INTEGRAL_CALC, IZ, ION, [WRANGE=WRANGE, /CHOOSE, DENS=DENS]
EXAMPLES:
INTEGRAL_CALC, 26, 13, WRANGE=[200,205], /CHOOSE
INTEGRAL_CALC, 14, 10, WRANGE=[250,270], DENS=10.
INPUTS:
IZ: The atomic number of the ion
ION: The spectroscopic number of the ion (e.g., 12 = XII)
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
DENS: The density at which the emissivities are calculated
(default=10.)
WRANGE: Wavelength range for which C_lambda functions are
calculated. If not given, then the 10 strongest lines
are printed.
INDEX: Particular elements in the emissivity structure can be
selected with INDEX. This allows integral_calc to be run
'silently'. The output is contained in the OUTSTR structure.
If index is given as, e.g., [7,8], then the C_lambda
functions for these two lines are summed and output.
PATH: Directly specify the directory path where the Chianti data
for the ion is found
ABUND_FILE The name of a CHIANTI abundance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio. Default is
!abund_file.
IONEQ_FILE The name of a CHIANTI ion balance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio and evaluating
the T_max of the ion. Default is !ioneq_file.
RADTEMP The blackbody radiation field temperature (default
6000 K).
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius
units. I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface.
(Default is infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
KEYWORDS:
CHOOSE: Allow ion balance calculations to be selected manually
(see choose_ioneq.pro routine).
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
OUTSTR: A structure with the following tags
.tmem - the T_mem for the line(s)
.dec - total( de * c_lambda )
.pidec - 4 * pi / total( de * c_lambda )
Only output when INDEX is specified.
COMMON BLOCKS:
None.
CALLS:
EMISS_CALC, CH_GET_FILE, READ_IONEQ
HISTORY:
Ver.1: PRY, 28-JUN-97.
Ver.2: PRY, 7-OCT-97. Added TEMPI and GOFT, for plotting.
Ver.3: PRY, 31-JUL-98. Added PATH.
Ver.4: PRY, 6-APR-99. Added INDEX, OUTSTR. Removed TEMPI and GOFT
(these can be got from the g_of_t routine).
Ver.5: PRY, 9-Dec-01. Modified for v.4 of CHIANTI.
V.6, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V.7, 06-Aug-02 GDZ
Changed the use of CHIANTI system variables.
VERSION : 7, 06-Aug-02
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
READ_ABUND
PURPOSE:
to read CHIANTI abundance files
CATEGORY:
science.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
READ_ABUND,File,Abundance,Reference
INPUTS:
File: the name (string) of the file containing the abundance values
(relative to hydrogen) usually of the form
'!xuvtop/abundance/*.abund'
OUTPUTS:
Abundance: an array of abuncance values
Reference: a string containing the reference to the chosen set
of abundances in the scientific literature
PROCEDURE:
You can describe the foobar superfloatation method being used here.
EXAMPLE:
> read_abund,'allen.abund',abundance,ref
abundance(26) = abundance of iron relative to hydrogen
quoted by C.W. Allen in Astrophysical Quantities
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1996: Version 2.0
V. 3, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
VERSION : 3, 21-May-2002
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
READ_DEM
PURPOSE:
to read values the differential emission measure as a function
of temperature
CATEGORY:
science.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
READ_DEM, File, T, Dem, Ref
INPUTS:
File: the name of the file containing the DEM values, usually in
!xuvtop/dem/*.dem
OUTPUTS:
T: Log10 values of temperature (K)
Dem: Log10 values of the differential emission measure
Ref: the reference to the DEM values in the scientific literature
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
Describe optional outputs here. If the routine doesn't have any,
just delete this section.
EXAMPLE:
> read_dem,!xuvtop+'/dem/active_region.dem',t,dem,ref
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1996: Version 2.0
V. 3, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
Ver.4, 20-Nov-2002, Peter Young
DEM values of -1 caused errors, so this has been corrected.
VERSION : 4, 20-Nov-2002
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
READ_IONEQ
PURPOSE:
to read files containing the ionization equilibrium values
CATEGORY:
science.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
READ_IONEQ, File, T, Ioneq, Ref
INPUTS:
File: for example, !xuvtop+'/ioneq/arnaud_rothenflug.ioneq'
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
None:
OUTPUTS:
T: array of log10 temperatures
Ioneq: 3-d array (T,element,ion)
of the fractional abundance of the ion in
ionization equilibrium.
Ref: reference in the scientific literature
EXAMPLE:
> read_ioneq,!xuvtop+'/ioneq/arnaud_rothenflug.ioneq'
> help,t,ioneq
> T FLOAT = Array(41)
> IONEQ FLOAT = Array(41, 28, 29)
> print, minmax(t)
> 4.00000 8.00000
> print,t(20)
> 6.0000
> print,ioneq(20,25,9)
> 0.269 = fractional abundance of Fe X in
ionization equilibrium
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere (KPD)
March 1996: Version 2.0
March 1999: KPD to read both number of temperature and number
of elements
25-Oct-2000 V. 4, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ).
Corrected to interpret the '-1' as a reference only
if within the first 3 columns
V. 5, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
v.6, 25-Oct-2004, Peter Young
modified format statement so that it will read any number of
temperatures.
V 7, 25-May-2005, GDZ
corrected routine header.
VERSION : 7, 25-May-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
http://wwwsolar.nrl.navy.mil/chianti.html
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME:
CH_READ_FITS
PURPOSE:
Read standard CHIANTI FITS binary table data containing the output from
CH_SYNTHETIC and output a TRANSITIONS structure.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
CH_READ_FITS, Filename, TRANSITIONS
INPUTS:
Filename = String containing the name of the CHIANTI FITS file written
by CH_WRITE_FITS.
OUTPUTS:
TRANSITIONS = Structure to be written.
OPTIONAL INPUTS: none
KEYWORDS: none
NOTES:
CALLS:
MRDFITS, ADD_TAG
COMMON BLOCKS: none.
RESTRICTIONS:
(3) The input FITS file must have been written by CH_WRITE_FITS
PREV. HIST. :
EXAMPLE:
ch_read_fits, 'file.fits', transitions
WRITTEN :
Ver.1, 8-Apr-02 Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
V.2 GDZ 31 May 2002 added more checks.
MODIfICATION HISTORY:
VERSION : 2, 31 May 2002
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
CH_WRITE_FITS
PURPOSE:
Write standard FITS binary table data from CHIANTI input structure.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
CH_WRITE_FITS, Input, Filename
INPUTS:
Input = Structure to be written to FITS file.
OUTPUTS:
Filename = String containing the name of the file to be written.
CH_WRITE_FITS creates two binary table extension in a single
FITS file. The second one is appended as a new extension.
OPTIONAL INPUTS: Header COMMENTS.
KEYWORDS:
head1, head2
Additional COMMENTS to be added at the bottom of the two binary tables.
NOTES:
Any existing FITS file can be over-written or not.
Use CH_READ_FITS to convert the FITS file back into a structure.
CALLS:
FXPAR(), FXADDPAR, IS_IEEE_BIG(), HOST_TO_IEEE, DIALOG_MESSAGE
COMMON BLOCKS: none.
RESTRICTIONS:
(1) Limited to 127 columns in tables by IDL structure limits.
(2) String columns with all columns of zero length crash the
program
(3) The input structure has to be of the type TRANSITIONS.
PREV. HIST. :
The subroutines in this procedure are extracted without modifications from
the MWRFITS.PRO routine, written by T. McGlynn Version 0.95 2000-11-06
and present in the ASTRON library (in SolarSoft under /gen/idl_libs/astron/).
EXAMPLE:
ch_write_fits, transitions , 'test.fits'
WRITTEN :
Ver.1, 22-May-02 Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
MODIfICATION HISTORY:
VERSION : 1, 22-May-02, GDZ
NAME
WHICH_LINE
PROJECT
CHIANTI
PURPOSE:
Upon given an ion name and wavelength, this routine prints out a list
of possible line IDs for the wavelength. Wavelengths within 1% of the
input wavelength are searched for.
INPUTS
IONNAME Name of an ion in the CHIANTI format. E.g., 'fe_13' for Fe XIII.
WVL A wavelength in angstroms.
OUTPUTS (to screen)
Prints a list of atomic transitions and wavelengths for lines close to
the input wavelength. A '*' is placed next to the closest wavelength
match.
KEYWORDS
NARROW Narrows the search range to 0.02% of the specified wavelength.
EXAMPLE
IDL> which_line,'o_6',1032
Wavelength i j Lower level Upper level A-value
1037.615 1 2 1s2.2s 2S1/2 - 1s2.2p 2P1/2 4.21e+008
1031.914 1 3 1s2.2s 2S1/2 - 1s2.2p 2P3/2 4.28e+008
CALLS
CONVERTNAME, ZION2FILENAME, READ_WGFA2, READ_ELVLC
HISTORY
Ver.1, 22-Jun-2004, Peter Young
Project : CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
Name : USE_CHIANTI
Purpose : Sets up system variables for use of CHIANTI routines
Explanation : The CHIANTI software uses system variables
that have to be defined. This routine is called by the
CHIANTI routines if these system variables are not defined.
** If one is using the solar-soft package, these should
already be defined*****.
** If the CHIANTI package is used as stand-alone, then
this routine can be used for the setup with e.g.:
use_chianti,'/home/data/chianti/'
if /home/data/chianti/ points to the actual place where
the CHIANTI top directory is.
Use : IDL> use_chianti, '/home/data/chianti/', $
[ioneq= , abund=]
Inputs : None
Opt. Inputs : The full pathname of the CHIANTI top directory.
Outputs : None
Opt. Outputs: None
Keywords : IONEQ - to define the default ionization eq. file to be used.
ABUND - to define the default abundance file to be used.
Calls : None
Common : None
Restrictions: None
Side effects: None
Category :
Prev. Hist. : Based on use_dere_chianti, written by C D Pike, RAL
Written : Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ) DAMTP (University of Cambridge, UK)
Modified : Version 1, GDZ 10-Oct-2000
Version 2, GDZ 10-Jan-2001
added the definition of the !abund_file
V. 3, GDZ, 2-May-2002 Modified substantially, adding a new
system variable.
V.4, 10-July-2002 GDZ
Removed the definition of !chianti_top, upon request.
V.5, 25-July-2002, GDZ
Fixed a problem with IDL versions earlier than 5.3 (the routine
would not compile). ALso, introduced the use of concat_dir for
cross-platform compatibility.
V.6, 06-Aug-02 GDZ
Changed the use of CHIANTI system variables. Added comments on
the which CHIANTI version is used.
V.7 12-Aug-02 GDZ Changed default abundance file. Removed '***'
V.8, GDZ 13-Feb-2003
Changed default ioneq file, to include ALL the elements.
V.9, 12-Aug-2005, GDZ
Changed default ioneq file from mazzotta_etal_ext to
mazzotta_etal_9.ioneq where ion fractions have been extended
up to 10^9 K. This is useful to avoid steps in the
emissivities at high-temperatures.
Version : V.9, 12-Aug-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
ASCII_WVL_DEM
PURPOSE:
create an ascii file of predicted spectral line intensities and
wavelengths corresponding to a selected abundance and differential
emission measure (DEM).
PROCEDURE:
Calculations are done assuming either constant density or
constant pressure. See CH_SYNTHETIC for details.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
ASCII_WVL_DEM, Wmin, Wmax, Pressure= , [density= ], $
[outfile= , mini= , sngl_ion=, /photons, /all, /masterlist], $
[/noprot, radtemp=, rphot=]
INPUTS:
Wmin: lower limit of the wavelength range of interest (Angstroms)
if kev keyword set, then wmin is in kev
Wmax: upper limit of the wavelength range of interest (Angstroms)
if kev keyword set, then wmax is in kev
Pressure: pressure in emitting region (cm^-3 K), or
Density: density in emitting region (cm^-3).
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
OUTFILE: the name of the output ascii file to be written.
MINI: Minimum intensity for a line to be included in the output.
SNGL_ION: specifies a single ion (e.g. SNGL_ION='Fe_10' to include
only Fe X lines) or an array (e.g. SNGL_ION=['Fe_10','Fe_11']
to include only Fe X and Fe XI lines) of ions to be used
instead of the complete set of ions specified in
!xuvtop/masterlist/masterlist.ions
MASTERLIST: string of a specific masterlist file (full path).
If defined as a keyword (i.e. MASTERLIST=1 or /MASTERLIST)
then a widget allows the user to select a user-defined
masterlist file. Shortcut for SNGL_ION.
OUTPUTS:
an ascii file: linelist.txt in the working directory by default
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
MINI: Minimum intensity for a line to be included in the output
SNGL_ION: specifies a single ion (e.g. SNGL_ION='Fe_10' to include
only Fe X lines) or an array (e.g. SNGL_ION=['Fe_10','Fe_11']
to include only Fe X and Fe XI lines) of ions to be used
instead of the complete set of ions specified in
!xuvtop/masterlist/masterlist.ions
MASTERLIST: string of a specific masterlist file (full path).
If defined as a keyword (i.e. MASTERLIST=1 or /MASTERLIST)
then a widget allows the user to select a user-defined
masterlist file. Shortcut for SNGL_ION.
PHOTONS: units will be in photons rather than ergs
KEV: wavelengths will be given in kev rather than Angstroms
ALL: if set, then all lines are included. This means that lines
for which
only an approximate wavelength is known (only theoretical energy
levels are known) are included.
OUTFILE: the name of the output ascii file to be written. By
default a
file 'linelist.txt' in the user's working directory will be
created.
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
RADTEMP Specify background radiation temperature (default: 6000 K)
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
CALLS:
CH_SYNTHETIC, CH_LINE_LIST
COMMON BLOCKS: None
RESTRICTIONS:
SIDE EFFECTS:
EXAMPLE:
IDL> ascii_wvl_dem,400.,800., out='linelist',$
pressure=1.e+15,mini=1.,sngl_ion='o_4'
CATEGORY:
spectral synthesis.
WRITTEN :
Version 1, 8-Nov-01, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ).
Compared to the previous ASCII_WVL_DEM, these are the main changes:
1-Rewritten as a wrapper routine using the new procedures.
2-Now the PRESSURE value is a keyword.
3-The calculations can be done at constant DENSITY.
4-Energies (keV) can be output instead of wavelengths in Angstroms
5-MASTERLIST can now be used both as an input string or as a keyword.
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
18-Nov-01, Peter Young
Added /noprot, rphot and radtemp keywords
V. 2, 22-May-2002 GDZ. Removed const_net definitions.
VERSION : 2, 22-May-2002
PROJECT: CHIANTI
NAME:
bb_rad_loss
PURPOSE:
calculates energy loss rate by line (bound-bound) radiation
CATEGORY:
synthetic spectra
CALLING SEQUENCE:
BB_RAD_LOSS,Temperature,Loss_rate
INPUTS:
None: the user will select various parameters such as the
choice of elemental abundances and ionization equilibria
KEYWORDS:
Pressure: pressure in emitting region (cm^-3 K)
density=pressure/temperature(K)
Density: density (cm^-3), constant for all temperatures
if neither density or pressure is set, then a
default constant density of 10^10 cm^-3 is used.
Sngl_ion: to calculate the loses spectrum for a single ion
NOPROT Switches off inclusion of proton rates.
RADTEMP The blackbody radiation field temperature (default
6000 K).
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius
units. I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface.
(Default is infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
OUTPUTS:
Temperature: array of temperatures (K)
Loss_rate: energy loss rate in erg cm^3 s^-1
PROCEDURE:
if keyword pressure is set then calculations performed at constant pressure
if keyword density is set then calculations performed at constant density
otherwise, density is set to 1.e+10
pressure = density * temperature (cm^-3 K)
the user will be asked to select an abundance file.
COMMON BLOCKS:
ELVLC, WGFA, UPSILON, RADIATIVE, PROTON, ELEMENTS, IONREC
CALLS
READ_MASTERLIST,
SETUP_ELEMENTS, POP_SOLVER, CONVERTNAME, R2W, PROTON_DENS,
ZION2SPECTROSCOPIC, ZION2FILENAME, SETUP_ION
EXAMPLE:
> bb_rad_loss,t,r
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
January 1999: version 1, adopted from synthetic.pro
14-Jul-2000 Peter Young, now calls pop_solver
Ver.2, 9-Dec-2001, Peter Young
Modified for v.4 of CHIANTI.
V.3, 4-Oct-2003, GDZ
modified the input to POP_SOLVER, now it is dealt with an
input structure. Also shorten the whole procedure, by calling
other procedures.
V.4, 5-Apr-2005, EL
modified the input to POP_SOLVER in order to add ion/rec
in the calculation of level populations. All the rest
is unchanged.
V 5, 25-May-2005, GDZ
corrected routine header.
VERSION : 5, 25-May-2005, GDZ
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
Name : CALC_DMM_DR
Purpose : Calculates CHIANTI density sensitive line ratios.
Explanation :
Use : Called from DMM_NE
Inputs : ciz - element number
cion - ion number
denmin, denmax - log density range
mess_win - message widget ID for DMM_NE use.
Opt. Inputs : None
Outputs : None
Opt. Outputs: None
Keywords : Temperature - if set use this temperature rather than
temp at max of ioneq.
Calls : EMISS_CALC
Common :
Restrictions: None
Side effects: None
Category : Spectral
Prev. Hist. : Based on density_ratios by K Dere.
Written : C D Pike, RAL, 22-Jan-96
Modified : Send warning message to widget. CDP, 27-Jan-96
Update generally. CDP, 7-Jun-97
Corrected typo in reading elvlc file. CDP, 14-Jul-97
Added minimum line ratio factor. CDP, 17-Jul-97
Added multiple wavelength ranges. CDP, 18-Jul-97
Fix typo for XXII stage. CDP, 05-Mar-98
Update list of elements. CDP, 18-Jun-99
v. 9. Correct hiccup in above. CDP, 13-Jul-99
Update for compatibility with CHIANTI v.3. Replaced populate
with pop_solver. Left out 'dielectronic' lines. ouput
temperature. plus various small additions.
Now ratios are calculated with 0.1 increment in log Ne
Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ) 10-Oct-2000
Ver.11, 7-Dec-01, Peter Young (PRY)
modified for v.4 of CHIANTI
Ver. 12, 1-May-02, GDZ
Fixed a bug: Added nlist = 0 when no lines are present.
V. 13, 21-May-2002, GDZ
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V.14, 06-Aug-02 GDZ
Changed the use of CHIANTI system variables.
V.15, 16-Sep-2004, GDZ
added /NO_DE in call to emiss_calc as chianti_te expects
emissivities in photon units
Version : Version 15, 16-Sep-2004
Project : SOHO - CDS
Name : CALC_DMM_TR
Purpose : Calculates CHIANTI temperature sensitive line ratios.
Explanation :
Use : Called from DMM_TE
Inputs : ciz - element number
cion - ion number
wmin, wmax - wavelength range
temmin, temmax - log temperature range
mess_win - message widget ID for DMM_TE use.
Opt. Inputs : None
Outputs : None
Opt. Outputs: None
Keywords : None
Calls : EMISS_CALC
Common :
Restrictions: None
Side effects: None
Category : Spectral
Prev. Hist. : Based on temperature_ratios by K Dere.
Written : C D Pike, RAL, 22-Jan-96,
Modified : H E Mason, 03-Oct-96 (density to temperature)
Modified : Send warning message to widget. CDP, 27-Jan-96
Update list of elements and cut call to
read_elvl. CDP, 18-Jun-99
V.3. Fix hiccupp in above. CDP, 13-Jul-99
V.4. Rewritten completely, adding possibility to pass on the
density at which the intensities are calculated, and making
this routine compatible ith CHIANTI v.3.
Giulio Del Zanna (DAMTP), 10 Oct-2000
Ver.5, 7-Dec-2001, Peter Young
Modified for v.4 of CHIANTI.
Ver. 6, 1-May-02, GDZ
Fixed a bug: Added nlist = 0 when no lines are present.
V.7, 16-Sep-2004, Peter Young
added /NO_DE in call to emiss_calc as chianti_te expects
emissivities in photon units
Version : Version 7, 16-Sep-04
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
Name : CHIANTI_DEM
Purpose : Calculates the Differential Emission Measure DEM(T) using
the CHIANTI database, from a given set of observed lines.
Constant pressure or density can be used.
Category : diagnostic analysis
Explanation : This routine has several options, all in the form of keywords.
First, the input file with the observed fluxes is read.
THE FIRST TIME YOU USE THIS ROUTINE
you'll have to do the calculation of the contribution
functions G(T), so the routine GET_CONTRIBUTIONS will come
into play. You'll have to specify the value of the
pressure or density, and you'll be asked to select an
ionization equilibrium file and an abundance file.
GET_CONTRIBUTIONS searches the CHIANTI database (ion per ion)
for all the theoretical lines corresponding to the observed
lines, i.e. that lie in a OBS_WVL(i) +/- DELTA_LAMBDA_OBS(i)
interval centered on the observed wavelength OBS_WVL(i).
The routine calculates the C(T) values (G(T)=Ab(element)*C(T))
for the temperature interval log(T)= 4.0 - 8.0
with steps of log(T) = 0.1 .
You can either select a constant pressure OR a constant
density for all the lines; if you select a constant pressure,
for each ion the contribution function is calculated at an
electron density N_e equal to the ratio of the pressure
and the temperature of maximum ionization fraction:
C=C( T, N_e= P/T_ion )
The C(T) values are stored by GET_CONTRIBUTIONS in the output
file OUTPUT.CONTRIBUTIONS that can be used later to calculate
the DEM, changing various parameters,
without having to start again and read the CHIANTI database,
which can take long time.
In the case no theoretical lines corresponding to an observed
line are found, the routine writes the wavelength of the line
(to be excluded from the fit) in the array
EXCLU_OBS_WVL_NO_TEO. The lines with no theoretical
counterparts are then automatically excluded from the fit by
CHIANTI_DEM. You might consider the possibility to start again
incrementing the DELTA_LAMBDA_OBS, to see if there are
theoretical lines in the vicinity.
Note: if you want to exclude some of the observed lines from
the fit, you just have to use the keyword EXCLUDE_OBS_WVL,
BUT GET_CONTRIBUTIONS will store anyway the results (if any)
in the C(T) file.
After having excluded the lines in EXCLUDE_OBS_WVL,
any *.abund file present in the CHIANTI database or in
the working directory can be selected, and eventually edited,
if you like to change some abundances.
Then the $G(T)$ are calculated, multiplying each theoretical
line by the abundance factor. Then the
theoretical lines contributing to each blend are sorted by
intensity and then their G(T) can be plotted if the keyword
PLOT_GT is activated. It is recommended to do this the first
time, to check if there are some observed lines terribly
blended with lines of other elements, in which case it is
better to exclude them with a second run (if you are not
sure about the abundances).
Then the G(T) for each blend are summed and plotted.
Then the fit starts calling DEM_FIT.
A series of parameters can change the
result (DEM), especially the number and position of the mesh
points of the spline that represents the DEM. The keyword
MESH_POINTS serves for this purpose.
The other keywords that control the fit are N_ITER, DCHISQ_M.
At the end of the fit, the files OUTPUT.DEM and OUTPUT.GENERAL
are created.
Use : IDL>chianti_dem,output='serts89',file_input='serts89.obs',$
pressure=3.e15
Examples :
Assume you have a file input 'serts89.obs' like this:
243.031 491. 97. 0.1 He II
256.323 1580. 186. 0.1 He II b
315.024 253. 31. 0.1 Mg VIII
335.401 10400. 1650. 0.1 Fe XVI
319.839 113. 14. 0.1 Si VIII
356.027 218. 25. 0.1 Si X
IDL>chianti_dem,output='serts89',file_input='serts89.obs',$
pressure=3.e15,cut_gt=1e-30,/plot_gt
After having selected the ionization file,
the C(T) (with MAX(C(T)) gt 1e-30) are stored in the file
'serts89.contributions'. Then select one of the abundance
files.
Have a look at the plots of the G(T), and annotate
if there is a line you want to exclude, let's say the second.
Have a look at the DEM obtained ('serts89.dem') and at
the details contained in the file 'serts89.general'.
Maybe there is another line you want to exclude, let's say
the last one. Maybe you want to change the mesh points, too.
So run
IDL>chianti_dem,output='serts89_2',file_input='serts89.obs',$
file_gt='serts89.contributions',$
exclude_obs_wvl=[243.031,356.027 ],$
mesh_points= [4.5,5.,5.5,6.2,7.5]
The files 'serts89_2.dem' and 'serts89_2.general' will be
created. They have the essential information about what you
did.
Inputs : various, all in form of keywords. The required ones are
OUTPUT and FILE_GT (or PRESSURE/DENSITY)
Opt. Inputs : various... see the software note.
Outputs : OUTPUT.CONTRIBUTIONS
Created only if the keyword FILE_GT is NOT set.
Is the file where all the contribution functions G(T) are
stored. In the first two lines the ionization equilibrium
file name, and the constant value of pressure or density
adopted are reported. Then for each line you have reported
the observed wavelength, the theoretical one, the element and
ionization stage, then the C(T) values. At the end the
specification for each transition.
OUTPUT.DEM
Is the file where the log T and log DEM values are
written, with a format suitable
as input for the DMM_SS procedure,that calculates the
synthetic spectrum. At the end some info on how it was
calculated are printed.
OUTPUT.GENERAL
Is the file where general information is stored.
The abundance file, the ionization equilibrium file and the
constant value of pressure or density used are reported.
Then there is one line for each
observed line, with the provisional identification, the
observed wavelength, the observed flux, the theoretical one
(corresponding to the DEM), the error on the flux,
the square of the difference between the theoretical and the
observed fluxes divided by the error (this number should be
close to zero if the line is well reproduced), and finally
the ratio of the theoretical flux versus the observed one
(which should be close to 1).
After this line, there is one line per each theoretical line
contributing to the blend, with the identification, the
theoretical wavelength, the configuration and terms, and the
contribution to the total theoretical flux (in percentage)
of each line in the blend.
OUTPUT.OUT
This file , toghether with OUTPUT.DEM ,
can be used to reproduce the results using
user-written software. See the software notes.
The ouput has this format:
format='(a20,1x, 1f10.3,1x, 3e10.3, 1x, f4.2,1x,f6.3)'
Opt. Outputs:
An abundance file with the modifications inserted.
Postscript files of the G(T).
A postscript file with the DEM (OUTPUT.DEM.PS)
A postscript file with other plots too (OUTPUT_4PLOTS.PS)
Keywords :
ARCSEC:
optional. If set, it means that the intensities in the input
file are per arcsec-2 .
These intensities are then converted to
sterad-1 .
CUT_GT:
optional. If set, only the those theoretical lines that
have a MAX(C(T)) greater than the value set, are kept;
it is useful to set this value in order to reduce the number
of lines in the file where the C(T) are stored.;
if not set, a default value of 1e-30 is adopted.
DCHISQ_M:
optional. If not set, a default value of DCHISQ_MIN=1.e-5
is assumed. For each iteration, the CHISQ and it's variation
are calculated. As long as the iteration achieves an
improvement in CHISQ greater than DCHISQ_MIN , another
iteration will be performed.
DEM_FILE:
optional.If set (,/DEM_FILE) you have to choose a DEM file to
be used as a start, instead of the default constant value of
10.^22.
You can either choose one of the files in the CHIANTI database
or any you have in the working directory.
The values in the file are marked as crosses, the mesh points
are marked with triangles.
DENSITY :
the value of the density (Ne). Required if you do NOT have
already the contribution functions G(T).
EXCLUDE_OBS_WVL:
optional.
If set, you can exclude some of the observed lines from
the fit. Note that even if you set this keyword and run
GET_CONTRIBUTIONS all the theoretical lines found corresponding
to all the lines in the input file are written in the C(T)
file. It is only in the fit that the lines are excluded.
FILE_GT:
optional.
If NOT set, the routine GET_CONTRIBUTIONS is called.
If set, it has to specify the name of the file created by
GET_CONTRIBUTIONS, where all the contribution functions G(T)
are stored. In the first two lines the ionization equilibrium
file name, and the value of the pressure or density
adopted is reported. Then for each line you have reported
the observed wavelength, the theoretical one, the element and
ionization stage, then the C(T) values. At the end the
specification for each transition.
FILE_INPUT:
optional.
if set, you are not requested to select the observation file
using a widget-type search.
The input file must contain 5 columns, unformatted:
1)the observed wavelength (A)
2)the observed flux in erg cm-2 s-1 st-1
3)the corresponding error on the flux in erg cm-2 s-1 st-1
4)half the width (A) of the range (centered on the observed
wavelength) where you want to look for the corresponding
theoretical lines. A value of HWHM or more would do.
5)The identification, written as string (max 20 characters)
MESH_POINTS:
optional. It is a vector that specifies the mesh points for the
spline that represent the fitted DEM, in log(T).
If not set, the default values
[4.,4.5,5.,5.5,6.,6.5,7.,7.5,8.0] are assumed.
N_ITER:
optional.It is the number of iterations of the fitting routine.
If not set, a default value of 20 is assumed.
Changing this value alone might not affect the fit, since
also the value of DCHISQ_MIN is checked during the fit.
N_MATCHES:
optional.
In the unlikely event that more than 50 (default value for
N_MATCHES) theoretical lines corresponding to an observed
line are found, the routine stops; in this case, you have to
start again setting N_MATCHES equal to a greater number.
OUTPUT :
required.
It is the output name. Suffixes will be added when creating
the various outputs.
PHOT:
optional.
If set, it means that in the input file the intensities
are in photons instead of ergs.
PLOT_GT:
optional.
If set (,/PLOT_GT), plots of the G(T) for each
observed line not excluded are created.
PRESSURE:
the value of the pressure (Ne T). Required if you do NOT have
already the contribution functions G(T).
QUIET:
optional. Set to avoid various messages and the details of the
result.
Calls : GET_CONTRIBUTIONS
DEM_FIT
ZION2SPECTROSCOPIC
print2d_plot
Common : obs, obs_int,obs_sig,n_obs
obs_o, obs_wvl,obs_id,obs_delta_lambda
dem, d_dem_temp,dem_temp,log_dem_temp,log_t_mesh,log_dem_mesh
contr, ch_tot_contr
ab, abund_name,abund_info,xuvtop,ioneq_name
these are the commons with GET_CONTRIBUTIONS.PRO:
various, exclu_obs_wvl_no_teo,const_net,$
dem_temp_min,dem_temp_max,n_dem_temp,$
ch_wvl,ch_l1,ch_l2,ch_id,ch_z,ch_ion,ch_contr_wa,$
ch_pop,ch_contr_list, ch_term,ch_n_contr
Restrictions:
In the unlikely event that more than 50 (default value for
N_MATCHES) theoretical lines corresponding to an observed
line are found, the routine stops; in this case, you have to
start again setting N_MATCHES equal to a greater number.
Also, if the starting DEM values are not proper, or you
don't have enough constraints at lower and higher temperatures,
you might get "strange" results, and should consider using
different starting values.
Of course you need to have the enviroment variable CDS_SS_DERE
pointing to the CHIANTI database top directory.
Side effects: None known yet.
Category : spectrum
Prev. Hist. :
Written by Ken Dere (NRL) as part of the CHIANTI package
in collaboration with Brunella Monsignori Fossi, Enrico Landi
(Arcetri Observatory, Florence), Helen Mason and Peter Young
(DAMTP, Cambridge Univ.). Incorporated into the CDS software.
Written :
V. 1.0 5 November 1997 Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ),
UCLAN (University of Central Lancashire, UK)
Modified : Removed the print2d_plot subroutine. Increased the default value
of N_MATCHES from 20 to 50. Changed way to deal with xuvtop.
GDZ, 31-Oct-2000
Version : 2.0 GDZ, DAMTP, 31-Oct-2000
V.3, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
VERSION : 3, 21-May-2002, GDZ
Project : SOHO - CDS
Name : CHIANTI_NE
Purpose : Calculate and plot CHIANTI density sensitive line ratios.
Explanation : CHIANTI_NE (density ratios)
calculates and plots density sensitive line ratios based on
the CHIANTI atomic database of Dere et. al.
Use : IDL> chianti_ne
Inputs : None
Opt. Inputs : None
Outputs : None
Opt. Outputs: None.
Keywords : None
Calls : CALC_DMM_DR, plot_dmm_dr_fig , make_ion_list
Common : dmm_dr_com dmm_lines(with plot_dmm_dr_fig),
Restrictions: None
Side effects: None
Category : Spectral
Prev. Hist. : Started life as 'density_ratios' by Ken Dere
Written : C D Pike, RAL, 13-Jan-96
Modified : Added selection of els/ions from master file. CDP, 21-Jan-96
Added hardcopy of line list, refs etc. CDP, 22-Jan-96
Include multiple lines in ratio. CDP, 27-Jan-96
General upgrade and added temp/unit selections. CDP, 6-Jun-97
Added intensity ratio selection. CDP, 17-Jul-97
Added wavelength ranges. CDP, 18-Jul-97
Fixed typos introduced in version 7. CDP, 22-Jul-97
Float the user-supplied Log Temperature. CDP, 1-Aug-97
Update for IDL v5.2. CDP, 20-Apr-99
v. 11 Update list of elements. CDP, 18-Jun-99
V.12. Added ratio plots and hardcopies in linear scale, added various
checks and minor things. Added a few tags to the
ratio output structure (temperature, units, comment).
Removed optional output structure.
Updated to be CHIANTI v.3-compatible.
Giulio Del Zanna, DAMTP, 7-Oct-2000
Version 13, 21-Dec-2000, William Thompson, GSFC
Modified for better cross-platform graphics capability
V. 14, 1-May-02, GDZ, commented out a few refs.
V. 15, 21-May-2002, GDZ, changed the way to deal with fonts.
V.16, 17-Sep-2002 (GDZ)
added !p.multi = 0 upon exit and added X-label.
Version : Version 16, 17-Sep-2002
Project : SOHO - CDS
Name : CHIANTI_TE
Purpose : Calculate and plot CHIANTI temperature sensitive line ratios.
Explanation : CHIANTI_TE (temperature ratios)
calculates and plots temp. sensitive line ratios based on
the CHIANTI atomic database of Dere et. al.
Use : IDL> chianti_te
Inputs : None
Opt. Inputs : None
Outputs : None
Opt. Outputs: none.
Keywords : None
Calls : CALC_DMM_TR, make_ion_list
Common : dmm_tr_com
Restrictions: None
Side effects: None
Category : Spectral
Prev. Hist. : Started life as 'temperature_ratios' by Ken Dere
Written : H.E. Mason, 3 Oct 1996
Modified : Update for IDL v5.2. CDP, 20-Apr-99
V.3. Update list of elements. CDP, 18-Jun-99
V.4 , Giulio Del Zanna (DAMTP), 10 Oct-2000
Rewritten completely, adding possibility to select the density
at which the intensities are calculated, making this routine
compatible ith CHIANTI v.3, and with the same characteristics as
CHIANTI_TE. Added ratio plots and hardcopies in linear scale, added various
checks and minor things. Added a few tags to the
ratio output structure (density, units, comment).
Removed optional output structure.
Version 5, 21-Dec-2000, William Thompson, GSFC
Modified for better cross-platform graphics capability
V. 6, 1-May-02, GDZ, commented out a few refs.
V.7, 21-May-2002, GDZ, fixed a bug with the fonts.
V.8, 17-Sep-2002 (GDZ)
added !p.multi = 0 upon exit and added X-label
Version : Version 8, 17-Sep-2002
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME: ch_check_str
PURPOSE:
To check that an input structure is of the right type
PROCEDURE:
This function checks that the input structure has at least the basic
tags that should be present. Two types of basci structures are checked:
1) the standard CHIANTI structure, output of the synthetic program
CH_SYNTHETIC, that contains line INTENSITIES
2) The standard CHIANTI structure output of MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC, that contains a
synthetic SPECTRUM.
CATEGORY:
spectral synthesis.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
IDL> result=ch_check_str (tran, [/int , /sp])
INPUTS: the IDL structure TRAN
OPTIONAL INPUTS :
OUTPUTS:
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
KEYWORDS:
intensities
spectrum
CALLS: required_tags
COMMON BLOCKS: none
RESTRICTIONS:
SIDE EFFECTS:
EXAMPLE:
PREV. HIST. :
WRITTEN :
Ver.1, 22-May-02, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ), DAMTP
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
VERSION : 1, 22-May-02, GDZ
NAME
CH_DRAWBOX()
EXPLANATION
Allows the selection of a sub-region within a plot using a
"rubberband box".
INPUTS
WID ID of window where box is drawn. (!D.Window by default.)
INTERACTIVE INPUTS
By clicking-and-holding the left mouse button (LMB), a box will
appear on the plot window. Moving the mouse will change the size
of the box. When the box is in the right position, let go of the
LMB.
OPTIONAL INPUTS
COLOR The color index of the box. (!D.N_Colors-1 by default.)
KEYWORDS
DATA Box coordinates returned in DATA coordinates.
NORMAL Box coordinates returned in NORMAL coordinates.
OUTPUT
The function returns the box coordinates, either in device (default),
data or normal coordinates. See keywords /DATA and /NORMAL.
PREVIOUS HISTORY
This is a modified version of the routine drawbox.pro that is
available from
http://www.dfanning.com/documents/tips.html
HISTORY
Ver.1, 11-Dec-2001, Peter Young
PROJECT : CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME : CH_GET_FILE
PURPOSE : to select a file from either a selected directory or the working
directory, having an extension.
EXPLANATION : a file in either a selected directory or the working
directory, having an extension can be selected using a
widget. Note that both directory and extension have to be
supplied. If no file is found, an empty string is returned. ;
USE : IDL> name = ch_get_file( '~/', '.pro', tit=' Select a procedure ')
EXAMPLES : dir= concat_dir(!xuvtop),'dem')
dem_name=ch_get_file(path=dir,filter='*.dem',title='Select DEM File')
INPUTS : directory, extension
OPT. INPUTS :
OUTPUTS : the file name
OPT. OUTPUTS:
KEYWORDS : title
CALLS : findfile, break_file
COMMON : co
RESTRICTIONS: both directory and extension have to be
supplied.
SIDE EFFECTS:
CATEGORY :
PREV. HIST. : extracted from CDS/CHIANTI routines.
WRITTEN :
Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ),
DAMTP (University of Cambridge, UK)
MODIFIED : Version 1, GDZ 10-Oct-2000
V.2, GDZ, corrected a typo at the end of the file.
V.3, GDZ, generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V. 4, 19-July-2002, GDZ
Added the option to select files also with the standard IDL
dialaog_pickfile, and changed a few things...
V.5, 2-Aug-02, GDZ
reduced the size of the widget.
V.6, 12-Aug-02, GDZ
corrected for a bug in the directory output.
V.7, 3-Nov-03 GDZ
Fixed a bug when using Windows, the returned path was not
correct.
VERSION : 7, 3-Nov-03
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
CH_LINE_LIST
PURPOSE:
Create a latex or an ascii file of predicted spectral line intensities and
wavelengths corresponding to selected parameters, as calculated by
CH_SYNTHETIC. Needs as input the line intensity structure calculated by
CH_SYNTHETIC (default) or the SPECTRUM structure output of
MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
IDL> ch_line_list, transitions, outname, latex=latex, ascii=ascii, $
abundfile=abundfile, min_abund=min_abund, $
wmin=wmin,wmax=wmax,$
SPECTRUM=SPECTRUM, minI=minI,photons=photons,kev=kev, $
all=all,no_sort=no_sort, sngl_ion=sngl_ion
PROCEDURE:
INPUTS:
The structure created by CH_SYNTHETIC
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
Wmin: lower limit of the wavelength/energy range of interest (Angstroms)
if kev keyword set, then wmin is in kev
Wmax: upper limit of the wavelength/energy range of interest (Angstroms)
if kev keyword set, then wmax is in kev
Mini: Minimum intensity for line to be included in output
SNGL_ION: specifies a single ion (or a list of ions) to be used instead
of the complete set of ions specified in the structure.
MIN_ABUND: If set, outputs only those elements which
have an abundance greater than min_abund.
For example, from Allen (1973):
abundance (H) = 1.
abundance (He) = 0.085
abundance (C) = 3.3e-4
abundance (O) = 6.6e-4
abundance (Si) = 3.3e-5
abundance (Fe) = 3.9e-5
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
LATEX: Create a latex file (default, exclusive with /ASCII)
ASCII: Create an ascii file (exclusive with /LATEX)
MINI: Minimum intensity for line to be included in output
PHOTONS: units will be in photons rather than ergs
KEV: wavelengths will be given in kev rather than Angstroms
ALL: if set, then all lines are included. This means that lines for which
only an approximate wavelength is known, denoted by a negative
wavelength value in the .wgfa file, are included.
These lines are listed in the file with a * preceding the wavelength.
NO_SORT:
If set, then the lines are *not* sorted in wavelength (or energy).
SPECTRUM
If set, IT IS ASSUMED that the input structure is the SPECTRUM
structure output of MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC, where the line
intensities have already been multiplied by the abundance factor!!
OUTPUTS:
A latex (default) or an ascii file with the line list
CALLS: Many SolarSoft routines.
COMMON BLOCKS:
none.
SIDE EFFECTS:
EXAMPLE:
> ch_line_list, trans,'linelist.tex',/latex, wmin=100.,wmax=200.,/all
CATEGORY:
spectral synthesis.
WRITTEN :
Version 1, Written by: Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ) Oct 31 2001.
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
V.2, 9-Nov-2001 GDZ.
Now correctly handles the case when no
abundances are passed to the routine.
v.3, 11-Dec-2001, PRY.
Removed calls to get_utc and anytim2cal. Replaced with
call to systime()
v.4, 29-Apr-02, GDZ
Fixed a few small bugs, some caused by a change in the
database file format for V4.
Added only_mini, file_effarea keywords to be able to use as
input the structure created by MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC.
V.5, 22-May-2002, GDZ
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS. changed tags.
Changed and added various things, including flabel
V.6, 12-Aug-02, GDZ
Modified the output labeling, and fixed two bugs: 1) when /all was used
the keyword /mini was not working. 2) min_abund was not working
properly when /spectrum was used. Reduced size of latex output (was
12pt)
Changed output in isothermal case (no Tmax given). Better info printed (GDZ)
V.7, 3-Nov-03 GDZ
Modified format e8.2 to e9.2 for Windows compatibility.
v.8, 18-Jul-2005 GDZ
Modified the use of the /kev keyword. Also, now the
routine accepts input structure with the units in keV.
v.9, 4-Aug-2005 GDZ
Corrected a bug introduced in the previous version.
Also switched to \documentclass when making the latex file.
VERSION : 9, 4-Aug-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
http://wwwsolar.nrl.navy.mil/chianti.html
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME:
CH_READ_FITS
PURPOSE:
Read standard CHIANTI FITS binary table data containing the output from
CH_SYNTHETIC and output a TRANSITIONS structure.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
CH_READ_FITS, Filename, TRANSITIONS
INPUTS:
Filename = String containing the name of the CHIANTI FITS file written
by CH_WRITE_FITS.
OUTPUTS:
TRANSITIONS = Structure to be written.
OPTIONAL INPUTS: none
KEYWORDS: none
NOTES:
CALLS:
MRDFITS, ADD_TAG
COMMON BLOCKS: none.
RESTRICTIONS:
(3) The input FITS file must have been written by CH_WRITE_FITS
PREV. HIST. :
EXAMPLE:
ch_read_fits, 'file.fits', transitions
WRITTEN :
Ver.1, 8-Apr-02 Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
V.2 GDZ 31 May 2002 added more checks.
MODIfICATION HISTORY:
VERSION : 2, 31 May 2002
PROJECT
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME
CH_SS
PURPOSE:
Widget-based multi-purpose routine
to calculate CHIANTI line intensities and continua, to create a
synthetic spectrum, to make tables of lines, etc.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
IDL> ch_ss
PROCEDURE:
This routine calculates a synthetic spectrum by merging line
intensities and continua.
The widget is organised into four Sections:
SECTION 1:
-The Calculation of the CHIANTI line intensities.
This can be done in two ways:
1-Restore a save file with the CHIANTI line intensities already
calculated.
2-Calculate CHIANTI line intensities with a call to CH_SYNTHETIC.
In this case, A series of parameters must be set:
- Minimum and maximum wavelengths in Angstroms
- The model used for the calculation. Three are the options:
1) a constant density (cm^-3)
2) a constant pressure (cm^-3 K)
3) a general (Te,Ne) model. In this case, a file will be read.
This file should have two columns, one with the Te (K)
values, and one with the Ne (cm^-3) values.
- The ionization fraction file to be used. "*.ioneq" files
can be selected from either the CHIANTI database, the
working directory or selected via a widget.
- All ions ? If set to yes (default), then all the ions present in the
database will be included.
If set to no, then it is possible to select a list of ions
with a widget
- All lines ? If set to no (default), only the lines for which there are
observed energy levels are included
If set to yes, also the lines that do not have
corresponding observed energy levels are included. In this
case, the wavelengths are calculated from the theoretical
energy levels, and might not be very accurate.
- Isothermal ? If set to no (default), a DEM file must be selected.
"*.dem" files (i.e. files with a .dem extension)
can be selected from either the CHIANTI database, the
working directory or selected via a widget.
If set to yes, then the user is requested to enter one
or more temperatures (as logarithmic values - Log T )
and correspondent column emission measures EM
logarithmic values.
NOTE: if more than one value is entered, then the
sequence must be separated by commas (e.g.: 6.0,
6.5, 7.), and both Log T and Log EM must have the
same number of values
- Photoexcitation ?
If set to yes, you have to define:
Trad: The blackbody radiation field temperature
R/Ro: Distance from the centre of the star in stellar
radius units
Units: Photons or Ergs'
Protons: If set to Yes, the proton data are used to calculate the level population
Once all the parameters have been defined, the user should click on the
"Calculate intensities" button to start the calculation (which calls
CH_SYNTHETIC).
Once the calculation is finished, an IDL structure is loaded into
memory. It is then possible to save it for later use by clicking on the
"SAVE" button.
The RESTORE button is to restore previously saved files into an IDL
structure in memory.
Once the IDL structure with the line intensities is in the memory, it is
then possible to calculate and plot a spectrum (SECTION 2).
SECTION 2:
This section controls the parameters that are needed to fold the
line intensities and the continua into a synthetic
spectrum. These parameters are used by MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC.
Before this is done, a set of line intensities MUST be in the
program memory. This is done either by calculating the
intensities or by restoring a save file with
previously calculated values (SECTION 1).
Setting the parameters:
-Minimum and maximum wavelengths in Angstroms
-spectrum bin size in Angstroms. Disallowed if an Effective area
file is used.
-instrumental FWHM: Setting this to a non-zero value broadens
each of the spectral lines with a Gaussian of
the specified FWHM (in Angstroms) so
mimicking the effects of instrumental
broadening.
-continuum: Add continua to the binned spectrum:
free-free, free-bound and two-photon.
Please note that the continuum calculation takes some
time and you may want to define a minimum abundance
value to speed the calculations.
- All lines ? If set to no (default), only the lines for which there are
observed energy levels are included.
If set to yes, the "unobserved lines" will be added, but
only if they are present in the structure.
-elemental abundances
"*.abund" files (i.e. files with a .abund
extension) can be selected either from the CHIANTI database,
the working directory, or via a widget.
-select a minimum abundance value
If set not null, only the lines of those elements
which have an abundance greater than the value set are
selected. Also, the continuum is calculated only for
those elements which have an abundance greater than
the value set. This can significantly speed up the
calculations. By default, the minimum value in the
selected abundance file is used. To have an idea of
what minimum abundance should be set, the abundances
of Allen (1973) give:
abundance (H) = 1.
abundance (He) = 0.085
abundance (C) = 3.3e-4
abundance (O) = 6.6e-4
abundance (Si) = 3.3e-5
abundance (Fe) = 3.9e-5
Eff. Area: Yes/No
If you want to fold the spectrum with an effective area.
If set to Yes, you are requested to choose an input ascii file
with two columns, the wavelength and the effective area values
(cm^2).
The wavelenghts in the file (that might not be linear) are used
to create the spectrum, that is multiplied with the effective
area values.
Note that this option only works well if a sufficient number
of bins is given. The line intensities contributing to each
bin are summed, and subsequently convolved with a gaussian
of full-width-half-maximum FWHM, if FWHM is not set = 0.
Please note that the convolution might not work if a small
number of bins is defined.
Also note that to have the correct output units (counts s-1
bin-1) the appropiately scaled DEM (or EM) values must be provided.
After this, by clicking on the "Calculate and plot" button the
program calculates and plots the synthetic spectrum.
Once the spectrum is displayed, it is then possible to
view the details of the lines by clicking with the mouse in the
plot window, and to perform various operations by clicking on
the buttons in SECTION 3
SECTION 3:
This Section allows the user to select a few parameters for the
plotting, and to create different types of OUTPUT.
Labels ? : Setting this to yes plots a vertical line for each
spectral line in the spectrum, and also writes a label
above the strongest lines indicating the ion from
which the line arises.
Min.: Only lines which have an intensity greater than the
value set here will be listed and, if requested,
labelled and selected for inclusion in the various
outputs. Setting the value=0. will result in all
lines being listed and written in the outputs.
X,Y, XOOM, UNZOOM: It si possible to select a region of the
spectrum, by zooming with the use of the mouse
or by setting the X,Y ranges.
NOTE that only the line details and portion of
the spectrum shown will be output.
LINEAR/LOG To plot the spectrum in linear or log scale
Create PS file: A postscript file is created.
Hardcopy: the postscript file "idl.ps" is created and sent to the
default printer.
Save Line details (latex): The details of the lines shown in the
plot will be saved in a latex file.
Save Line details (ascii): The details of the lines shown in the
plot will be saved in an ascii file.
Save Spectrum (ascii): The X,Y values of the plot are saved in
an ascii file.
Save Spectrum (IDL/FITS): The details of all the lines and the arrays
of the X,Y values of the plot are saved into
an IDL or FITS file. The IDL structure
has the following tags:
.LAMBDA: The array of wavelength X values
.SPECTRUM: The array of spectrum Y values
.UNITS The units of LAMBDA, SPECTRUM
.INSTR_FWHM The Instrumental FWHM
.BIN_SIZE Width of the Bins (fixed) in angstroms
.ABUND_NAME The CHIANTI abundance file name
.ABUND The abundance values
.MIN_ABUND The minimum abundance value used
.ABUND_REF The references
.CONTINUUM The values of the continuum (if
calculated)
.EFFAREA The array of effective area
values (optional)
.FILE_EFFAREA The name of the effective area file used (optional).
.IONEQ_NAME The ion balance file used (full path).
.IONEQ_LOGT The Log10 T values associated.
.IONEQ_REF The references.
.DEM_NAME The differential emission measure file eventually used
(full path).
.DEM The Log10 DEM values
.DEM_LOGT The Log10 T values associated.
.DEM_REF The references.
.MODEL_NAME A string indicating the model used
(e.g. constant density or constant pressure).
.MODEL_NE the Ne value.
.MODEL_PE the Pe value.
.WVL_UNITS The wavelength units.
.WVL_LIMITS The wavelength limits specified by the user.
.INT_UNITS The intensity units
.LOGT_ISOTHERMAL
The Log10(T) values used.
.LOGEM_ISOTHERMAL
The Log10(EM) values used.
.TIME The date and time when the structure was created.
.VERSION The version number of the CHIANTI database used.
.ADD_PROTONS
A flag (0/1) to indicate whether proton data were used (1)
or not (0) to calculate the level population.
.PHOTOEXCITATION
A flag (0/1) to indicate if photoexcitation was included (1)
or not (0).
.RADTEMP
The blackbody radiation field temperature used (if
photoexcitation was included).
.RPHOT
Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units
(if photoexcitation was included).
THEN, FOR EACH LINE USED TO CALCULATE THE
SPECTRUM:
.LINES A structure containing information about the lines.
Its size is the number of lines in the spectrum. The
tags are:
.peak The peak intensity value
.iz The atomic number of the elements (e.g., 26=Fe)
.ion The ionisation stage (e.g., 13=XIII)
.snote The identification of the ion (e.g., 'Fe XXIV d')
.ident The identification of the transition, configuration
and terms in text form.
.ident_latex
The identification of the transition, configuration
and terms in latex form.
.lvl1 The lower level of the transition (see .elvlc
file for ion)
.lvl2 The upper level for transition.
.tmax The temperature of maximum emission of the line
(i.e., the temperature at which the product of
the emissivity and the ion fraction has its
maximum). Rounded to nearest 0.1, and zero in case
the isothermal approximation is used.
.fwhm
.wvl Wavelength of the transition, in Angstroms.
.flag A flag, =-1 if the line has only theoretical energy
levels. Otherwise flag=0.
.int Intensity of line (with the abundance factor multiplied)
Save Spectrum (FITS): The entire information contained in the
IDL structure is stored in a FITS file.
SECTION 4:
Here, text information messages are printed.
INPUTS
None.
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
The font
OUTPUTS:
Many.
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
FONT the font to be used. Can be useful to customize the appearance of
the widget.
CALLS:
CH_SYNTHETIC, CH_LINE_LIST, CH_DRAWBOX, MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC, CH_XMENU_SEL,
plus many other CHIANTI and SolarSoft routines.
PROGRAMMING NOTES
Within CH_SS, there are several other routines which are:
OPLOT_LINES This overplots lines and a label on the displayed
spectrum.
SYN_CURSOR When the mouse is clicked when on the spectrum window,
this routine prints out the list of nearby lines and
their IDs in the text window.
CALC_SYN_SPECTRUM
Calculates line intensities with a call to CH_SYNTHETIC
PLOT_SYN_SPECTRUM This calls make_chianti_spec to produce the
intensity vs. wavelength plot.
SYN_MAIN_EVENT This handles the widget operations
SYN_WID This creates the widgets.
COMMON BLOCKS:
many
RESTRICTIONS:
SIDE EFFECTS:
EXAMPLE:
IDL> ch_ss
CATEGORY:
spectral synthesis.
WRITTEN :
Ver.1, 7-Nov-01, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ) and Peter Young (PRY)
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
V.2, 7-Nov-01, GDZ . Fixed a small bug (now the spectrum plot is always
plotted within the widget), and modified the option to add continua.
Changed the suggested names of the outputs.
Corrected a bug when creating an IDL save file with the spectrum, when
no line details are present.
V.3 28-Jan-02 GDZ
fixed a bug in the density text widget, added a few buttons
and options, including the effective area.
Added noprot, rphot, radtemp keywords to the call to ch_synthetic
V 4, 18-Apr-2002, GDZ
Added photoexcitation, changed IDL save files to FITS files,
V.5, 21-May-2002, GDZ
fixed a few small bugs: checking min_abund before calculating the
spectrum; checking the ioneq file when
restoring the structure; changed the status of
all lines; chnaged the font system.
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V.6, 15-July-2002, GDZ - New major revision.
Changed the chianti top directory (for Effective areas).
Changed Linear/Log button.
Rearranged the sizes of the buttons and added a special cursor to
highlight the area where details of the lines will be given. Works
only in linear scale.
Added quite a lot of new checks to avoid crashes and
fixed the problem with the zoom/unzoom/change units.
V.7, 2-Aug-02, GDZ
Modified the output labels on the plot, inside and on the axis.
Also modified a few minor things like the appearance of the Log T,EM
values.
Fixed a bug when creating the latex output.
Now it restores at the end previous colors and settings.
V.8, 8-Aug-02, GDZ
Changed the CHIANTI system variables. Fixed.
Also fixed a problem with the element ab. file.
V.9, 13-Aug-02, GDZ
Restored the correct use of ch_line_int, now only the lines in the
plot window are listed, and the ALL keyword is in use.
Now the correct xrange is loaded into COMMON when line int. are
restored. Now it checks if all ions were in the structure, when
restoring the line intensities, and flags the widget button accordingly.
Added a device,decomposed=0. to remove problems with colors.
Corrected the use of the DEM, IONEQ and ABUND pulldown menus,
avoiding conflicts between files in the working and CHIANTI
directory having the same name.
Added printing of references for ancillary files, and a check on the
element abundances vs. the elements present in the structure.
V.10, 7-Nov-03 GDZ
Modified format e8.2 to e9.2 for Windows compatibility.
Replaced f9.4 with f11.4 format for the wavelengths.
Some minor modifications to the widget.
Added extended details in the ascii output spectrum.
Added more explanations in the HELP buttons.
V.11, 22-Jul-2005 GDZ
-Added keV option and a few more extra checks.
V.12, 2-Aug-2005 GDZ
put RETAIN=2 in the main plotting window.
TO DO LIST:
Control the range of Angstroms when clicking
kev
Allow plots in intensities instead of intensities A-1
VERSION : V.12, 2-Aug-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
CH_SYNTHETIC
PURPOSE:
to calculate CHIANTI line intensities or G(T) and output an IDL structure.
PROCEDURE:
This routine calculates as default line intensities for a user-specified
differential emission measure and ionisation balance. The actual
creation of a synthetic spectrum (i.e., wavelength vs. intensity)
is performed by other routines - see CH_SS.PRO and
MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC.PRO.
Note that this routine does not include the element abundances
in the line intensities, as this will be performed by
make_chianti_spec. One of the reasons why element abundances are not
included in the line intensities calculation is so that it is easier
for the user to see how modifying abundances affects their spectra in
e.g. CH_SS.PRO.
The calculations are performed at constant pressure or
at constant density.
The routine can also output line intensities calculated with an
isothermal approximation.
If the isothermal approximation is not used, then the user will be asked
to select two files, that can either be in the
standard CHIANTI database or in the working directory.
These files are:
- an ionization fraction file
- a differential emission measure (DEM) file.
The routine can also output the contribution functions G(T) of the lines,
instead of the intensities, if the keyword GOFT is used. In this case,
only the ionization equilibrium file needs to be selected.
The G(T), or intensity per emission measure, is calculated as:
G=(hc/lambda_ij)*A_ji*(N_j(X^+m)/N(X^+m))*(N(X^+m)/N(X))/ N_e /(4.*!pi)
where A_ji is the A-value of the transition;
(N_j(X^+m)/N(X^+m)) is the population of the upper level,
calculated by solving the statistical equilibrium equations;
(N(X^+m)/N(X)) is the ionization equilibrium
N_e is the electron density.
unless /PHOTONS is set, in which case the (hc/lambda_ij) factor
is not included.
If not specified otherwise, with the use of the MASTERLIST or SNG_ION
keywords, then the standard masterlist of the ions, which has
all the ions in the current CHIANTI database, is used.
PROGRAMMING NOTES
The DEM is not assumed to be specified at 0.1 logT intervals (which
is how the ion fraction are specified). Thus this routine reads
in the DEM vs. logT information and then uses the IDL spline
function to tabulate the DEM over 0.1 logT intervals. The minimum
and maximum temperatures are those in the DEM file, rounded up to
the nearest 0.1. The new DEM function tabulated over 0.1 logT
intervals is contained in 'dem_int'.
For some of the dielectronic files, radiative decays that were in
the standard .wgfa file will also be present in the dielectronic
version of the .wgfa file. In these cases the line intensity
produced from the latter file needs to be ignored and so we have a
check in ch_synthetic to do this. An example is the 1-7 decay in
the ca_19.wgfa and ca_19d.wgfa files. In the latter case, the
model of the ion does not include electron excitation to level 7
and so the model for the 1-7 decay is incorrect, hence we ignore
it.
CATEGORY:
spectral synthesis.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
IDL> ch_synthetic,wmin,wmax, output=output, pressure=pressure,$
[MODEL_FILE=MODEL_FILE, err_msg=err_msg, msg=msg, $
density=density,all=all,sngl_ion=sngl_ion, $
photons=photons, masterlist=masterlist, $
save_file=save_file , verbose=verbose, $
logt_isothermal=logt_isothermal,$
logem_isothermal=logem_isothermal,$
goft=goft, ioneq_name=ioneq_name, dem_name=dem_name,$
noprot=noprot, rphot=rphot, radtemp=radtemp, progress=progress ]
INPUTS:
Wmin: minimum of desired wavelength range in Angstroms
Wmax: maximum of desired wavelength range in Angstroms
PRESSURE: pressure in emitting region (Pe, cm^-3 K).
Only a single value is accepted, and the calculation is
performed at constant pressure.
OPTIONAL INPUTS :
DENSITY: density in emitting region (Ne, cm^-3).
Only a single value is accepted, and the calculation is
performed at constant density, unless LOGT_ISOTHERMAL is
defined. In this case, DENSITY can be an array of values, but
has to have the same number of elements as LOGT_ISOTHERMAL.
MODEL_FILE Full path of the (Te,Ne) file if defined.
This file should have two columns, one with the Te (K)
values, and one with the Ne (cm^-3) values. If these
values are not sorted in ascending order of Te, the
routine does sort them.
SNGL_ION: specifies a single ion (e.g. SNGL_ION='Fe_10' to include
only Fe X lines) or an array (e.g. SNGL_ION=['Fe_10','Fe_11']
to include only Fe X and Fe XI lines) of ions to be used
instead of the complete set of ions specified in
!xuvtop/masterlist/masterlist.ions
MASTERLIST: string of a specific masterlist file (full path).
If defined as a keyword (i.e. MASTERLIST=1 or /MASTERLIST)
then a widget allows the user to select a user-defined
masterlist file. Shortcut for SNGL_ION.
IONEQ_NAME: Name of the ionization equilization name to use. If not
passed, then the user is prompted for it.
DEM_NAME: Name of the DEM file to used. If not passed, then the user
is prompted for it.
LOGT_ISOTHERMAL
Array of logarithmic temperatures.
If defined, the emissivities are calculated with an
isothermal approximation. The values are sorted in ascending
order.
LOGEM_ISOTHERMAL
Array of logarithmic emission measures.
If defined, the emissivities are calculated with an
isothermal approximation. The values are sorted in ascending
order. If LOGT_ISOTHERMAL is specified without
LOGEM_ISOTHERMAL then the emission measures are set to 1
(logem_isothermal=0).
RADTEMP The blackbody radiation field temperature (default 6000 K).
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
OUTPUTS:
OUTPUT: The name of the structure containing the line intensities and
details.
The tags of the structure are:
.lines A structure containing information about the lines.
Its size is the number of lines in the spectrum. The
tags are:
.iz The atomic number of the elements (e.g., 26=Fe)
.ion The ionisation stage (e.g., 13=XIII)
.snote The identification of the ion (e.g., 'Fe XXIV d')
.ident The identification of the transition, configuration
and terms in text form.
.ident_latex
The identification of the transition, configuration
and terms in latex form.
.lvl1 The lower level of the transition (see .elvlc
file for ion)
.lvl2 The upper level for transition.
.tmax The temperature of maximum emission of the line.
If the G(T) are output, tmax is the maximum of G(T).
If the isothermal approximation is used tmax=0.
If a DEM is used, tmax is the maximum of the
emissivity that includes the product of the ion
fraction and the DEM.
Rounded to nearest 0.1
.wvl Wavelength of the transition, in Angstroms.
.flag A flag, =-1 if the line has only theoretical energy
levels. Otherwise flag=0.
.int Intensity of line (erg/cm2/s/sr or phot/cm2/s/sr),
divided by the element abundance (exclusive with .goft).
.goft The G(T) of the line (optional /exclusive with .int).
.ioneq_name The ion balance file used (full path).
.ioneq_logt The Log10 T values associated.
.ioneq_ref The references.
.dem_name The differential emission measure file eventually used
(full path).
.dem The Log10 DEM values
.dem_logt The Log10 T values associated.
.dem_ref The references.
.model_name A string indicating the model used:
1- Constant density
2- Constant pressure
3- Function (Te,Ne)
.model_file Full path of the (Te,Ne) file if defined. Null string otherwise.
.model_ne the Ne value(s).
- a scalar if 'Constant density' is selected.
- an array if 'Function' is selected.
- 0. if constant pressure is selected.
.model_pe the Pe value.
- a scalar if constant pressure is selected.
- 0. if 'Constant density' is selected.
- an array=density*temperature if 'Function' is selected.
.model_te the Te values if 'Function' is selected. Otherwise 0.
.wvl_units The wavelength units.
.wvl_limits The wavelength limits specified by the user.
.int_units The intensity units.
1) If LOGT_ISOTHERMAL is defined, we have two cases:
a) LOGEM_ISOTHERMAL is not defined, and is therefore
assumed to be 0 (EM=1). In this case, units are
'photons cm+3 sr-1 s-1' or 'erg cm+3 sr-1 s-1'.
b) LOGEM_ISOTHERMAL is defined. In this case, units are
'photons cm-2 sr-1 s-1' or 'erg cm-2 sr-1 s-1'.
2) If LOGT_ISOTHERMAL is not defined, we have two cases:
a) intensities are calculated. In this case, units are
'photons cm-2 sr-1 s-1' or 'erg cm-2 sr-1 s-1'.
b) Contribution functions G(T) are calculated. In this
case, units are
'photons cm+3 sr-1 s-1' or 'erg cm+3 sr-1 s-1'.
.logt_isothermal
The Log10(T) values used.
.logem_isothermal
The Log10(EM) values used.
.date The date and time when the structure was created.
.version The version number of the CHIANTI database used.
.add_protons
A flag (0/1) to indicate whether proton data were used (1)
or not (0) to calculate the level population.
.photoexcitation
A flag (0/1) to indicate if photoexcitation was included (1)
or not (0).
.radtemp
The blackbody radiation field temperature used (if
photoexcitation was included).
.rphot
Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units
(if photoexcitation was included).
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
SAVE_FILE: If defined, then an IDL save file is created, with the output
structure.
GOFT: If set, the G(T) of the lines are calculated, and put in
the output structure, instead of the line intensities.
Units are 'photons cm+3 sr-1 s-1' or 'erg cm+3 sr-1 s-1'
KEYWORDS:
ALL: if set, then all lines are included. This means that lines for
which only an approximate wavelength is known,
denoted by a negative wavelength value in the .wgfa file, are
included. These are the lines for which there are no observed
energy levels.
PHOTONS: The output intensities will be in photons instead of
ergs.
VERBOSE: If set, the routine will list each ion it is looking at,
and how many lines from each ion it is including in the
spectrum.
GOFT: If set, the G(T) of the lines are calculated, and put in
the output structure, instead of the line intensities.
Units are 'photons cm+3 sr-1 s-1' or 'erg cm+3 sr-1 s-1'
NOPROT Switch off the inclusion of proton rates in the level
balance (default).
PROGRESS If set, a widget appears, showing the progress of the
calculation and allowing the user to halt the calculation.
NO_SUM_INT Prevents the summing of intensities over temperature.
Only works in conjunction with the LOGT_ISOTHERMAL
option, and is implemented in order to work the
ISOTHERMAL routine. The .INT tag in OUT.LINES becomes
an array with the same number of elements as
LOGT_ISOTHERMAL, corresponding to the intensities at
each temperature.
CALLS: CH_GET_FILE
many CHIANTI standard routines, including:
READ_IONEQ, READ_DEM, READ_MASTERLIST, ION2SPECTROSCOPIC,
ZION2FILENAME, READ_WGFA,READ_ELVLC,READ_SPLUPS,POP_SOLVER,
DESCALE_UPS, CONVERT_TERMS.
CONVERT_TERMS uses some standard SolarSoft routines:
REPSTR, STR_INDEX, DATATYPE,
VALID_NUM, DELVARX, INFO_PROGRESS, SAVEGEN
COMMON BLOCKS:
wgfa, wvl,gf,a_value
upsilon,splstr
elvlc,l1a,term,conf,ss,ll,jj,ecm,eryd,ecmth,erydth,eref
elements,abund,abund_ref,ioneq,ioneq_logt,ioneq_ref
radiative, radt, dilute
proton, pstr
ionrec,rec_rate,ci_rate,temp_ionrec,luprec,lupci,status
RESTRICTIONS:
SIDE EFFECTS:
CATEGORY:
spectral synthesis.
EXAMPLE:
This routine can be called in this way:
IDL> ch_synthetic,5.,10., output=structure, pressure=1.e+15
To make use of the output structure, use MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC or CH_SS
PREV. HIST. :
Based on synthetic.pro, written by Ken Dere
WRITTEN :
Ver.1, 22-Jun-00, Peter Young (PRY) and Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Ver.1, 22-Jun-00, Peter Young and Giulio Del Zanna
Ver.2, 25-Jul-00, PRY
Removed /all keyword; make_chianti_spec can be
used to filter out negative wavelengths.
Added flabel tag to output in order to pick out
dielectronic recombination lines.
Ver.3, 4-Oct-00, PRY
Replaced /all keyword.
Corrected bug when .wgfa files contain two A-values
for the same transition.
Ver.4, 5-Oct-00, PRY
Corrected bug that gave rise to lines from the same
transition when the dielectronic file existed.
V.5, 11-Oct-2000, GDZ
eliminate the abundance call; reinstate the /masterlist keyword;
added the tag ident_latex to have the identification in
late-style format; added a tag flag=-1 for the unobserved lines,
and =0 otherwise; reinstated all wavelengths > 0. ;
added the calculation of the G(T);
added a few other tags in the output, and various checks and
comments.
V.6 15-Oct-2000 ,GDZ
Replaced calls to solarsoft routines to standard IDL ones.
Corrected an error in the output creation, in relation to the
isothermal case. Added isothermal in the output. added checks to
the wavelengths. Default output name is TRANSITIONS. changed
const_net and added const_net_value + a few other things.
v.7, 27-Nov-2000, GDZ. Corrected an error in the calculation of the
G(T).
Version 8, 5-Dec-2000, GDZ, DAMTP. Fixed a bug when checking the
values in the .splups files.
V. 9, GDZ, 10-Apr-2001, corrected another error in the G(T) calc.
V. 10, GDZ, 30-Oct-2001 added CHIANTI Version number, changed isothermal
to logt_isothermal and added logem_isothermal to the output.
Removed the use of log T values, and the calculation.
Added err_msg, a text string with an error message.
Version 11, 8-Nov-01, GDZ
Changed the MASTERLIST keyword. Allowed double use, as a keyword
and as a string.
Version 12, 18-Nov-01, Peter Young
Added /NOPROT, RPHOT and RADTEMP keywords; changed upsilon
common block.
Version 13, 29-Apr-02, GDZ
Added no_protons, photoexcitation, rphot, radtemp
tags into the output structure.
Revised Header. Added the PROGRESS widget.
Added a check if the ion is present in the Ion. Frac. file.
Added informative MSG keyword.
Now uses savegen.pro to save the structure.
V. 14, 28-May-2002, GDZ:
generalize directory concatenation to work for Unix, Windows
and VMS.
modified tags:
limits -> wvl_limits
ioneq_t -> ioneq_logt
wvlunits -> wvl_units
intunits -> int_units
time --> date
no_protons -> add_protons
dem_t -> dem_logt
const_nte -> model_name
const_nte_value -> model_ne, model_pe, model_te
removed from the main STR: .ioneq ctemp
removed from the LINES STR: fwhm flabel
Added model_file input for model Ne(T). Had to considerably
modify the routine.
V. 15, 16-Jul-2002, Peter Young
Added keyword /NO_SUM_INT.
V. 16, 22-Jul-2002, Peter Young
Corrected a bug related to /NO_SUM_INT; logt_isothermal
can now be specified without logem_isothermal.
V. 17, 23-July-2002, GDZ
Modified a few checks on the input. Also, now it prints the
error message whenever the program aborts
V.18, 2-Aug-02, GDZ
Replaced all DBLARR and DOUBLE calls with floats.
Added a comment at the end of the routine when it finishes.
V.19, 8-Aug-02, GDZ
Added more error info. Changed the use of the DENSITY
keyword. It is possible to input an array of values if
LOGT_ISOTHERMAL is defined.
V. 20, 17-Sep-02, GDZ
Corrected a bug: the functional (T,N) form
is now only accepted if DENSITY is an array with at least two
values.
V. 21, 19-Sep-02, GDZ
Corrected the definition of the UNITS in case LOGT_ISOTHERMAL
is defined.
V. 22, 19-Aug-03, Peter Young
when logem_isothermal is input, the derived EM is now a
DOUBLE array rather than FLOAT, preventing infinities when
logem_isothermal values are large.
V. 23, 4-Oct-2003, GDZ
modified the input to POP_SOLVER, now it is dealt with an
input structure.
V.24, 10-Oct-2003, K.Dere
added modifications from K.Dere, regarding the satellite
lines.
V 25, 3-Nov-2003, GDZ
Added GROUP keyword, and modified so the progress widget can
be stopped within IDL Windows.
V 26, 17-Apr-2004, Enrico Landi (EL)
Added the recombination/ionization population processes.
V.27, 13-Apr-2005, EL
Replaced the main loop to calculate individual line intensities
with operations among arrays, to speed the whole program in case
of large numbers of lines.
VERSION : 27, 13-Apr-2004
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
CH_WRITE_FITS
PURPOSE:
Write standard FITS binary table data from CHIANTI input structure.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
CH_WRITE_FITS, Input, Filename
INPUTS:
Input = Structure to be written to FITS file.
OUTPUTS:
Filename = String containing the name of the file to be written.
CH_WRITE_FITS creates two binary table extension in a single
FITS file. The second one is appended as a new extension.
OPTIONAL INPUTS: Header COMMENTS.
KEYWORDS:
head1, head2
Additional COMMENTS to be added at the bottom of the two binary tables.
NOTES:
Any existing FITS file can be over-written or not.
Use CH_READ_FITS to convert the FITS file back into a structure.
CALLS:
FXPAR(), FXADDPAR, IS_IEEE_BIG(), HOST_TO_IEEE, DIALOG_MESSAGE
COMMON BLOCKS: none.
RESTRICTIONS:
(1) Limited to 127 columns in tables by IDL structure limits.
(2) String columns with all columns of zero length crash the
program
(3) The input structure has to be of the type TRANSITIONS.
PREV. HIST. :
The subroutines in this procedure are extracted without modifications from
the MWRFITS.PRO routine, written by T. McGlynn Version 0.95 2000-11-06
and present in the ASTRON library (in SolarSoft under /gen/idl_libs/astron/).
EXAMPLE:
ch_write_fits, transitions , 'test.fits'
WRITTEN :
Ver.1, 22-May-02 Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
MODIfICATION HISTORY:
VERSION : 1, 22-May-02, GDZ
NAME:
CH_XMENU_SEL
PURPOSE:
Allow user to select a set of items from a list. Widget equivalent
of WMENU_SEL
CALLING SEQUENCE:
ss = ch_xmenu_sel(array)
ss = ch_xmenu_sel(array, /one)
ss = ch_xmenu_sel(array, /fixed) - use fixed font (keep column alignement)
INPUTS:
ARRAY A string or string array of values to be displayed for
selection
OPTIONAL KEYWORD INPUT:
ONE If set then only one button may be turned on at a time.
TIT The title of the widget
GROUP The parent widget id (so that if the parent widget exits,
this widget is destroyed too)
FIXED_FONT If set, use fixed font (keep columns aligned)
SIZE_FONT Size of (fixed) font to use - default=15 (implies /FIXED)
NLINES How many lines to display. Default is 20
OUTPUTS:
The result returns the select indices of the array ARRAY.
RESTRICTIONS:
Must have widgets available.
HISTORY:
Written 30-Jan-95 by M.Morrison using Elaine Einfalt
YO_TAPE_WIDG as a starting point
10-Jul-96 (MDM) - Ajustment to make the output scaler if it
is a single item
11-nov-96 (SLF) - add FIXED_FONT and SIZE_FONT keywords
15-Apr-97 (MDM) - Re-added the 9-Jan-97 (MDM) modification
to merge with 11-Nov-96 version
9-Jan-97 (MDM) - Added NLINES option
22-Jul-97 (MDM) - Added call to WMENU_SEL if the device is
not X (so that terminal prompting is
enabled.
9-may-2001 Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
added keywords text and include, renamed ch_xmenu_sel
V.7, 15-Aug-2002 GDZ
Modified a few cosmetics, and add the option to have a TEXT string
array to add as a comment in the top widget.
V.8 30 Jan 2002, GDZ
Now it returns an ordered list, according to how the lines where
selected. It works only the first time the routine is called.
V.9, 30-Jun-2003, Peter Young
Added call to CHIANTI_FONT to correct problem with fixed font in
Windows.
V.10 3-Oct-2003, GDZ
inserted the ,/MODAL keyword within the main widget, for
compatibility with IDL v.5.4
VERSION : 10 3-Oct-2003
NAME
CI_REC_INTERP()
PROJECT
CHIANTI
EXPLANATION
For including ionization and recombination into the level balance, it's
necessary to interpolate the data stored in the CHIANTI files and, in
addition, perform extrapolation to lower or higher temperatures.
This routine performs the interpolation and extrapolation for general
input arrays.
INPUTS
TEMP Temperature at which rate required. Units: K. Must be a scalar
quantity.
RATE_TEMP Temperatures at which RATE is tabulated. Input as Log (base 10)
values.
RATE The rate coefficient, tabulated at temperatures RATE_TEMP.
KEYWORDS
EXTRAP_ABOVE Extrapolation to higher temperatures will only take place
if this keyword is set.
EXTRAP_BELOW Extrapolation to lower temperatures will only take place
if this keyword is set.
OUTPUT
The value of the rate coefficient at the temperature TEMP. If no data is
available at the specified temperature then a value of zero is returned.
HISTORY
Ver.1, 29-Jun-2005, Peter Young
adapted from original code by Enrico Landi
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME:
CONF2N
PURPOSE:
Extract the highest principal quantum number from the configuration
CALLING SEQUENCE:
CONF2N,conf,n
INPUTS:
Conf: the configuration returned from read_elvlc_direct
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
None
OUTPUTS:
N: the principal quantum number
EXAMPLE:
> conf2n,'2s2.3p 2P1.0',n
> print,n
> 3
CALLS:
None
RESTRICTIONS
If the principal quantum number is 10 or greater, it will not be
picked up.
If the configurations are written in upper case (e.g., 3S2.3P2),
then the principal quantum numbers will not be picked up (a value
of 0 will be returned).
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Ver.1, April-2000, Ken Dere
Ver.2, 17-Oct-2000, Peter Young
removed call to str_index
PROJECT: CHIANTI
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME:
convertname
PURPOSE:
Ion names as character strings are converted into
numerical values (note c_2 is C II or C^+1
in spectroscopic or atomic notation)
CATEGORY:
naming utility
CALLING SEQUENCE:
CONVERTNAME,Name,Iz,Ion
INPUTS:
Name: such as 'c_2'
OUTPUTS:
Iz: nuclear charge Z (6 for 'c_2', the equivalent of C II)
Ion: ionization stage: (2 for 'c_2')
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS
DIELECTRONIC Set to 1 if NAME has a 'd' appended to it
(indicating dielectronic recombination data) else
set to 0
EXAMPLE:
> convertname,'c_2',iz,ion
> print,iz,ion
> 6,2
> convertname,'o_6d',iz,ion
> print,iz,ion
> 8,6
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1996: Version 2.0
October 1999: Version 3. by kpd
Ver.4, 11-Dec-01, Peter Young
Revised routine, removing ch_repstr call.
Added DIELECTRONIC optional output.
PROJECT : CHIANTI
CHIANTI http://wwwsolar.nrl.navy.mil/chianti.html
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME : CONVERT_TERMS
PURPOSE :
to convert the transition information into readable formats.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
IDL>this_design = convert_terms(l1, l2, result_latex =result_latex)
PROCEDURE:
This function is used to convert the transition information into
readable formats, including spaces and calulating the J values.
The process is quite complex since the notation of the level
designations in the CHIANTI files is not standard.
A very useful latex-style output is also created.
INPUTS :
l1: the index of the lower level
l2: the index of the upper level
the rest of the input info is taken from the COMMON.
OPT. INPUTS : none
OUTPUTS :
a string with the transition information.
OPT. OUTPUTS:
a string with the transition information in latex format.
KEYWORDS :
RESULT_LATEX: the name of an output string.
CALLS :
CONVERT_CONFIG (included here) and other SolarSoft routines.
COMMON BLOCKS: elvlc,l1a,term,conf,ss,ll,jj,ecm,eryd,ecmth,erydth,eref
from here, all the information needed is taken.
RESTRICTIONS: It will not convert every case.
SIDE EFFECTS: None known yet.
EXAMPLES :
this_design = convert_terms(l1, l2, result_latex =result_latex)
CATEGORY :
spectral synthesis.
PREV. HIST. :
parts of the function convert_terms are derived from the CHIANTI
routines.
WRITTEN :
Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ), 10-Oct-2000
DAMTP (University of Cambridge, UK)
MODIFIED : Version 1, GDZ 10-Oct-2000
Version 2, GDZ 10-Oct-2001
Uses standard SolarSoft routines.
V. 3, 18-Sep-2002, GDZ
Fixed a bug with the jvalue
VERSION : 3, 18-Sep-2002
PROJECT : CHIANTI
CHIANTI http://wwwsolar.nrl.navy.mil/chianti.html
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME : CONVERT_TERMS_ALL
PURPOSE :
to convert level information into readable formats for all the levels
of an ion.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
IDL>convert_terms_all, res_ascii, res_latex
PROCEDURE:
This function is used to convert the level information into
readable formats, including spaces and calculating the J values.
A very useful latex-style output is also created.
It has been adapted to manage all the levels of a given ion
at once from the original routine CONVERT_TERMS.PRO.
INPUTS : all the input info is taken from the COMMON.
OPT. INPUTS : none
OUTPUTS :
RES_ASCII: a string array with the transition information in ASCII format.
RES_LATEX: a string array with the transition information in LATEX format.
CALLS :
CONVERT_CONFIG (included here) and other SolarSoft routines.
COMMON BLOCKS: elvlc,l1a,term,conf,ss,ll,jj,ecm,eryd,ecmth,erydth,eref
from here, all the information needed is taken.
RESTRICTIONS: It will not convert every case.
SIDE EFFECTS: None known yet.
EXAMPLES :
convert_terms_all, res_ascii, res_latex
CATEGORY :
spectral synthesis.
PREV. HIST. :
convert_terms_all has been derived from the existing CHIANTI
routine CONVERT_TERMS.
WRITTEN :
Enrico Landi, 11-Apr-2005
Naval Research Laboratory
MODIFIED : Version 1, EL 11-Apr-2005
VERSION : 1, 11-Apr-2005
NAME
CORRECT_POPS()
PROJECT
CHIANTI
EXPLANATION
Corrects CHIANTI level populations with the ionization and recombination
rate coefficients
INPUTS
PP The level populations that need to be corrected.
T Temperature at which calculation is performed. Units: K.
XNE Electron density at which calculation is performed. Units: cm^-3
IONREC Structure with the following tags
.rec Effective recomb. rate coefficients
.ci Effective ionization rate coefficients
.temp Temperatures at which rates are tabulated
.lev_up_rec Levels to which recombination takes place
.lev_up_ci Levels to which ionization takes place
.status Either +1 (ion/rec data exists) or -1 (dosen't exist)
.ioneq Ion fractions of the 3 ions
CC 2D matrix produced by MATRIX_SOLVER that contains the rate
coefficents from the standard CHIANTI processes.
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS
CRATE A 1D array of same size as POP containing the collisional
ionization rate coefficients (units: cm^3 s^-1).
RECRATE A 1D array of same size as POP containing the recombination
rate coefficients (units: cm^3 s^-1).
CORRECTION A 1D array of same size as POP containing the correction
factors for each level.
FRAC_LOW The ratio of the current ionization fraction to the fraction
of the one lower ion (i.e., less ionized).
FRAC_HIGH The ratio of the current ionization fraction to the fraction
of the one higher ion (i.e., more ionized).
CALLS
ION_FRAC_INTERP(), CI_REC_INTERP()
HISTORY
Ver.1, 10-Jun-2005, Peter Young
Taken original code of Enrico Landi and inserted it into a separate
routine.
Ver.2, 16-Aug-2005, Peter Young
Changed total_exc to be dblarr in order to prevent NaNs.
Project : SOHO - CDS
Name : DEM_FIT
Purpose : Calculates the Differential Emission Measure DEM(T) using
a set of values in common with other routines.
Category : diagnostic analysis
Explanation : This routine (called by CHIANTI_DEM.PRO) performs
a series of iterations in order to
find the DEM that minimize the chi^2. The values in common
with CHIANTI_DEM.PRO are used.
As a least squares fit to a non-linear
function, see pages 237-239, Bevington, Data Reduction and Error
Analysis for the Physical Sciences.
Use : IDL> dem_fit,y,chisqr
It has to be noted that a general use of this routine
is limited.
Inputs : the values stored in common.
Opt. Inputs : None
Outputs : log_dem_mesh,y ,chisqr
i.e. the DEM mesh values, the intensity values as resulted
from this model DEM, and the chi^2.
Opt. Outputs: None
Keywords :
FLAMBDA: the initial value of the parameter flambda.
SCALE: the initial value of the parameter scale, that
controls the steps of the iteration.
N_ITER:
optional.It is the number of iterations of the fitting routine.
If not set, a default value of 20 is assumed.
Changing this value alone might not affect the fit, since
also the value of DCHISQ_MIN is checked during the fit.
DCHISQ_M:
optional. If not set, a default value of DCHISQ_MIN=1.e-5
is assumed. For each iteration, the CHISQ and it's variation
are calculated. As long as the iteration achieves an
improvement in CHISQ greater than DCHISQ_MIN , another
iteration will be performed.
FAILED: If the fit fails,the routine returns and flags FAILED=1
QUIET:
optional. Set to avoid various messages
Calls : DEM_DERIV, DEM_FUNCTN, DEM_CHISQR
Common :
obs, obs_int,obs_sig,n_obs
dem, d_dem_temp,dem_temp,log_dem_temp,log_t_mesh,log_dem_mesh
contr,ch_tot_contr
Restrictions: Not always the fit is successful.
Side effects: None known.
Prev. Hist. :
Written by Ken Dere (NRL) as part of the CHIANTI package
in collaboration with Brunella Monsignori Fossi, Enrico Landi
(Arcetri Observatory, Florence), Helen Mason and Peter Young
(DAMTP, Cambridge Univ.). Incorporated into the CDS software.
Written :
Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ),
UCLAN (University of Central Lancashire, UK) 5 November 1997
HISTORY:
Ver 1, GDZ 5-Nov-97
Ver 2, EL 6-Apr-05
Renamed the variable "deriv" to "deriv1" to avoid conflicts
with an IDL routine with the same name.
Version : 2.0 6 April 2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
DENSITY_RATIOS
PURPOSE:
to calculate line intensity ratios as a function of electron density
CATEGORY:
scientific analysis
CALLING SEQUENCE:
DENSITY_RATIOS,Ion,Wmin,Wmax,Dmin,Dmax,Density,Ratio,Description
INPUTS:
Ion: the CHIANTI style name of the ion, i.e., 'c_5' for C V
wmin: minimum of the wavelength range of interest in Angstroms
wmax: maximum of the wavelength range of interest in Angstroms
dmin: log10 of the minimum desired density (8. = 10^8 cm^(-3) )
dmax: log10 of the maximum desired density range
INTERACTIVE INPUTS:
Must select the line for the numerator and denominator
It is possible to select multiple lines to be summed
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
OUTFILE: the (optional) name of the output ascii file where a
listing of the line ratio intensity as a function of
density is saved. For example, outfile='den_rat.lis'
PSFILE: the (optional) name of the output postscript file
where a plot of the choses density sensitive line
ratio is saved. For example, psfile='den_rat.ps'
TEMP: to specify the temperature, otherwise the temperature at
the peak
of the ionization equilibrium is used. For example,
temp=1.e+6
/PHOTONS: if set, the ratio will be in photon units, as opposed
to ergs
RADTEMP Specify background radiation temperature (default: 6000 K)
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
VERBOSE To print out information about the lines.
OUTPUTS:
Density: an array of the density values for which the selected
intensity ratio calculated
Ratio: an array of line intensity ratios
Description: a string describing the transitions selected
Plots the intensity ratio of the selected line as a function of density
COMMON BLOCKS:
None.
CALLS
EMISS_CALC, ION2SPECTROSCOPIC, CONVERTNAME, READ_IONEQ,
CH_XMENU_SEL
EXAMPLE:
density_ratios,'o_5',1000.,1500.,8.,13.,den,rat,desc
choose the ratio of 1371.294 to 1218.393
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1996: Version 2.0
May 28, 1996: Ken Dere added psfile keyword/option
Sept 1996: modified to work with VMS
and added keyword TEMP, Ken Dere
Feb. 2000: Modified for Version 3, K. Dere
14-Jul-2000 Peter Young, now calls pop_solver
26-Sep-2001 Modified for 9-point splines and proton rates;
added radtemp and rphot keywords for photoexcitation.
20-Nov-2001 Routine now calls emiss_calc to get emissivities.
V.9, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V.10, 1-Aug-02 GDZ
Changed all the formats.
V.11, 06-Aug-02 GDZ
Changed the use of CHIANTI system variables.
V.12, 15-Aug-02, GDZ
Major revision:
-Added the keyword VERBOSE, to avoid printing out long lists of lines.
-Removed the call to ch_xselect_s, that did not work for long lists.
-Added a '*' in the line lists, to identify 'unobserved' lines.
-Replaced the commands to create PS file, to make it
cross-platform compatible.
-Added a large number of cosmetics, mainly lables to the axes and
titles, that were missing.
-Removed plotting in windows already present.
-Added the CHIANTI version number in the outputs.
V.13, 3-Nov-03 GDZ
Modified format e8.2 to e9.2 for Windows compatibility.
VERSION : 13, 3-Nov-03
PROJECT
CHIANTI http://wwwsolar.nrl.navy.mil/chianti.html
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME
dens_plotter
PURPOSE:
A widget-based routine to allow the analysis of density sensitive
ratios. **** See RATIO_PLOTTER for details. *****
CALLING SEQUENCE:
IDL> dens_plotter, name,$
EM, PATH=PATH, NOPROT=NOPROT, $
IONEQ_FILE=IONEQ_FILE, ABUND_FILE=ABUND_FILE
INPUTS:
The ion name (e.g. 'si_3' for Si III)
OPTIONAL INPUTS : none
OUTPUTS:
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
EM: Save the displayed emissivities to structure EM.
**** See RATIO_PLOTTER for details. *****
KEYWORDS:
PATH: Data in the CHIANTI format that is not in the CHIANTI
database can be read by specifying the directory in which
it lies through PATH.
ABUND_FILE The name of a CHIANTI abundance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio. Default is
!abund_file.
IONEQ_FILE The name of a CHIANTI ion balance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio and evaluating
the T_max of the ion. Default is !ioneq_file.
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
CALLS: CONVERTNAME RATIO_PLOTTER
COMMON BLOCKS: none
RESTRICTIONS:
SIDE EFFECTS:
CATEGORY:
spectral synthesis.
EXAMPLE:
IDL> dens_plotter, 'si_9'
WRITTEN :
Ver.1, 18-Apr-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ) written as a wrapper
routine to call RATIO_PLOTTER.
MODIFIED: V.2, 2-Aug-2005, GDZ
Now the routine handles the dielectronic case
VERSION : 2, 2-Aug-2005
EXPLANATION
This routine descales all types of spline fits into upsilons or
rates, i.e., it does both electron upsilons and proton rates,
and both 5-point and 10-point splines. In addition it can
simultaneously descale several temperatures at once.
INPUTS
TEMP Temperature(s), K.
SPLSTR Structure output by read_splups.
INDEX Index of structure.
OUTPUTS
UPS Upsilon value(s) at temperature(s) TEMP.
EXAMPLES
read_splups,splupsfile,splstr
descale_all,[1.e6,2.e6],splstr,5,ups
print,ups
HISTORY
Ver.1, 15-Mar-01, Peter Young
adapted from Ken Dere's descale_ups.pro.
Ver.2, 12-Nov-01, Peter Young
added type 6 transitions (for protons)
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME:
DESCALE_UPS
PURPOSE:
convert from Burgess-Tully scaling spline fits to Upsilons
CATEGORY:
science.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
DESCALE_UPS,Index,Jndex,xt,upsilion
INPUTS:
Index: index of lower energy level (lowest level is 1)
Jndex: index of upper energy level (lowest level is 1)
xt: scaled temperature
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
None:
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
None:
OUTPUTS:
Upsilon: the Maxwellian averaged collision strength
COMMON BLOCKS:
common elvlc,l1a,term,conf,ss,ll,jj,ecm,eryd,ecmth,erydth,eref
common wgfa, wvl,gf,a_value
common upsilon,t_type,c_ups,splups
PROCEDURE:
see Burgess and Tully, 1992, Astron and Astrophys, 254, 436.
EXAMPLE:
;
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1996: Version 2.0
December 1998: Include transition type 5 (kpd)
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME: EMISS_CALC()
PURPOSE:
To compute the emissivities of all lines of a specified ion over
given ranges of temperature and density.
CATEGORY:
Scientific analysis
EXPLANATION:
This routine calculates:
hc
-- * N_j * A_ji
lamb
where hc = 1.986 * 10^-8 erg AA, lamb is in angstroms, N_j is the
fraction of ions in the upper emitting level j, and A_ji is the
radiative decay rate for the transition.
The emissivities are stored in a structure called EMISS that also
holds the wavelength of the transition, the level numbers i and j
and also a 'flag', which is set to -1 if the wavelength is negative.
The temperature and density ranges can be specified directly using
the TEMP and DENS keywords. Setting TMAX to the log T_max of the
ion, gives emissivities for 3 temperatures: log T_max +- 0.15.
If DENS is not set, then it is set to 8 to 12 in 0.5 dex intervals.
STDENS allows the start density (of 8) to be changed to some other
value; ND allows the number of densities to be varied (default 9);
DINT allows the density interval to be varied (default 0.5).
CALLING SEQUENCE:
EMISS=EMISS_CALC (IZ, ION, [ TEMP=TEMP, DENS=DENS, RADT=RADT, $
DIL=DIL, PATH=PATH, /NO_DE, /PROTON, $
QUIET, PRESSURE=PRESSURE)
EXAMPLES:
EMISS=EMISS_CALC(26,13)
EMISS=EMISS_CALC(26,13,temp=[6.2],dens=findgen(5)+8)
EMISS=EMISS_CALC(26,13,temp=findgen(11)/100.+5.5,press=10.^15)
INPUTS:
IZ The atomic number of the ion
ION The spectroscopic number of the ion (e.g., 12 = XII)
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
TEMP Direct specification of the temperature range (log T)
DENS Direct specification of the density range (log Ne)
RADTEMP Specify background radiation temperature (default: 6000 K)
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
PATH If specified, the routine will look for the atomic data in
the PATH directory, rather than in the CHIANTI database
PRESSURE If a temperature array is given, and PRESSURE set,
then the emissivities will be evaluated at the
specified temperatures, but for densities =
pressure/temperature. If DENS is set, then it will
be ignored. The pressure is assumed to be in units
K * cm^-3.
ABUND_FILE The name of a CHIANTI abundance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio. Default is
!abund_file.
IONEQ_FILE The name of a CHIANTI ion balance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio and evaluating
the T_max of the ion. Default is !ioneq_file.
SUM_MWL_COEFFS An array of coefficients of the same length as
the array of temperatures. Electron and proton rate
coefficients will be calculated at each temperature
and then a weighted sum of the coefficients is
performed using SUM_MWL_COEFFS. This allows
non-Maxwellian energy distributions to be
incorporated into the level balance equations.
This keyword is not compatible with the PRESSURE
keyword.
RADFUNC The name of a user-defined function that will generate
a radiation spectrum as a function of temperature.
This radiation field will replace the black-body that
is assumed when using the RADTEMP keyword in the call
to pop_solver.
KEYWORDS:
NO_DE Drops the hc/lambda factor in the computation of the
emissivities. Useful for emission measure analyses involving
photon fluxes
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
QUIET If set, don't list the temperatures and densities at which
the emissivities are caculated.
DIEL If the dielectronic recombination files exist for the ion,
then these are used to derive the emissivities.
NO_SETUP If emiss_calc is called from a routine where the ELEMENTS
common block has already been set up, then this keyword
stops emiss_calc loading up the common block
OUTPUT:
The structure that is output has the following tags:
.ion_name string; contains ion name, e.g., 'Fe XIII'
.lambda float; contains wavelength
.level1 integer; contains lower level of transition
.lvl1_desc string; gives config. and term of lower level
.level2 integer; contains upper level of transition
.lvl2_desc string; gives config. and term of upper level
.flag integer; a flag to mark particular transitions
.em fltarr(nt,nd); contains emissivities at particular
temperatures and densities.
PROGRAMMING NOTES:
Transitions where only theoretical energies are available for at
least one of the two levels are assigned negative wavelengths in
the .wgfa file. With emiss_calc, the wavelength is set to be
positive, but emiss.flag is set to -1 for that transition, so
that other routines can keep track of the theoretical wavelengths.
COMMON BLOCKS:
ELVLC, WGFA, UPSILON, RADIATIVE, PROTON, ELEMENTS, IONREC
CALLS:
SETUP_ION, POP_SOLVER
ZION2FILENAME, ZION2SPECTROSCOPIC
READ_PROT, PROTON_DENS
HISTORY:
Ver 1, PRY 28-Jun-97
Ver 2, PRY 26-Jul-97 - corrected problem with size of emiss
Ver 3, PRY 22-Sep-97 - allowed photo-excitation to be included
Ver 4, PRY 6-Jul-98 - added PATH
Ver 5, PRY 5-Sep-98 - added call to choose_ioneq
Ver 6, PRY 3-Dec-98 - dosen't crash if no params given
Ver 7, PRY 9-Jan-99 - allowed proton rates to be added through
/PROTON keyword.
Ver 8, PRY 10-Feb-99 - added /QUIET keyword
Ver 9, PRY 8-Oct-99 - for H-like ions, there's a 2-photon
transition with a non-zero A-value that is
assigned a zero wavelength (as it does not
produce an emission line). This caused
problems for dens_plotter, so emiss_calc
now removes this transition from the emiss
structure.
Ver 10, PRY 15-Dec-99 - added deu to the upsilon common block in
order to be consistent with the main Chianti
routines.
Ver 11, PRY 8-May-00 - added PRESSURE
Ver 12, PRY 17-Aug-00 - changed elvlc common block to match new
version of pop_solver
Ver 13, PRY 10-Oct-00 - now calls setup_ion to read ion data
Ver 14, PRY 1-Jun-00 - removed call to choose_ioneq; now makes use
of the !ioneq_file system variable.
Ver 15, PRY 25-Sep-01 - modified for 9-point splines and proton rates
Ver 16, PRY 9-Dec-01 - completed changes for v.4
V. 17, 29-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
Now we only call zion2filename, corrected the call to
zion2spectroscopic (dielectronic cases were not handled
correctly).
V.18, 6-Aug-2002, Peter Young
Theoretical wavelengths weren't being flagged so this
has now been corrected.
V.19, 7-Aug-2002, Peter Young
Stopped "lines" with zero wavelength being included in
the structure.
Changed the use of CHIANTI system variables.
V.20 14-Aug-2002, GDZ
Modified the use of Version, to make it compatible with the
other CHIANTI v.4 routines.
V.21 10-Sep-2002, Peter Young
Allowed a density of 1 cm-3 to be input.
V.22 7-Aug-2003, Peter Young
Added keyword /NO_SETUP
V.23 4-Oct-2003, GDZ
modified the input to POP_SOLVER, now it is dealt with an
input structure.
V.24 5-Mar-2004, Enrico Landi (EL)
included ionization and recombination as level population
processes
V.25 6-May-2005, EL
corrected a minor incompatibility with IDL 5.6
V.26 5-Jul-2005, Peter Young
added RADFUNC= and SUM_MWL_COEFFS= keywords
V.27 1-Aug-2005, Peter Young
re-ordered code for setup to prevent crash
V.28 3-Aug-2005,GDZ
fixed bug, only define ioneq_ionrec when files are
there (it was failing with neutrals)
VERSION : 28 3-Aug-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
astrophysical emission line spectra. It is a collaborative project
involving Ken Dere (Naval Research Laboratory, Washington DC),
Brunella Monsignori-Fossi and Enrico Landi (Arcetri Observatory,
Florence), and Helen Mason and Peter Young (DAMTP, Cambridge Univ.).
NAME
EMISS_SELECT()
PURPOSE
Allows emissivity arrays within EMISS structures to be selected
via a widget.
CATEGORY:
Atomic data analysis
CALLING SEQUENCE
em=emiss_select(emiss,index,sel_ind=sel_ind)
EXAMPLES
emiss=emiss_calc(26,13) ; calculate emiss for FeXIII
em=emiss_select(emiss)
em=emiss_select(emiss,indgen(10))
em=emiss_select(emiss,wra=[200,300],sel_ind=sel_ind)
INPUTS
EMISS A structure that is output by the routine EMISS_CALC
OPTIONAL INPUTS
INDEX A list of indices that allow a sub-set of wavelengths to
be displayed in the widget. If not specified, then
complete list of wavelengths is shown.
WRANGE Only show wavelengths lying in the specified wavelength
range, e.g., wrange=[200,300]
SEL_IND Contains the emiss index/indices of the selected
wavelengths.
GROUP If emiss_select is being called from another widget-based
routine, then one needs to set GROUP to the widget ID of
the top-level widget.
OUTPUTS
An array that contains the emissivities. If two or more lines were
selected, then the arrays are added together.
CALLS
HISTORY
Ver.1, PRY 1-Sep-97.
Ver.2, PRY 23-Feb-99, added WRANGE keyword
Ver.3, PRY 13-Sep-00, changed format of wavelengths in the
widget list
Ver.4, PRY 20-Nov-00, removed call to xselect_s - the widget
is now created internally.
Ver.5, PRY 27-Dec-00, changed switch to tst1 for IDL v5.4
Ver.6, PRY 6-Aug-02, added transition information to the widget,
and tidied up some of the code.
V.7, 15-Aug-2002 Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
Replaced the entire widget with a call to ch_xmenu_sel.
This works fine with very long lists of lines, while previously
the widget was very slow and sometimes would hang.
VERSION : 7, 15-Aug-2002
NAME
ZETA_0
EXPLANATION
Returns the value of zeta_0 (the number of vacancies in the ion given
by IZ and ION). See Sect. 2.2 of Mewe et al. (1986, A&AS 65, 511).
INPUTS
IZ Atomic number of ion (e.g., 26 -> Fe)
ION Spectroscopic number of ion (e.g., 13 -> XIII)
OUTPUTS
Value of zeta_0.
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME:
FF_RAD_LOSS
PURPOSE:
Calculate the free-free radiative energy losses losses.
Uses the free-free integrated gaunt factor calculations of
Sutherland, 1998, MNRAS, 300, 321
CALLING SEQUENCE:
FF_RAD_LOSS,Temperature,LossRate
INPUTS:
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
None
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
NO_SETUP: If the procedure setup_elements has already been called then
the keyword /no_setup should be set to avoid repeating this step
MIN_ABUND: If set, calculates the continuum only from those elements which
have an abundance greater than min_abund. Can speed up the
calculations. For example:
abundance (H) = 1.
abundance (He) = 0.085
abundance (C) = 3.3e-4
abundance (Si) = 3.3e-5
abundance (Fe) = 3.9e-5
OUTPUTS:
Temperature: temperature in degrees Kelvin, can be a 1 D array
LossRate: radiative energy loss rate in erg s^-1 cm^3
(radiative loss rate per emission measure (N_e N_H V)
COMMON BLOCKS:
common elements,abund,abund_ref,ioneq,ioneq_t,ioneq_ref
EXAMPLE:
> ff_rad_loss,t,rad
> ff_rad_loss,t,rad,min_abund=3.e-5
> ff_rad_loss,t,rad,/no_setup,min_abund=1.e-6
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
April 2000: Version 3.0
ROUTINE: findex
PURPOSE: Compute "floating point index" into a table using binary
search. The resulting output may be used with INTERPOLATE.
USEAGE: result = findex(u,v)
INPUT:
u a monitically increasing or decreasing 1-D grid
v a scalor, or array of values
OUTPUT:
result Floating point index. Integer part of RESULT(i) gives
the index into to U such that V(i) is between
U(RESULT(i)) and U(RESULT(i)+1). The fractional part
is the weighting factor
V(i)-U(RESULT(i))
---------------------
U(RESULT(i)+1)-U(RESULT(i))
DISCUSSION:
This routine is used to expedite one dimensional
interpolation on irregular 1-d grids. Using this routine
with INTERPOLATE is much faster then IDL's INTERPOL
procedure because it uses a binary instead of linear
search algorithm. The speedup is even more dramatic when
the same independent variable (V) and grid (U) are used
for several dependent variable interpolations.
EXAMPLE:
; In this example I found the FINDEX + INTERPOLATE combination
; to be about 60 times faster then INTERPOL.
u=randomu(iseed,200000) & u=u(sort(u))
v=randomu(iseed,10) & v=v(sort(v))
y=randomu(iseed,200000) & y=y(sort(y))
t=systime(1) & y1=interpolate(y,findex(u,v)) & print,systime(1)-t
t=systime(1) & y2=interpol(y,u,v) & print,systime(1)-t
print,f='(3(a,10f7.4/))','findex: ',y1,'interpol: ',y2,'diff: ',y1-y2
AUTHOR: Paul Ricchiazzi 21 Feb 97
Institute for Computational Earth System Science
University of California, Santa Barbara
paul@icess.ucsb.edu
REVISIONS:
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME
FREEBOUND
PURPOSE:
Calculates the free-bound (radiative recombination) continuum.
INPUTS
TEMP Temperature in K (can be an array).
WVL Wavelength in angstroms (can be an array).
OUTPUTS
INT Free-bound continuum intensity in units of
10^-40 erg cm^3/s/sr/Angstrom
( integral(N_H N_e dh) in cm^-5) if a DEM is not defined.
If DEM values are defined, it is assumed that they are given
as N_H N_e dh/dT. The units are 10^-40 erg/cm^2/s/srAngstrom
If T is given as a 1-D array, then the output will be a
2-D array, with one element for each temperature and
wavelength (but also see SUMT).
OPTIONAL INPUTS
DEM_INT The intensity array is multiplied by a DEM number for
each temperature. DEM_INT needs to be of the same size
as TEMPERATURE. It is needed for the synthetic spectrum
routines.
IZ Only calculate continuum for the element with atomic
number IZ
ION (To be used in conjunction with IZ.) Calculated continuum
for a single ion (IZ, ION).
KEYWORDS
NO_SETUP If the procedure setup_elements has already been called
then the keyword /nosetup should be set to avoid
repeating this step
MIN_ABUND If set, calculates the continuum only from those
elements which have an abundance greater than
min_abund. Can speed up the calculations. For
example:
abundance (H) = 1.
abundance (He) = 0.085
abundance (C) = 3.3e-4
abundance (Si) = 3.3e-5
abundance (Fe) = 3.9e-5
PHOTONS The output spectrum is given in photon units rather
than ergs.
SUMT When a set of temperatures is given to FREEBOUND, the
default is to output INTENSITY as an array of size
(nwvl x nT). With this keyword set, a summation over
the temperatures is performed.
VERBOSE Output information from FREEBOUND.
COMMON BLOCKS
ELEMENTS
CALLS
FREEBOUND_ION, SETUP_ELEMENTS, READ_KLGFB, GET_IEQ
HISTORY
Ver.1, 24-Jul-2002, Peter Young
Ver.2, 26-Jul-2002, Peter Young
revised call to freebound_ion; corrected ion fraction problem
V 3, 25-May-2005, GDZ
corrected routine header.
VERSION : 3, 25-May-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME
FREEBOUND
EXPLANATION
Calculates the free-bound (radiative recombination) continuum
from a single ion. Note that the output does not contain the ion
fraction, element abundance or differential emission measure term.
INPUTS
TEMP Temperature in K (can be an array).
WVL Wavelength in angstroms (can be an array).
IZ Atomic number of ion (e.g., 26 = Fe)
ION Spectroscopic number of ion (e.g., 13 = XIII)
OUTPUTS
INT Free-bound continuum intensity. Needs to be multiplied by
element abundance, ion fraction and DEM to obtain the final
continuum intensity.
OPTIONAL INPUTS
IP The ionization potential of the ion.
VDATA An array containing the Verner & Yakovlev data array.
PE An array containing the PE data from READ_FBLVL
KLGFB An array containing the KLGFB data from READ_FBLVL
[Note: the above 3 inputs are used when calling freebound_ion from
freebound]
KEYWORDS
NOVERNER If set, then the Verner & Yakovlev cross-sections will
not be used.
COMMON BLOCKS
None.
CALLS
READ_FBLVL, ZION2FILENAME, VERNER_XS, KARZAS_XS, CONCAT_DIR,
READ_IP, READ_KLGFB, FILE_EXIST
PROGRAMMING NOTES
The way I treat the exponential function in the expression for the
emissivity may seem strange, but it saves a bit of time in the
calculation. Basically calculating exp(E-IP+E_i/T) for each level
was time consuming so I split it into exp(E-IP/T)*exp(E_i/T). The
first term comes out of the for loop, while the second term is the
exponential of a vector rather than an array. This made a ~30%
time-saving for freebound.
HISTORY
Ver.1, 24-Jul-2002, Peter Young
Ver.2, 26-Jul-2002, Peter Young
Added /noverner keyword.
Ver.3, 30-Jul-2002, Peter Young
Speeded up routine by modifying treatment of exponential.
PROJECT : CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME
FREEFREE
PURPOSE:
This routine computes the free-free continuum (bremsstrahlung)
using the fitting formulae of Itoh et al. (ApJS 128, 125, 2000)
and Sutherland (MNRAS 300, 321, 1998).
The Itoh et al. data are valid for smaller ranges for temperature
and wavelength than Sutherland and so for points outside of their
ranges we use the data of Sutherland.
INPUTS
TEMP Temperature (in K).
WVL Wavelengths in angstroms. Can be a scalar or vector.
OUTPUTS
INT Free-free continuum intensity in units of
10^-40 erg cm^3/s/sr/Angstrom
[ integral(N_H N_e dh) in cm^-5 ] if a DEM is not defined.
If DEM values are defined, it is assumed that they are given
as N_H N_e dh/dT. The units are 10^-40 erg/cm^2/s/sr/Angstrom.
If T is given as a 1-D array, then the output will be a 2-D array,
with one element for each temperature and wavelength
(but also see SUMT).
OPTIONAL INPUTS
DEM_INT An array of same length as TEMP which contains the
differential emission measure values at each temperature.
The emissivity at each temperature is multiplied by the
DEM value and the d(logT) value.
MIN_ABUND This keyword allows the specification of a minimum abundance,
such that any elements with an abundance (relative to
hydrogen) less than MIN_ABUND will not be included in the
calculation. E.g., MIN_ABUND=1e-5.
KEYWORDS
NO_SETUP By default the routine asks the user which ion balance
and abundance files to use via pop-up widgets. If
/no_setup is used then this data is taken from the common
block.
SUMT The default is to output the intensity array as an array
of size (nwvl x nT). Setting this keyword performs a sum
over the temperatures to yield a vector of same size as
the input wavelengths, thus producing the complete
free-free spectrum.
PHOTONS Gives output emissivity in photon units rather than ergs.
CALLS
SUTHERLAND, ITOH
COMMON BLOCKS
ELEMENTS
PROGRAMMING NOTES
The Itoh fitting formula is only valid for (6.0 LE logT LE 8.5).
For temperatures below this, we thus switch to the Sutherland
fitting formula. There is very little (<1%) between the two at
logT=6.
Itoh also has a constraint on the quantity u=hc/kTl (l=wavelength),
such that (-4 LE log u LE 1.0). The upper limit corresponds to the
continuum being cut-off prematurely at low wavelengths. E.g., for
T=10^6 the cutoff is at 14.39 angstroms. For these low wavelengths
we also use the Sutherland data to complete the continuum. Note that
the continuum at these wavelengths is very weak
MODIFICATION HISTORY
Ver.1, 5-Dec-2001, Peter Young
Completely revised to call the separate itoh.pro and
sutherland.pro routines.
V. 2, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ),
Corrected the description of the units.
Added verbose keyword and a printout.
V. 3, 22-May-2002, Peter Young (PRY)
Added MIN_ABUND optional input.
Changed ioneq_t to ioneq_logt (GDZ).
V 4, 25-May-2005, GDZ
corrected routine header.
VERSION : 4, 25-May-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME:
GET_ATOMIC_WEIGHT
PURPOSE:
to produce an atomic weight.
PROCEDURE:
This routine converts the ion atomic number into an atomic weight. Where
an element has more than one isotope, the weight is that of the most
common.
I've written this routine in order to apply a thermal broadening to
lines in a CHIANTI synthetic spectrum (see routine make_chianti_spec.pro).
CALLING SEQUENCE:
IDL>
EXAMPLES:
INPUTS:
IZ
OPT. INPUTS :
OUTPUTS:
the atomic weight
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
KEYWORDS:
CALLS:
COMMON:
RESTRICTIONS:
I go up to zinc (iz=30)
SIDE EFFECTS:
CATEGORY:
synthetic spectra
PREV. HIST. :
WRITTEN :
Ver.1, 22-Jun-00, Peter Young (PRY)
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
VERSION : V 1, 22-Jun-00, Peter Young (PRY)
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
Purpose : calculates the contribution functions G(T) at constant
pressure or density of the lines present in the CHIANTI
database, corresponding to a given set of observed lines.
Category :
Explanation : This routine is called by CHIANTI_DEM. It cannot be used as
a stand-alone routine.
The observation file is read by CHIANTI_DEM.
GET_CONTRIBUTIONS starts reading
the ionization equilibrium file and the masterlist of the
ions present in the CHIANTI database.
GET_CONTRIBUTIONS then searches the
CHIANTI database (ion per ion) for all the
theoretical lines corresponding to the observed lines, i.e.
that lie in a OBS_WVL(i) +/- DELTA_LAMBDA_OBS(i) interval
centered on the observed wavelength OBS_WVL(i).
Then calculates the G(T) values for the temperature interval
log(T)= 4.0 - 8.0 with steps of log(T) = 0.1
A constant pressure OR a constant density for all the lines
is used. If you select a constant pressure,
for each ion the contribution function is calculated at an
electron density N_e equal to the ratio of the pressure
and the temperature of maximum ionization fraction:
C=C( T, N_e = P/T_ion)
The C(T) values are stored by GET_CONTRIBUTIONS in the output
file OUTPUT.CONTRIBUTIONS.
In the case no theoretical lines corresponding to an observed
line are found, the routine writes the wavelength of the line
to be excluded from the fit in the array EXCLU_OBS_WVL_NO_TEO;
these lines are then excluded from the fitting by
CHIANTI_DEM. You might consider the possibility to start again
incrementing the DELTA_LAMBDA_OBS, to see if there are
theoretical lines in the vicinity.
Use : called by CHIANTI_DEM to calculate the contribution functions
Examples :
Inputs : Various, in form of keywords.
Opt. Inputs : none
Outputs : OUTPUT.CONTRIBUTIONS
Is the file where all the contribution functions G(T) are
stored. In the first two lines the ionization equilibrium
file name, and the constant value of pressure or density
adopted are reported. Then for each line you have reported
the observed wavelength, the theoretical one, the element and
ionization stage, then the C(T) values. At the end the
specification for each transition.
Opt. Outputs: None
Keywords : (all passed by CHIANTI_DEM)
CUT_GT: if set, only those
theoretical lines that have a MAX(G(T)) greater
than the value set, are kept; it is useful to
set this value in order to reduce the number
of lines in the file where the G(T) are stored.
DENSITY : the value of the density (Ne).
FILE_INPUT: if set, you are not
requested to select the observation file.
N_MATCHES:
In the unlikely event that more than 20 (default value for
N_MATCHES) theoretical lines corresponding to an observed
line are found, the routine stops; in this case, you have to
start again setting N_MATCHES equal to a greater number.
PRESSURE: the value of the pressure (Ne T)
OUTPUT : -the core name for the output
Calls :
READ_IONEQ
read_masterlist
CONVERTNAME
ion2spectroscopic
ZION2FILENAME
READ_WGFA2
READ_SPLUPS
POP_SOLVER
READ_ELVLC
READ_IONREC
CONVERT_TERMS
Common : elvlc - energy levels
wgfa - radiative data
upsilon - upsilon data
obs, obs_int,obs_sig,n_obs
obs_o, obs_wvl,obs_id,obs_delta_lambda
dem, d_dem_temp,dem_temp,log_dem_temp,log_t_mesh,log_dem_mesh
contr, ch_tot_contr
ab, abund_name,abund_info,xuvtop,ioneq_name
these are the commons with GET_CONTRIBUTIONS.PRO:
various, exclu_obs_wvl_no_teo,const_net,$
dem_temp_min,dem_temp_max,n_dem_temp,$
ch_wvl,ch_l1,ch_l2,ch_id,ch_z,ch_ion,ch_contr_wa,$
ch_pop,ch_contr_list, ch_term,ch_n_contr
Restrictions: ;
THIS IS NOT A STAND-ALONE PROCEDURE.
It is called by CHIANTI_DEM,
and has a lot of common blocks with other procedures.
In the unlikely event that more than 20 (default value for
N_MATCHES) theoretical lines corresponding to an observed
line are found, the routine stops; in this case, you have to
start again setting N_MATCHES equal to a greater number.
Of course you need to have the enviroment variable CDS_SS_DERE
pointing to the CHIANTI database top directory.
Side effects: None known.
Category : spectrum
Prev. Hist. :
Written by Ken Dere (NRL) as part of the CHIANTI package
in collaboration with Brunella Monsignori Fossi, Enrico Landi
(Arcetri Observatory, Florence), Helen Mason and Peter Young
(DAMTP, Cambridge Univ.). Incorporated into the CDS software.
Written :
Version 1, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ) 5 November 1997
UCLAN (University of Central Lancashire, UK)
Modified :
Version 2, 31-Oct-2000, GDZ, DAMTP. Rewritten completely the routine,
to make it compatible with CHIANTI v.3. Based the core calculations on
new implementations due to Peter Young, CfA.
Version 3, 5-Dec-2000, GDZ, DAMTP. Fixed a bug when checking the
values in the .splups files.
Ver. 4, 25-Apr-02, GDZ
Revised to account for v.4 variations. By default the proton
rates are included in the calculation of the level population.
V.5, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V. 6, 10-July-2002 GDZ
Corrected a bug. It now properly includes by default the
proton rates in the population solver.
V. 7, 4-Oct-2003, GDZ
modified the input to POP_SOLVER, now it is dealt with an
input structure.
V. 8, 3-Nov-03 GDZ
Modified format e8.2 to e9.2 for Windows compatibility.
V. 9, 4-May-05 Enrico Landi (EL)
Modified in order to include ionization and recombination
data in the input to POP_SOLVER
VERSION : 9, 4-May-05
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME
GET_IEQ()
EXPLANATION
For a specified ion (IZ, ION) and set of temperatures (TEMP) this
routine takes the ion fraction values tabulated in one of the CHIANTI
.IONEQ files, interpolates and extracts the values of the ion
fraction at the input temperatures.
INPUTS
TEMP The temperature(s) at which the ion fractions are required.
IZ The atomic number of the element (e.g., 26 = iron).
ION The spectroscopic number of the ion (e.g., 13 = XIII).
OPTIONAL INPUTS
IONEQ_LOGT The temperature output from the READ_IONEQ routine.
IONEQ_FRAC The ion fractions from the READ_IONEQ routine.
OUTPUT
A vector of same length as the input TEMP containing the ion
fractions at these temperatures.
CALLS
READ_IONEQ
HISTORY
Ver.1, 24-Jul-2002, Peter Young
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
GOFNT
PURPOSE:
calculate G(n,T) function (line intensity per unit emission measure)
PROCEDURE:
Must specify line to form numerator and denominator
Multiple lines can be selected and summed
This can now be done interactively or not.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
GOFNT,Ion,Wmin,Wmax,Temperature,G,Desc,density=
INPUTS:
Ion: the CHIANTI style name of the ion, i.e., 'c_5' for C V
Wmin: minimum of wavelength wavelength range of interest in Angstroms
Wmax: maximum of wavelength wavelength range of interest
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
Many - see the keywords below.
OUTPUTS:
Temperature: an array of temperatures
G: Intensity per unit emission measure N_e*N_H*dh [cm^-5].
The resulting units are therefore erg cm^+3 s^-1 sr-1
C(T)= 1/(4*!pi)* A_ji*(N_j(X^+m)/N(X^+m))*(N(X^+m)/N(X))*(N(X)/N(H))/N_e
unless /NOABUND is set, in which case
C(T)= 1/(4*!pi)* A_ji*(N_j(X^+m)/N(X^+m))*(N(X^+m)/N(X))/N_e
G(T)=(hc/lambda_ij)*C(T)
G(T)= C(T) if /PHOTONS is set
Desc: a short string description of the selected line
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
Postscript file withthe plot of G(T).
Ascii file with the values of G(T).
VALUE The array of G(T) values corresponding to logt0.
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
PRESSURE: specifies the pressure in units of NeT (cm^-3 K). G is then
calculated at that constant pressure
DENSITY: specifies the electron density in units of cm^-3. G is then
calculated at that value of the electron density. If neither the
density or pressure keywords are specified, a constant
density of 1.e+10 cm^-3 is assumed
PHOTONS: sets output in photons/s
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
RADTEMP The blackbody radiation field temperature (default 6000 K).
OUTFILE: the (optional) name of the output ascii file where a
listing of the line ratio intensity as a function of
temperature is saved.
PSFILE: the (optional) name of the output postscript file
where a plot of the chosen G(T) is saved.
NOABUND: If set, the G(T)'s are not multiplied by the abundance
factor.
NOPROT If set, then proton rates are not included.
ABUND_NAME: Name of the abundance file to use. If not passed, then
the user is prompted for it.
IONEQ_NAME: Name of the ionization equilization name to use. If not
passed, then the user is prompted for it.
ALL If set, all lines are calculated, including
the 'unobserved' ones.
LOWER_LEVELS
UPPER_LEVELS
Arrays with the indices of the lower and upper levels
pertaining to the transitions you want to get.
If more than one couple is given, the G(T) of the
lines are summed.
Obviously, the given indices must correspond to transitions
that are present in the database.
ARCSECS
If set, units are photons (ergs) cm^+3 s^-1 arcsecs^-2
VERBOSE
LOGT0 An array of log T values for which the G(T) are wanted.
VALUE The array of G(T) values corresponding to logt0.
If logt0 is defined, and within the limits of the
temperatures for which G(T) NE 0, the array VALUE
is returned with a simple spline interpolation.
CALLS:
CH_SYNTHETIC, CH_XMENU_SEL
COMMON BLOCKS: None
RESTRICTIONS:
SIDE EFFECTS:
EXAMPLE:
IDL> gofnt,'o_5',1000.,1500.,temp,goft,desc,density=1.e+16
CATEGORY:
spectral diagnostics
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
October 4, 1996: Version 1
14-Jul-2000 Peter Young, now calls pop_solver
26-Oct-2000 GDZ, added keyword NOABUND to not multiply for the abundence
factor. Corrected header for a wrong description.
Version 4, 21-Dec-2000, William Thompson, GSFC
Modified for better cross-platform graphics capability
Version 5, 8-Nov-01, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ).
Rewritten as a wrapper routine using the new procedures.
Corrected a few inconsistencies in the plots.
Version 6, 18-Nov-01, Peter Young
Added /noprot, rphot and radtemp keywords.
Version 7, 11-Dec-01, Peter Young
Changed call to ch_strpad to strpad.
V. 8, GDZ, 28-Apr-02 Added abund_name,ioneq_name keywords.
v. 9 21-May-2002, GDZ
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V.10, 15-Aug-02, GDZ
Major revision:
-Removed the call to ch_xselect_s, that did not work for long lists.
-Added a '*' in the line lists, to identify 'unobserved' lines.
-Replaced the commands to create PS file, to make it
cross-platform compatible.
-Added a large number of cosmetics, mainly lables to the axes and
titles.
-Added keyword ALL. If set, all lines are calculated, including
the 'unobserved' ones.
-Added the CHIANTI version number in the outputs.
V. 11, 19-Sep-02, GDZ
Clarified output units.
V.12, 25-Jun-03, GDZ,
Added many new keywords. Now is possible to use the routine
with background jobs, in not-interactive mode.
Rounded the wavelengths.
V.13, 24-Sept-2003, GDZ
Corrected a bug when logt0 is not defined.
V.14, 3-Nov-03 GDZ
Modified format e8.2 to e9.2 for Windows compatibility.
VERSION : 14, 3-Nov-03
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME: G_OF_T()
PURPOSE:
To compute DE * F(T) * n_j * A_ji / N_e for selected emission lines.
Option to also multiply by abundance.
CATEGORY:
Atomic data analysis
EXPLANATION:
The G-of-T function has a number of different definitions in the
literature. In the most basic form it contains only the temperature
dependent parts (i.e., 0.83*n_j*A_ji*F(T)/N_e), but often a Delta-E
and Ab(X) are added as well. Here, the _default_ form is:
Delta-E * 0.83 * n_j * A_ji * F(T) / N_e
By using the NO_DE keyword, the Delta-E can be omitted, while the
ABUND keyword allows the abundance to be added.
The function that is output is tabulated over 4.0 <= logT <= 8.0
in 0.1 dex intervals. If you want the function tabulated over
smaller intervals, run the ION_INTERP routine afterwards.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
EXAMPLES:
RESULT=G_OF_T(26,13)
RESULT=G_OF_T(26,13,DENS=7)
RESULT=G_OF_T(26,13,GOFTFILE='my_gofts.dat')
RESULT=G_OF_T(26,13,/ABUND)
RESULT=G_OF_T(26,13,ABUND_FILE=ABUND_FILE, IONEQ_FILE=IONEQ_FILE)
INPUTS:
IZ: The atomic number of the ion (e.g., 26 = Fe)
ION: The spectroscopic number of the ion (e.g., 12 = XII)
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
DENS: The logarithm (to base 10) of the density at which the
emissivities are calculated (default=10.)
WRANGE: Wavelength range from which lines are required. If not
specified, then the 10 strongest lines are displayed.
PATH: If specified, the routine will look for the atomic data in
the PATH directory, rather than in the CHIANTI database
GOFTFILE: By specifying GOFTFILE as a filename, the G-of-T
function can be stored in this file. It is stored
in the form a structure (called goft_list) with the following
labels:
goft_list.label: user-specified string, e.g., 'Si XII 520.7'
goft_list.func: fltarr(41), the G-of-T function
If the same GOFTFILE is specified for another ion, then the
G-of-T function is added to the existing structure. The GOFTFILE
option only works when the ABUND keyword is set. The GOFTFILE is
meant to be read by another routine called GOFT_PLOTTER.
INDEX: Allows the direct specification of indices within the
emiss structure. This allows the g_of_t routine to be
run without the menu widget appearing. If the /quiet
keyword is also used, then the routine will run "silently".
RADTEMP Specify background radiation temperature (default: 6000 K)
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
IONEQ_FILE Directly specify the name of the ion balance file
(including directory path). If not set, then a widget will
pop up allowing you to select a file.
ABUND_FILE Directly specify the name of the abundance file
(including directory path). One can also use /ABUND_FILE
to include the abundances in the G(T) function, but allow
the abundance file to be picked through a widget.
KEYWORDS:
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
NO_DE: If set, then the output function will *not* contain the
Delta-E. Be careful using this if you are using blends
(as Delta-E is different for different wavelengths).
QUIET If set, then don't plot the G(T) function or print out
information to the screen.
CALLS:
EMISS_CALC, READ_IONEQ, READ_ABUND, EMISS_SELECT, CH_GET_FILE
RESTRICTIONS:
HISTORY:
Ver.1, PRY 28-Jul-97.
Ver.2, PRY 22-Jun-98, added CHOOSE keyword and removed RAY
Ver.3, PRY 4-Aug-98, cosmetic changes following comments of Giulio
Del Zanna
Ver.4, PRY 5-Sep-98, added call to choose_ioneq
Ver.5, PRY 23-Sep-98, added GOFTFILE input
Ver.6, PRY 3-Mar-99, now calls EMISS_SELECT
Ver.7, PRY 6-Nov-00, removed the /CHOOSE keyword; also changed
PICKFILE call to DIALOG_PICKFILE and removed call
to the CHIANTI routine ADD\_SUBDIR
Ver.8, PRY 18-Oct-01, adjusted for proton rates, and
photoexcitation.
Ver.9, PRY 9-Dec-01, completed modifications for v.4 of CHIANTI.
V. 10, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
Ver. 11, 9-Feb-2005, Peter Young
changed keyword_set(abund) to keyword_set(abund_file)
VERSION : 11, 9-Feb-2005
function hastogram returns a frequency histogram over a specified grid, calculated in a fast and clever way. really. works in haste, without waste. syntax f=hastogram(list,x,wts=wts) parameters list [INPUT; required] list of numbers to bin x [I/O] the required binning scheme 1: if not set, assumes a linear grid of size 100 from min(LIST) to max(LIST) 2: if scalar or 1-element vector, assumes this to be the number of bins * if -ve, log grid, else linear 3: if vector with more than 1 element, assumes it to be all the bin-beginning values and the final bin-ending value. * overwrites variable by adopted grid keywords wts [INPUT] if given, appropriately weights each element of LIST * default is unity * if size does not match size(LIST), will be appropriately interpolated _extra [JUNK] here only to prevent crashing the program description the problem is the following: if the number of bins is large, accumulating a frequency histogram by linear search takes too long, esp. in IDL if one uses for-loops. so, first create a monster array containing both the list elements and the grid values. then sort this array. this results in an array where the list elements are all nicely placed within the correct bins. now, if we've been keeping track of the positions of the list elements, it's an easy job to count up the number in each bin of the grid. to do the latter, we first create a new array made up of -1s in positions of list elements and position indices for grid values and reorder according to the above sort. then, replace each -1 by the nearest non-(-1) from the left. now each list element is assigned the correct bin number. voila! restrictions X must be sorted in increasing order. subroutines history vinay kashyap (Jan98) PINT_of_ALE added kludge to speed up in case max(X) < max(LIST) (VK; Sep98) added quit in case X is not sorted in ascending order (VK; JanMMI)
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME: INTEGRAL_CALC
PURPOSE:
To compute the atomic data integral for use in column or volume
emission measure work.
CATEGORY:
Scientific analysis
EXPLANATION:
Defining
G(T) = 0.83 * Fr(T) * N_j * A_ji / N_e
where Fr(T) is the ionisation fraction (e.g., from Arnaud &
Rothenflug), N_j the relative population of level j, A_ji the
A-value for the j->i transition and N_e the electron density. The
0.83 is the ratio of hydrogen to free electrons, which is constant
above around 10^4 K. This function is sharply-peaked at a
temperature T_mem (the temperature of maximum emission, which can
be different from the temperature of maximum ionisation, T_max)
and so an oft-used approximation is to take G(T) constant in the
range log T_mem - 0.15 to log T_mem + 0.15 and zero outside. The
value of the constant, which we call C_lambda here, is then given
by
C_lambda = integral { G(T) dT }
--------------------
T_mem * (10^0.15 - 10^-0.15)
If EM(s) is the column emission measure, F the flux (erg cm-2 s-1)
in a line lambda, Ab the abundance of the element and DE (erg) the
energy for the transition, then:
F = DE * Ab * C_lambda * EM(s)
If we are dealing with intensities I (erg cm-2 s-1 sr-1) then:
4pi * I = DE * Ab * C_lambda * EM(s)
This program extracts the ionisation balance and emissivities from
the CHIANTI database and calculates C_lambda for all lines in the
specified wavelength interval WRANGE by integrating over
0.02 dex temperature intervals, using the IDL INT_TABULATED function.
The C_lambda functions for all the lines in the selected wavelength
range WRANGE are displayed as well as the temperature of maximum
emission (T_mem), DE*C_lambda and 4pi/(DE*C_lambda). These latter
two quantities are useful for the emission measure analysis.
Any combination of the displayed lines can then be blended and the
corresponding quantities for the blend will be displayed.
The function Fr(T) * N_j * A_ji can also be plotted at this stage.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
INTEGRAL_CALC, IZ, ION, [WRANGE=WRANGE, /CHOOSE, DENS=DENS]
EXAMPLES:
INTEGRAL_CALC, 26, 13, WRANGE=[200,205], /CHOOSE
INTEGRAL_CALC, 14, 10, WRANGE=[250,270], DENS=10.
INPUTS:
IZ: The atomic number of the ion
ION: The spectroscopic number of the ion (e.g., 12 = XII)
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
DENS: The density at which the emissivities are calculated
(default=10.)
WRANGE: Wavelength range for which C_lambda functions are
calculated. If not given, then the 10 strongest lines
are printed.
INDEX: Particular elements in the emissivity structure can be
selected with INDEX. This allows integral_calc to be run
'silently'. The output is contained in the OUTSTR structure.
If index is given as, e.g., [7,8], then the C_lambda
functions for these two lines are summed and output.
PATH: Directly specify the directory path where the Chianti data
for the ion is found
ABUND_FILE The name of a CHIANTI abundance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio. Default is
!abund_file.
IONEQ_FILE The name of a CHIANTI ion balance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio and evaluating
the T_max of the ion. Default is !ioneq_file.
RADTEMP The blackbody radiation field temperature (default
6000 K).
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius
units. I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface.
(Default is infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
KEYWORDS:
CHOOSE: Allow ion balance calculations to be selected manually
(see choose_ioneq.pro routine).
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
OUTSTR: A structure with the following tags
.tmem - the T_mem for the line(s)
.dec - total( de * c_lambda )
.pidec - 4 * pi / total( de * c_lambda )
Only output when INDEX is specified.
COMMON BLOCKS:
None.
CALLS:
EMISS_CALC, CH_GET_FILE, READ_IONEQ
HISTORY:
Ver.1: PRY, 28-JUN-97.
Ver.2: PRY, 7-OCT-97. Added TEMPI and GOFT, for plotting.
Ver.3: PRY, 31-JUL-98. Added PATH.
Ver.4: PRY, 6-APR-99. Added INDEX, OUTSTR. Removed TEMPI and GOFT
(these can be got from the g_of_t routine).
Ver.5: PRY, 9-Dec-01. Modified for v.4 of CHIANTI.
V.6, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V.7, 06-Aug-02 GDZ
Changed the use of CHIANTI system variables.
VERSION : 7, 06-Aug-02
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
ion2filename
PURPOSE:
Ion names as character strings are converted to
provide their complete file name (with out suffix)
CATEGORY:
naming utility
CALLING SEQUENCE:
ION@FILENAME,Ion,Filename
INPUTS:
Name: such as 'c_2'
OUTPUTS:
Filename: !xuvtop/c/c_2/c_2
EXAMPLE:
> ion2filename,'c_2d',filename
> print,filename
> !xuvtop/c/c_2d/c_2d
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
V.2, September 1999: added for use with Version 3
V.3, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
VERSION : 3, 21-May-2002
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
ION2SPECTROSCOPIC
PURPOSE:
provide identification string
CATEGORY:
database.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
ION2SPECTROSCOPIC, Ion, Spectroscopic
INPUTS:
Ion: CHIANTI notation for an ion, i.e., 'c_2' for C II
OUTPUTS:
Name: the spectroscopic notation for the ion, i.e. 'C II'
EXAMPLE:
> ion2spectroscopic,'fe_13',name
> print,name
> Fe XIII
> ion2spectroscopic,'o_6d',name
> print,name
> O VI d
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
September 1999: Version 3.0
Ver.2, 11-Dec-2001, Peter Young
Revised routine; removed call to repstr
V.3, 29-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
Added output keyword dielectronic.
V.4, 12-Aug-02, GDZ
Corrected a typo concerning XXII.
VERSION : 4, 12-Aug-02
NAME
ION_FRAC_INTERP
PROJECT
CHIANTI
EXPLANATION
Performs interpolation of an ion fraction array (such as contained in
the CHIANTI .ioneq files) to yield ion fractions at temperatures TEMP.
Note that the ion must already have been selected before calling this
routine, since IONEQ_FRAC is a 1D array. The routine GET_IEQ is an
alternative if the ion has not been selected.
INPUTS
TEMP Temperature(s) for which ion fractions are required.
Units: K.
IONEQ_LOGT Log (base 10) of temperature (units: K). A 1D array of
temperatures for which the ion fraction is defined.
IONEQ_FRAC A 1D array of ion fractions at the temperatures defined by
ioneq_logt
OUTPUT
The ion fraction defined at the temperatures TEMP. If values of TEMP lie
outside the range of the ion fraction or the range of IONEQ_LOGT, then
values of 0 are returned at these temperatures.
HISTORY
Ver.1, 10-Jun-2005, Peter Young
EXPLANATION: When accessing ionisation balance data from the CHIANTI database, it is output at log temperature values from 4 to 8 at 0.1 intervals. For display purposes it is often nice to perform spline interpolation to give a smoother function. This interpolation should be performed on the logarithm of the data as this is more slowly varying. This routine performs such an interpolation. It is only essential to input G_T and N. Specifying T is optional (see below), while TI and G_TI are output. N gives the number of points within an interval over which interpolation is performed. INPUTS: G_T: Data for which interpolation required OPTIONAL INPUTS: T: Values at which is G_T is tabulated. If not specified, then taken as 4 to 8 in 0.1 intervals. N: Specifies `smoothness' of fit. E.g., N=5 means that single intervals are divided into 5 intervals. TI: If some temperatures are specified, then the SPLINE call is used to work out the values of G_TI that correspond to these temperatures. Only works if N is not specified. OUTPUTS T: If not specified, then output as an array from 4 to 8 in 0.1 intervals TI: Interpolated T values. If the TI are specified on the command line, then these values are returned. G_TI: Interpolated G_T values KEYWORDS PLOT - The interpolated data is displayed together with the original data. EXAMPLE: g_t=g_of_t(26,13,/ray) ion_interp,t,g_t,ti,g_ti,5,/plot plot,t,g_t,psym=2,xra=[5.8,6.7] oplot,ti,g_ti ion_interp,t,g_t,[6.112,6.254],g_ti,/plot CALLS: SPLINE HISTORY: Ver 1, PRY 17-JUN-98 Ver 2, PRY 10-AUG-98, corrected minor bug Ver 3, PRY 22-SEP-98, corrected interpolation error Ver 4, PRY 3-MAR-99, now allows TI to be specified CONTACT: Peter Young, Cambridge University (P.R.Young@damtp.cam.ac.uk)
NAME
ISOTHERMAL
PURPOSE:
Computes spectra from isothermal plasmas. A number of isothermal
plasmas can be included.
Note that this routine has a number of unique features that
distinguish it from the other CHIANTI synthetic spectra routines.
See the Programming Notes section.
INPUTS:
WMIN Minimum of desired wavelength range in Angstroms.
WMAX Maximum of desired wavelength range in Angstroms.
WAVESTEP Bin size of spectrum (in Angstroms)
TEMP Electron temperature (or array).
OPTIONAL INPUTS
PRESSURE Electron pressure in units of cm^-3 K.
EDENSITY Electron density in units of cm^-3.
EM Emission measure. The units of EM govern the intensity
units of the emission lines (i.e., column or volume
emission measure units). If EM is not specified, then the
emission measure is set to (N_e * N_H) where N_e is
derived from the user-specified PRESSURE or EDENSITY,
and N_H is derived from the routine PROTON_DENS.PRO.
SNGL_ION Rather than include the entire list of CHIANTI ions in
the calculation, this input can be used to select a
single ion, or a number of different ions. E.g.,
SNGL_ION='s_2' or SNGL_ION=['s_2','s_3','s_4'].
RADTEMP The blackbody radiation field temperature (default 6000 K).
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
MASTERLIST The list of ions that will be considered for the
spectrum is contained in the masterlist file in the
CHIANTI directories. The user can specify his own file
through this keyword. E.g.,
masterlist='/user/home/masterlist.ions'
ABUND_NAME: Name of the abundance file to use. If not passed, then
the user is prompted for it.
IONEQ_NAME: Name of the ionization equilization name to use. If not
passed, then the user is prompted for it.
KEYWORDS
NOPROT Switch off the inclusion of proton rates in the level
balance.
ERGS The units of the output spectrum are by default in photons.
Setting /ERGS switches to erg units.
CONT Adds continuum (free-free, free-bound, two-photon) to
spectrum.
OUTPUTS:
LAMBDA Wavelength array of calculated synthetic spectrum.
SPECTRUM Intensity array. The units depend on the user inputs to
ISOTHERMAL -- see note below.
LIST_WVL A list of wavelengths for use with synthetic_plot.pro
LIST_IDENT A list of line identifications for use with
synthetic_plot.pro
PROGRAMMING NOTES
Intensity Units
---------------
The units are of the form photons cm^3 s^-1 sr^-1 * (units of EM),
changing to ergs if the /ergs keyword is set.
The volume emission measure (N_e*N_H*V) has units cm^-3.
The column emission measure (N_e*N_H*h) has units cm^-5.
Unique features
---------------
The emission lines in the final spectrum have no width and thus
each occupies a single pixel of the spectrum. The size of the
pixels are set by WAVESTEP.
As stated above, the units of the output spectrum are
photons cm^3 s^-1 sr^-1, i.e., there is no "per angstrom" term.
This means that (i) the height of the emission lines in the
spectrum does not change with varying WAVESTEP, and (ii) the height
of continuum does change with WAVESTEP.
COMMON BLOCKS
ELEMENTS
CALLS
CH_SYNTHETIC, READ_ABUND, CH_GET_FILE, CONCAT_DIR, FREEFREE,
FREEBOUND, TWO_PHOTON
HISTORY
Ver.1, 8-Apr-02, Peter Young Rutherford Appleton Laboratory,
p.r.young@rl.ac.uk
Tries to replicate the behaviour of the original ISOTHERMAL which
was found in earlier versions of CHIANTI (v.3 and earlier).
MODIFICATION HISTORY
Ver. 2, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ), 28-Apr-02
Added abund_name,ioneq_name keywords.
Also, added photons keyword in call to MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC.
Ver. 3, Peter Young, 24-May-02
Modified to produce arrays of spectra when an array of
temperatures is given
V.4, GDZ, 28-May-02
Added a couple of checks on file existence and modified the call
to ch_synthetic and make_chianti_spec due to change of keyword
names.
V.5, Peter Young, 16-Jul-02
Restructured routine to avoid crashes when a large number of
temperatures is input.
V.6, 8-Aug-02 GDZ
Added one error checking
V.7, 18-Aug-03, Peter Young
Added EM= keyword.
VERSION :
Version 6, 8-Aug-02
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME
ITOH
EXPLANATION
Calculates the relativistic free-free continuum using the fitting
formula of Itoh et al. (ApJS 128, 125, 2000).
INPUTS
TEMP Temperature (in K).
WVL Wavelengths in angstroms. Can be a scalar or vector.
OUTPUTS
INT Free-free continuum emissivity in units of
10^-40 erg cm^3 / s / sr / Angstrom per unit emission
measure [ integral(N_e N_H dh) in cm^-5 ]. If T is given as
a 1-D array, then RAD will be output as a 2-D array,
with one element for each temperature and wavelength
(but also see SUMT).
OPTIONAL INPUTS
DEM_INT An array of same length as TEMP which contains the
differential emission measure values at each temperature.
The emissivity at each temperature is multiplied by the
DEM value and the d(logT) value.
MIN_ABUND This keyword allows the specification of a minimum abundance,
such that any elements with an abundance (relative to
hydrogen) less than MIN_ABUND will not be included in the
calculation. E.g., MIN_ABUND=1e-5.
KEYWORDS
NO_SETUP By default the routine asks the user which ion balance
and abundance files to use via pop-up widgets. If
/no_setup is used then this data is taken from the common
block.
SUMT The default is to output the intensity array as an array
of size (nwvl x nT). Setting this keyword performs a sum
over the temperatures to yield a vector of same size as
the input wavelengths, thus producing the complete
free-free spectrum.
PHOTONS Gives output emissivity in photon units rather than ergs.
CALLS
Chianti: SETUP_ELEMENTS
PROGRAMMING NOTES
In the Itoh et al. paper they state that their fitting formula is
valid for ion charges (Z_j) of 1-28. The data-file they provide
actually goes up to Z_j=30, and so you will see that the loop over
z (see below) goes up to 30.
There is no restriction on the elements for which the fitting
formula is valid, and so all elements are allowed to be included
(subject to their abundances being non-zero).
HISTORY
Ver.1, 3-Dec-2001, Peter Young
Ver.2, 22-May-2002, Peter Young
Added MIN_ABUND optional input.
Ver.3, 28-May-2002, Peter Young
Corrected way in which DEM is handled.
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME
KARZAS_XS()
EXPLANATION
Outputs the photoionization cross-section at the wavelengths WVL for
ionization of an N,L electron with ionization energy IONIZ_EN,
calculated using the Karzas & Latter (ApJS 6, 167, 1961) formulation.
The bound-free gaunt factor is derived from the tables of Karzas &
Latter.
INPUTS
WVL Wavelengths (in angstroms) for which cross-sections are
required (1-D array).
N Principal quantum number of the electron being removed in the
ionization.
L The orbital angular momentum of the electron being removed in the
ionization.
IONIZ_EN The ionization energy (in cm^-1) of the electron being
removed.
OPTIONAL INPUTS
PE Allows the PE array from READ_KLGFB to be directly input to
KARZAS_XS thus avoiding the need to read the K&L data
repeatedly for many ions. Requires KLGFB to also be input.
KLGFB Allows the KLGFB array from READ_KLGFB to be directly input to
KARZAS_XS thus avoiding the need to read the K&L data
repeatedly for many ions. Requires PE to also be input.
OUTPUT
The photoionization cross-section for the ionization of the outer
electron in units of mega-barns (Mb = 10^-18 cm^2) at the input
wavelengths. E.g., for Fe XIII (ground configuration
1s2.2s2.2p6.3s2.3p2) it is the cross-section for the removal of the
3p electron.
CALLS
READ_KLGFB
HISTORY
Ver.1, 24-Jul-2002, Peter Young
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME:
LANDSCAPE
PURPOSE:
:
CALLING SEQUENCE:
LANDSCAPE
INPUTS:
None
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
None
OUTPUTS:
None
COMMON BLOCKS:
None
EXAMPLE:
to make a postscript file in landscape orientation
> set_plot,'ps'
> landscape
> plot,x,y
> device,/close
> set_plot,'x'
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1996: Version 2.0
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
LATEX_WVL_DEM
PURPOSE:
create a latex file of predicted spectral line intensities and
wavelengths corresponding to a selected abundance and differential
emission measure (DEM)
PROCEDURE:
Calculations are done assuming either constant density or
constant pressure. See CH_SYNTHETIC for details.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
LATEX_WVL_DEM, Wmin, Wmax, Pressure= , [density= ], $
[outfile= , mini= , sngl_ion=, /photons, /all, /masterlist]
INPUTS:
Wmin: lower limit of the wavelength/energy range of interest (Angstroms)
if kev keyword set, then wmin is in kev
Wmax: upper limit of the wavelength/energy range of interest (Angstroms)
if kev keyword set, then wmax is in kev
Pressure: pressure in emitting region (cm^-3 K), or
Density: density in emitting region (cm^-3).
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
OUTFILE: the name of the output latex file to be written.
MINI: Minimum intensity for a line to be included in the output.
SNGL_ION: specifies a single ion (e.g. SNGL_ION='Fe_10' to include
only Fe X lines) or an array (e.g. SNGL_ION=['Fe_10','Fe_11']
to include only Fe X and Fe XI lines) of ions to be used
instead of the complete set of ions specified in
!xuvtop/masterlist/masterlist.ions
MASTERLIST: string of a specific masterlist file (full path).
If defined as a keyword (i.e. MASTERLIST=1 or /MASTERLIST)
then a widget allows the user to select a user-defined
masterlist file. Shortcut for SNGL_ION.
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
RADTEMP The blackbody radiation field temperature (default 6000 K).
OUTPUTS:
a latex file: 'linelist.tex' in the working directory by default
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
MINI: Minimum intensity for a line to be included in the output
SNGL_ION: specifies a single ion (e.g. SNGL_ION='Fe_10' to include
only Fe X lines) or an array (e.g. SNGL_ION=['Fe_10','Fe_11']
to include only Fe X and Fe XI lines) of ions to be used
instead of the complete set of ions specified in
!xuvtop/masterlist/masterlist.ions
MASTERLIST: string of a specific masterlist file (full path).
If defined as a keyword (i.e. MASTERLIST=1 or /MASTERLIST)
then a widget allows the user to select a user-defined
masterlist file. Shortcut for SNGL_ION.
PHOTONS: units will be in photons rather than ergs
KEV: wavelengths will be given in kev rather than Angstroms
ALL: if set, then all lines are included. This means that lines for which
only an approximate wavelength is known (only theoretical energy
levels are known) are included.
OUTFILE: the name of the output latex file to be written. By default a
file 'linelist.tex' in the user's working directory will be
created.
NOPROT If set, then proton rates are not included.
CALLS:
CH_SYNTHETIC, CH_LINE_LIST
COMMON BLOCKS: None
RESTRICTIONS:
SIDE EFFECTS:
EXAMPLE:
> latex_wvl_dem, 400.,800., mini=1, pressure=1.e+15,sngl_ion='o_4'
CATEGORY:
spectral synthesis.
WRITTEN :
Version 1, 8-Nov-01, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ).
Compared to the previous LATEX_WVL_DEM, these are the main changes:
1-Rewritten as a wrapper routine using the new procedures.
2-Now the PRESSURE value is a keyword.
3-The calculations can be done at constant DENSITY.
4-MASTERLIST can now be used both as an input string or as a keyword.
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Version 2, 18-Nov-01, Peter Young
Added /noprot, rphot and radtemp keywords.
V. 3, 22-May-2002 GDZ. Removed const_net definitions.
VERSION : Version 3, 22-May-2002
PROJECT : CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME : MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC
PURPOSE :
To create a CHIANTI synthetic spectrum
CALLING SEQUENCE:
IDL> make_chianti_spec, TRANSITIONS, LAMBDA, SPECTRUM,$
[BIN_SIZE= , ,INSTR_FWHM= , PIXEL=PIXEL, BINSIZE = BINSIZE, $
WRANGE= , ALL=ALL, continuum=continuum, $
ABUND_NAME= , MIN_ABUND=, photons=photons, effarea=effarea
PROCEDURE :
From information contained in the structure TRANSITIONS, constructs
a synthetic spectrum
By default, routine assumes thermal widths for lines.
PROGRAMMING NOTES
The line profile is constructed using the IDL gaussint routine.
For a wavelength pixel centred at l and with width dl, gaussint
is used to integrate the Gaussian up to l-dl/2 and up to l+dl/2.
The difference between the two is the intensity in this pixel.
INPUTS :
TRANSITIONS, the structure created by ch_synthetic.pro.
OPT. INPUTS :
LAMBDA Array of wavelengths (X-values). If not defined as input, it is
calculated on the basis of BIN_SIZE, and returned as an output.
If defined as input, the routine checks that there are at least
10 points in the wavelength range defined by WRANGE. If there
are, the corresponding subset of LAMBDA is returned, otherwise
the routine exits with an error.
BIN_SIZE Bin size in Angstroms of the spectrum to be created. A linear
spectrum is assumed. In case an effective area file is used, the
wavelenghts in the file (that might not be linear) are used to
create the spectrum, and this bin size looses any meaning.
WRANGE Allows a subset of the wavelength range to be turned into
a spectrum. When using syn_plot, this speeds up the routine
a lot if you've elected to zoom in on a region.
INSTR_FWHM Instrumental FWHM (Angstroms).
In case an effective area file is used, The line intensities
contributing to each bin are summed, and subsequently convolved
with a gaussian of full-width-half-maximum FWHM if FWHM is not
set = 0 . Please make sure that the FWHM value (if not set to
zero) is larger than the bin size.
ABUND_NAME A CHIANTI abundance file name can be set.
It allows the abundance file given in transitions.abund_name
(if present) to be over-ridden. Note that it also used for
the continuum calculation.
MIN_ABUND: If set, calculates line intensities only from those elements
which have an abundance greater than min_abund.
Can speed up the calculations. For example, from Allen
(1973):
abundance (H) = 1.
abundance (He) = 0.085
abundance (C) = 3.3e-4
abundance (O) = 6.6e-4
abundance (Si) = 3.3e-5
abundance (Fe) = 3.9e-5
FILE_EFFAREA
The Effective Area File (TWO COLUMNS - wavelengths in
Angstroms and cm^2 values) If defined, then the spectrum is
multiplied with these values. Any input LAMBDA value is
over-written by the wavelenghts in the file (that might not
be linear) and are used to create the spectrum.
Note that this option only works well if a sufficient number
of bins is given. The line intensities contributing to each
bin are summed, and subsequently convolved with a gaussian
of full-width-half-maximum FWHM, if FWHM is not set = 0.
Please note that the convolution might not work if a small
number of bins is defined.
OUTPUTS :
LAMBDA Array of wavelengths (X-values).
If not defined as input, it is
calculated on the basis of BIN_SIZE, and returned as an output.
If defined as input, the routine checks that there are at least
10 points in the wavelength range defined by WRANGE. If there
are, the corresponding subset of LAMBDA is returned, otherwise
the routine exits with an error.
SPECTRUM A structure containing all the information:
LAMBDA The array of X-values
SPECTRUM The array of Y-values
UNITS The units of LAMBDA, SPECTRUM
INSTR_FWHM The Instrumental FWHM
BIN_SIZE Width of the Bins (fixed) in angstroms
ABUND_NAME The CHIANTI abundance file name
ABUND The abundance values
MIN_ABUND The minimum abundance value used
ABUND_REF The references
CONTINUUM The values of the continuum (if calculated)
FILE_EFFAREA The Effective Area File used (optional)
EFFAREA The array of effective area values
(optional - same size of LAMBDA)
.LINES An array of structures, for all the lines used
to calculate the SPECTRUM.
The tags are the same as those created by
CH_SYNTHETIC, plus
.PEAK The peak intensity of the line in the spectrum
(approx. value)
OPT. OUTPUTS:
BINSIZE If BIN_SIZE is not specified, then the spectrum
bin-sizes are computed automatically, and the size of the
bin returned in BINSIZE.
KEYWORDS :
PIXEL The spectrum is given in /pixel units rather /ang
(DISABLED)
ALL Add lines that originally had negative wavelengths
PHOTONS If set=1, the output intensities will be in photons instead of
ergs.
CONTINUUM
If set, then the continuum is added to the
spectrum.
verbose
CALLS :
PRY: GET_ATOMIC_WEIGHTS
Chianti: FREEBOUND, FREEFREE
COMMON (with freefree freebound and two_photon):
elements,abund,abund_ref,ioneq,ioneq_logt,ioneq_ref
RESTRICTIONS: The input structure has to be of the type created by ch_synthetic.
The LAMBDA, EFFAREA values must be ordered in wavelength and the
LAMBDA values must be in Angstroms.
SIDE EFFECTS: None known yet.
EXAMPLES :
make_chianti_spec, output_struct, LAMBDA, SPECTRUM,$
bin_size=0.01, instr=0.1
CATEGORY :
spectral synthesis.
PREV. HIST. :
WRITTEN :
Peter Young , CfA, pyoung@cfa.harvard.edu 1-Sept-2000
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Version 1, PRY 1-Sept-2000
Version 2, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ) 10-Oct-2000
put ALL keyword, removed the FWHM obsolete and
confusing call. Reorganised various minor things.
Version 3, PRY 19-Oct-2000
Corrected the way continuum is treated for an isothermal
spectrum.
V. 4, 2-Nov-2001 GDZ. Now MIN_ABUND is effective not only in the
continuum calculation but also in the line spectrum.
Modified for the use of logt_isothermal
V.5, GDZ, added EFFAREA keyword: an ascii file with lambdas and
effective areas can be read
in. The line intensities are
calculated in a different way.
Also, changed the output.
V.6, GDZ, 28-Apr-02 redefined completely the OUTPUT structure.
Major revision (added two_photon verbose).
V.7, GDZ, 3-May-2002
fixed a bug, when negative angpix values occur.
V.8, GDZ, 22 May 2002, changed some tags of the output, and
added min_abund in the continuum call.
V.9, GDZ, 30-May-02 replaced fix() with round()
V. 10, 15-July-2002 , GDZ
changed the location of Effective area files.
V.11 14-Aug-02, GDZ
speeded up the routine, by changing the way the PEAK tag is
added to the structure. The drawback is that only the
'standard v.4 tags' are allowed, and future additions will
have to be dealt properly.
v.12 2-Dec-2002, GDZ.
Fixed a bug: Removed the plotting of the window with the effective areas.
v.13 26-Apr-2005, Enrico Landi (EL)
Fixed a minor bug: if the lines were more than 32768 (2^15), the main
loop crashed.
v.14 22-Jul-2005 GDZ
-fixed a bug. When the routine was run once without
defining the lambdas, and then with the lambdas
defined (the units were switched to photons)
-fixed a bug. When the effective areas were used,
all lines were used to create the spectrum.
-added hard-wired switch to photons when using
effective area files.
-added the keV option
-now can output a spectrum only with the continuum
(i.e. even if no emission lines are present).
15, 2-Aug-2005, GDZ
Added a check on the input structure. If it was
calculated with ch_synthetic and the keyword
/no_sum_int, it cannot be used here.
VERSION : 15, 2-Aug-2005
STILL TO DO:
-speed up the routine with the use of arrays.
-add the option to select only a list of ions, also in the
continuum procedures.
-Allow the use of user-defined line profiles.
-Enable PIXEL keyword
Project : SOHO - CDS
Name : MAKE_ION_LIST
Purpose : Reads masters ions list and interprets.
Explanation : Reads the CHIANTI master ion list and returns the list of
available elements and ions in suitable arrays.
Use : IDL> make_ion_list, elements, ions
Inputs : None
Opt. Inputs : None
Outputs : elements - string array of all elements available
ions - 2-d string array of roman ionization stages
available for each element. (N,M) where N is
number of elements and M is large enough to
contain all ionization stages (Null if not used)
Opt. Outputs: None
Keywords : None
Calls : None
Common : None
Restrictions: None
Side effects: None
Category : Spectrum
Prev. Hist. : None
Written : C D Pike, RAL, 19-Jan-96
Modified : V.2 Increased array sizes. CDP, 25-Jun-96
V.3. Further increase of the array sizes, and removed the 'd'
directories from the masterlist, to be compatible with CHIANTI
removed call to concat_dir Giulio Del Zanna 16-Oct-2000.
V.4 21-May-2002, GDZ:
generalize directory concatenation to work for Unix, Windows
and VMS.
Version : Version 4 21-May-2002
NAME
MATRIX_SOLVER()
PROJECT
CHIANTI
EXPLANATION
Takes the matrices for the various atomic processes employed in
CHIANTI and returns the level populations.
INPUTS
XNE Electron density (cm^-3). Scalar.
AA 2-D array of transition probabilities.
QQ 2-D array of electron excitation rates.
PPR 2-D array of proton rates
AAX 2-D array of photoexcitation/stimulated emission rates.
OPTIONAL INPUT
FRAC_CUTOFF The fraction of non-zero elements in the C matrix below
which the sparse matrix solver is used. The default value
is zero (i.e., don't use sparse matrix solver).
OPTIONAL OUTPUT
C The 2D matrix containing all rate coefficients.
OUTPUT
A 1-D array of level populations, scaled so that the sum of the
populations is 1.
HISTORY
Ver.1, 1-Jul-2005, Peter Young
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
Name : MAX_TEMP
Purpose : Calculates temperature at max ionisation ratio for an ion
Explanation :
Use : IDL> print,max_temp(ion)
Inputs : ion - the specific ion in the form eg 'Fe_XII' or 'Fe XII'
Opt. Inputs : None
Outputs : Function returns log of max temperature
Opt. Outputs: None
Keywords : ALL - if set produces a plot of all temperatures
Calls : Other CHIANTI routines
Common :
Restrictions: None
Side effects: None
Category : Spectral
Prev. Hist. : None
Written : C D Pike, RAL, 9-Jun-97
Modified : V.2 Update element list. CDP, 18-Jun-99
V.3 modified definition of XUVTOP, and allowed selection of
ionization eq. file. Giulio Del Zanna (DAMTP) 10-Oct-2000
V.4, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
VERSION : 4, 21-May-2002, GDZ
function mid2bound given mid-bin values, make an intelligent determination of the bin boundaries and return said boundaries (actually, it's not all that intelligent. uses spline interpolation) given input array of N elements, returns array of N+1 elements. parameters m [INPUT; required] the mid-bin values from which to expand out keywords eps [INPUT] a small number, default is 1e-6 verbose [INPUT] controls chatter _extra [JUNK] here only to prevent crashing the program history vinay kashyap (OctMM)
Project : SOHO - CDS
Name : PLOT_CHIANTI_NE
Purpose : Plots a density sensitive ration saved from CHIANTI_NE
Explanation : The routine CHIANTI_NE allows the calculated ratio to be
saved in an IDL save file. This routine retrieves and
plots the ratio.
Use : IDL> plot_chianti_ne, file, data
Inputs : file - save file name (an extension of .CH_NE will have
been added, specifying this is optional)
Opt. Inputs : None
Outputs : None
Opt. Outputs: data - returns the retrieved ratio structure
Keywords : log. If set, a log-log plot is produced.
Calls : print2d_plot
Common : None
Restrictions: None
Side effects: None
Category : Synthetic spectra
Prev. Hist. : None
Written : C D Pike, RAL, 7-Oct-96
Modified : v.2 Added a few extra things, including possibility to create a
postscript file.
Giulio Del Zanna (DAMTP), 10-Oct-2000
Version : Version 2, GDZ 10-Oct-2000
Project : SOHO - CDS
Name : PLOT_CHIANTI_TE
Purpose : Plots a temperature sensitive ratio saved from CHIANTI_TE
Explanation : The routine CHIANTI_TE allows the calculated ratio to be
saved in an IDL save file. This routine retrieves and
plots the ratio.
Use : IDL> plot_chianti_te, file, data
Inputs : file - save file name (an extension of .CH_TE will have
been added, specifying this is optional)
Opt. Inputs : None
Outputs : None
Opt. Outputs: data - returns the retrieved ratio structure
Keywords : log. If set, a log-log plot is produced.
Calls : None
Common : None
Restrictions: None
Side effects: None
Category : Synthetic spectra
Prev. Hist. : None
Written : C D Pike, RAL, 7-Oct-96
Modified : v.2 Added a few extra things, including possibility to create a
postscript file.
Giulio Del Zanna (DAMTP), 10-Oct-2000
Version : Version 2, GDZ 10-Oct-2000
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
PLOT_DEM
PURPOSE:
To plot differential emission measure (DEM) values
CATEGORY:
Widgets.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
PLOT_DEM,filename
INPUTS:
filename: the name of the DEM file to be plotted. The file must b
in the standard CHIANTI format for DEM files. If filename
is a blank string ('') then an interactive window will come
up to allow the user to select a DEM file from the CHIANTI
DEM directory or some other directory.
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
PSFILE: If set, the a postscript plot will be place in the
file 'psfile' specified by the user
OUTPUTS:
None, other than a plot
EXAMPLE:
> plot_dem,'ademfile.dem'
or
> plot_dem,''
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
June 1998: Version 1.0
Version 2, 21-Dec-2000, William Thompson, GSFC
Modified for better cross-platform graphics capability
V. 3, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
VERSION : 3, 21-May-2002
Project : SOHO - CDS
Name : PLOT_DMM_DR_FIG
Purpose : Plots line intensities in DMM_DR
Explanation : Internal routine used by CHIANTI_NE for plotting individual
line intensities.
Use : Called by CHIANTI_NE
Inputs : Uses common
Opt. Inputs : None
Outputs : None
Opt. Outputs: None
Keywords : None
Calls : None
Common : dmm_lines
Restrictions: None
Side effects: None
Category : Spectral, plotting
Prev. Hist. : Originally included in density_ratios by K Dere
Written : C D Pike, RAL, 15-Jan-96
Modified : V.3 Fix bug in searching for peak line (IMAX). CDP, 27-Jan-96
Changed charsize in plots. CDP, 17-Jul-97
V.4 changed yranges in the plots. Removed common calls not
needed. Giulio Del Zanna 6-Oct-2000
Version : Version 4, 6-Oct-2000
Project : SOHO - CDS
Name : PLOT_DMM_TR_FIG
Purpose : Plots line intensities in DMM_TR
Explanation : Internal routine used by CHIANTI_TE for plotting individual
line intensities.
Use : Called by CHIANTI_TE
Inputs : Uses common
Opt. Inputs : None
Outputs : None
Opt. Outputs: None
Keywords : None
Calls : None
Common : dmm_lines
Restrictions: None
Side effects: None
Category : Spectral, plotting
Prev. Hist. : Originally included in density_ratios by K Dere
Written : C D Pike, RAL, 15-Jan-96
Modified : Fix bug in searching for peak line (IMAX). CDP, 27-Jan-96
V.1 H E Mason, 03-Oct-96
V.2 changed yranges in the plots. Removed common calls not
needed. reinstated the two plots. Changed various things.
Giulio Del Zanna (DAMTP), 10-Oct-2000
Version : Version 2,
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
Name : PLOT_IONEQ
Purpose : Plots the ionisation equilibrium values for an element.
Explanation :
Use : IDL> plot_ioneq, element [ ion=ion]
Inputs : element - the element name
Opt. Inputs : Ion (as keyword)
Outputs : None
Opt. Outputs: a postscript file.
Keywords : ION_RANGE - specify range of ions. E.g., ion_range=[5,8]
means V to VIII inclusive.
IONEQ_NAME: Name of the ionization equilization name to use.
If not passed, then the user is prompted for it.
NOT_INTERACTIVE Avoid interactive use.
Calls : Other CHIANTI routines
Common :
Restrictions: None
Side effects: None
Category : Spectral
Prev. Hist. : None
Written : C D Pike, RAL, 9-Jun-97
Modified : V.2. Update element list. modified definition of XUVTOP, and
allowed selection of ionization eq. file and creation of
postscript file.
Giulio Del Zanna (DAMTP) 10-Oct-2000
V.3, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V 4, 15-July-2002, GDZ
Added keywords ioneq_name, not_interactive
V.5, 9-Feb-2005, Peter Young
Changed ion= keyword to ion_range=
VERSION : 5, 9-Feb-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
PLOT_POPULATIONS
PURPOSE:
plot the population of a number of the lowest levels as a function of
electron density for a specific temperature
CATEGORY:
science.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
PLOT_POPULATIONS,Ion,T,Nlevels
INPUTS:
Ion: CHIANTI style name for the ion, i.e., 'c_6' for C VI
T: electron temperature (K)
OPTIONAL INPUT:
Nlevels: the number of levels for which populations are plotted
starts from level 1 (the ground level)
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
OUTFILE: the (optional) name of the output file where the listing
is produced
PSFILE: the (optional) name of the output file where a postscript
plot produced
RADTEMP Specify background radiation temperature (default: 6000 K)
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
NOT_INTERACTIVE Avoid interactive use.
OUTPUTS:
COMMON BLOCKS:
common elvlc,l1a,term,conf,ss,ll,jj,ecm,eryd,ecmth,erydth,eref
common wgfa, wvl,gf,a_value
common upsilon,t_type,c_ups,splups
CALLS
POP_SOLVER, ION2SPECTROSCOPIC, ION2FILENAME, READ_IP,
CONVERTNAME, READ_ELVLC, READ_WGFA2, READ_SPLUPS
EXAMPLE:
to plot populations of the 5 ground configuration levels of Fe XIII
and store these values in a file 'Fe_XIII.lis' for a temperature of 1.5 MK
> plot_populations,'fe_13',1.5e+6,5,outfile='Fe_XIII.lis'
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1996: Version 2.0
November 1997: Ken Dere, added psfile keyword
September 1999: Ken Dere, for Version 3,
14-Jul-2000 Peter Young, now calls pop_solver
Version 6, 21-Dec-2000, William Thompson
Modified for better cross-platform capability.
V. 7, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ), modified the plotting bit
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V 8, 15-July-2002, GDZ
Added keyword not_interactive
V 9, 4-Oct-2003, GDZ
modified the input to POP_SOLVER, now it is dealt with an
input structure.
V 10, 4-May-2005, Enrico Landi (EL)
Modified in order to include ionization and recombination
data in the input to POP_SOLVER, now it allows choice of .ioneq
file needed to include ionization and recombination.
V 11, 12-Aug-2005, GDZ
The number of levels is now optional. Also, a check that the
number of levels must be less than the levels in the file is
now enforced.
VERSION : 11, 12-Aug-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME: POP_PLOT
PURPOSE:
To compute n_j A_ji / N_e for a selected transition(s) and plot it
against N_e. If it is insensitive to N_e, then the line(s) is
suitable for emission measure analysis.
CATEGORY:
Atomic data analysis
EXPLANATION:
The routine calls EMISS_CALC to give values of DE*n_j*A_ji at the
temperature TEMP and densities from 10^8 to 10^12. You are then
asked to select which transition(s) you are interested in. (If
more than one line is selected, the lines are blended.)
DE*n_j*A_ji/N_e is then plotted against density.
If TEMP is not specified, then the temperature at which the
ionisation fraction has its maximum is calculated. For the iron
ions, the ion balance calcs of Arnaud & Raymond are used,
otherwise Arnaud & Rothenflug are used. If TEMP is specified,
and the value is less than 20, then it is assumed that the log
of the temperature has been specified.
In emission measure work it is important to isolate lines for
which DE*n_j*A_ji/N_e is insensitive to density. If only such lines
are used, then the derived emission measure curve is independent
of density.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
POP_PLOT, IZ, ION, WRANGE=WRANGE, [TEMP=TEMP, /QUICK, DATA=DATA, $
DENS_RANGE=DENS_RANGE, DILUTE=DILUTE]
EXAMPLES:
POP_PLOT, 26, 14, WRANGE=[330,360]
- 3 lines should appear in the widget. Selecting 334.17 should show
a curve that falls off with density. Choosing 353.83 shows a curve
that rises with density. By selecting a blend of the two lines,
the curve will be insensitive to density, telling us that only a
blend of 334.17 and 353.83 is suitable for emission measure work.
POP_PLOT, 8, 4, WRANGE=[550,560], TEMP=6.0, /QUICK, DENS_RANGE=[6,10]
- O IV is a member of the boron sequence, and so calculations take a
lot longer. Giving the QUICK keyword speeds things up. The
temperature is well away from the T_max of the ion
INPUTS:
IZ The atomic number of the ion
ION The spectroscopic number of the ion (e.g., 12 = XII)
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
DILUTE Used to set radiative dilution factor. (Default: 0.0)
TEMP The temperature at which calculations are required. Usually
this will be the Tmax of the ion.
DENS_RANGE The default density range is log Ne = 8 to 12. By
inputting two integers, a different range can be chosen.
WRANGE Wavelength range from which lines are required. If not
given, then the user is allowed to choose from the complete
set of lines for the ion.
ABUND_FILE The name of a CHIANTI abundance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio. Default is
!abund_file.
IONEQ_FILE The name of a CHIANTI ion balance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio and evaluating
the T_max of the ion. Default is !ioneq_file.
RADTEMP The blackbody radiation field temperature (default
6000 K).
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius
units. I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface.
(Default is infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
DATA: An array that contains the data that is plotted: data(*,0)
contains
the densities, while data(*,1) contains the Y-axis values.
KEYWORDS:
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
QUICK: The density range over which the calculations are done is
8 to 12 in 0.2 intervals. This keyword forces the
calculations to be done at 0.5 intervals.
CALLS:
EMISS_CALC, EMISS_SELECT, READ_IONEQ
HISTORY:
Ver.1, PRY 28-Jul-97.
Ver.2, PRY 23-Sep-97 - added DILUTE keyword for photo-excitation
Ver.3, PRY 30-May-98 - added DENS_RANGE
Ver.4, PRY 5-Sep-98 - added call to choose_ioneq
Ver.5, PRY 7-Apr-99 - tidied up, and introduced call to emiss_select
Ver.6, PRY 7-Dec-01 - modified for v.4 of CHIANTI
V. 7, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V.8, 06-Aug-02 GDZ
added ABUND_FILE to the call to emiss_calc (was missing).
Changed the use of CHIANTI system variables.
VERSION : 8, 06-Aug-02
NAME
POP_PROCESSES
PROJECT
CHIANTI
PURPOSE:
Outputs to the screen the contributions of the different physical
processes to the population of the specified level within the ion.
E.g., for Fe XIII, level 4, the output is:
Population leaving level 4
rad. decay: 1.51e+01 39.17%
e de-exc: 3.56e-01 0.92%
e exc: 2.28e+01 59.12%
p de-exc: 2.63e-01 0.68%
p exc: 4.05e-02 0.11%
stim. emiss: 0.00e+00 0.00%
photoexc: 0.00e+00 0.00%
--------
TOTAL 3.85e+01
Population entering level 4
rad. decay: 3.59e+01 93.19%
e de-exc: 3.81e-02 0.10%
e exc: 1.46e+00 3.79%
p de-exc: 3.18e-03 0.01%
p exc: 1.12e+00 2.91%
stim. emiss: 0.00e+00 0.00%
photoexc: 0.00e+00 0.00%
--------
TOTAL 3.85e+01
which shows that the level population is dominated by electron
excitation and cascading into the level, and by radiative decay
out of the level.
Note that the rates for each physical process are multiplied by the
population of originating level (this results in the totals for
entering and leaving the level to balance).
For some ions, ionization and recombination are additional processes
included when working out the level balance. Because of the way these
processes are included (see the v.5 paper for details), the populations
entering and leaving some levels *will not balance*.
INPUTS
IZ The atomic number of the ion
ION The spectroscopic number of the ion (e.g., 12 = XII)
OPTIONAL INPUTS
LEVEL The ion level for which information is required.
DENS Electron density at which rates calculated (units: cm^-3).
If not specified, a value of 10^10 is assumed.
TEMP Temperature at which rates calculated (units: K). If not set,
then T_max of the ion is used
PATH If the ion data-files are not in the CHIANTI directories,
then PATH allows you to choose an alternative location.
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
RADTEMP Specify background radiation temperature (default: 6000 K)
N_LEVELS Restrict the ion model to this number of levels. E.g., if
the CHIANTI model contains 40 levels for the ion, then
setting N_LEVELS=12 reduces the model to 12 levels.
RADFUNC The name of a user-defined function that will generate
a radiation spectrum as a function of temperature.
This radiation field will replace the black-body that
is assumed when using the RADTEMP keyword in the call
to pop_solver.
KEYWORDS
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
CALLS
R2W, ZION2FILENAME, PROTON_DENS, POP_SOLVER, SETUP_ION
EXAMPLES
One can compare the effect of cascading on a level population by using
the N_LEVELS keyword. Consider the case of Fe XIV:
IDL> pop_processes,'fe_14',lev=5
IDL> pop_processes,'fe_14',lev=5,n_levels=12
With the first call there are two dominant terms to the population
entering level 5: approximately 47% for radiative decays (cascading)
and 53% for electron excitation. Setting n_levels=12, one finds that
the cascading contribution disappears as there are no longer any
high-lying levels that cascade into level 5. The cascading provides
a strong contribution to the population of this level.
HISTORY
Ver.1, 11-Sep-2002, Peter Young
Ver.2, 15-Jan-2004, Peter Young
modified call to pop_solver following recent revision to
pop_solver; changed input from IZ,ION to IONNAME to match other
CHIANTI routines
Ver.3, 26-May-2005, Peter Young
changed TEMP and DENS keywords
Ver.4, 10-Jun-2005, Peter Young
added common block for ionization/recombination data and modified
INPUT structure.
Ver.5, 14-Jun-2005, Peter Young
routine now prints the percentage contribution of each process;
added N_LEVELS= keyword
Ver.6, 1-Jul-2005, Peter Young
added warning for ions with ionization/recombination
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
astrophysical emission line spectra. It is a collaborative project
involving Ken Dere (Naval Research Laboratory, Washington DC),
Brunella Monsignori-Fossi and Enrico Landi (Arcetri Observatory,
Florence), and Helen Mason and Peter Young (DAMTP, Cambridge Univ.).
NAME: POP_SOLVER
PURPOSE:
To solve the level balance equations for Chianti ions.
CATEGORY:
Scientific analysis
EXPLANATION:
This routine solves the level balance equations for the CHIANTI ions.
Atomic data is pre-loaded into the COMMON blocks, and so POP_SOLVER
can only be called indirectly through other routines.
The matrix equation Ax=b is solved where A contains all the atomic
data (electron rate coefficients, radiative decay rates, proton rate
coefficients, photoexcitation rates), x are the level populations,
and b a vector set to zeros except for the first element which is 1.
To solve the matrix equation, pop_solver calls out to the CHIANTI
routine matrix_solver.
The matrix A is created from the atomic data in the COMMON blocks.
In order to optimise POP_SOLVER, A is created where possible through
array operations rather than FOR loops.
With v.5 of CHIANTI the additional atomic processes of ionization
and recombination can be included when calculating the level
populations. These processes are not included in the matrix A.
Instead the level populations x are 'corrected' for ionization and
recombination afterwards. This correction is performed by the routine
correct_pops. More details of this method are found in the CHIANTI
v.5 paper.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
POP_SOLVER, T, XNE, POP, N_LEVELS=N_LEVELS
INPUTS:
T Temperatures, e.g., 10.^6
XNE Densities, e.g., 10.^8
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
N_LEVELS This allows the number of levels in the model to
be reduced. E.g., if the full model contains 100
levels, one could set n_levels=50. This can be
useful if one is interested in looking at the
effects of cascading from higher levels
SUM_MWL_COEFFS An array of coefficients of the same length as
the array of temperatures. Electron and proton rate
coefficients will be calculated at each temperature
and then a weighted sum of the coefficients is
performed using SUM_MWL_COEFFS. This allows
non-Maxwellian energy distributions to be
incorporated into the level balance equations.
RADFUNC The name of a user-defined function that will generate
a radiation spectrum as a function of temperature.
This radiation field will replace the black-body that
is assumed when using the RADTEMP keyword in the call
to pop_solver.
FRAC_CUTOFF The fraction of non-zero elements in the C matrix below
which the sparse matrix solver is used. See the routine
matrix_solver for more details.
OUTPUT:
POP An array of level populations of size
n_T x n_XNE x n_levels
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS
DATA_STR If POP_SOLVER is called for just 1 temperature and density,
then the individual data arrays for each of the physical
processes can be output through DATA_STR. This allows the
user to check for the dominant processes affecting the
population of a given level. DATA_STR is a structure with
the following tags:
.aa A-values (2D array)
.aax Photoexcitation/stimulated emission (2D array)
.cc Electron rate coefficients (2D array)
.ccp Proton rate coefficients (2D array)
.ion_rate Ionization rate (1D array)
.rec_rate Recombination rate (1D array)
.correction Correction factor for level pop (1D array)
.frac_low Ratio of N+1 ion fraction to N (scalar)
.frac_high Ratio of N-1 ion fraction to N (scalar)
The 2D arrays are such that, e.g., aa[0,20]
corresponds to an excitation, while aa[20,0] is a
de-excitation.
The 1D arrays are simply the rate coefficients into the
individual levels.
PROGRAMMING NOTES:
PROTON RATES
------------
To include the proton rates, it is necessary to have the
proton-to-electron ratio. This needs to be calculated before the
call to pop_solver, and the resulting ratio(s) passed through
'pe_ratio' in the common block 'proton'.
Note that there is no keyword to switch off proton rates (i.e.,
no /NOPROT keyword). To switch off proton rates, it is necessary
to set pstr=-1. This should be done by the calling routine.
COMMON BLOCKS:
None.
CALLS:
DESCALE_ALL, PROTON_DENS(), MATRIX_SOLVER(), CORRECT_POPS()
HISTORY:
Ver 1, PRY 29-Mar-99
Ver 2, PRY 30-Apr-99, added call to get_prot_rates
Ver 3, PRY 15-Dec-99, added deu to upsilon common block in order
to be consistent with the main Chianti routines.
Ver 4, PRY 9-May-00, corrected problem with threshold when dealing
with sparse matrices. Basically values less than 1.e-30 in
the c-matrix were being set to zero and giving rise to
NaN's in certain circumstances.
Ver.5, PRY 14-Jul-00, changed elvl common block to the elvlc common
block which is now the Chianti standard. Also, when
descaling upsilons, the routine now uses the Delta-E from
the .splups file.
Ver.6, PRY 9-Aug-00, changed routine to deal better with the
dielectronic recombination files
Ver.7, PRY 17-Aug-00, routine does not call LINBCG now if radtemp
is non-zero.
Ver.8, PRY 29-Aug-00, the sparse matrix section has been disabled.
Ver.9, PRY 12-Nov-01, calls routine proton_dens() to calculate the
proton to electron ratio.
Ver.10, PRY, 6-Dec-01, corrected bug when there are more levels
in .splups file than in .elvlc file (ZnXXV).
Ver.11, PRY, 11-Jul-02, removed ION keyword
Ver.12, PRY, 9-Aug-02, within the equation solving section, I've set
the population of the ground level (rather the n_level level)
to 1, and this seems to stop negative populations appearing
in extreme conditions.
Ver.12, PRY, 21-Aug-02, changed exp(-1/1/a) to exp(-a) in electron
excitation section which caused a hang-up in some
circumstances. Also, the routine now uses vector ECMC
(combined experimental and theoretical energies) in
determining if a level lies above or below another level.
Previously only used the observed energy vector. Also, the
exponential in the electron excitation section now uses the
(accurate) .elvlc energy separation rather than the .splups
energy separation, which can cause significant (~20-30%)
differences in level populations of high-lying levels at
low temperatures.
Ver.13, PRY, 10-Sep-02, corrected bug for proton rates. The excitation
and de-excitation rates were being swapped.
V. 14 4-Oct-2003 Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ).
-removed all COMMON blocks (note that only proton_dens.pro has
one: COMMON elements,abund,abund_ref,ioneq,ioneq_logt,ioneq_ref)
-only the essential information input is passed to the routine
via a new input structure.
-fixed a bug, that affected all the satellite lines, and was
introduced in v.12, included in CHIANTI v.4.0.
basically the ionization potential was not subtracted when
calculating the Delta E in the exponential.
V. 15 7-Oct-2004 Enrico Landi (EL)
Included ionization and recombination as level population
processes.
V. 16 6-Apr-2005 Enrico Landi (EL)
Included extrapolation of ionization and recombination rates
for temperatures beyond those provided in the .ci and .rec
files.
V. 17 10-Jun-2005 Peter Young
Tidied up code, introduced call to correct_pops for
ionization/recombination, and added radfunc= and
sum_mwl_coeffs= keywords
V. 18 12-Jul-2005, Peter Young
Improved implementation of RADFUNC keyword
V. 19 27-Jul-2005, Peter Young
Corrected bug when the ionrec structure does not exist.
V. 20 16-Aug-2005, Peter Young
Routine now catches any NaN values in the level populations
and prints a warning. All pops are set to zero in this case.
VERSION : 20, 16-Aug-2005
Project : SOHO - CDS
Name : print2d_plot
Purpose : this routine optionally changes the ranges of a 1D plot
and print the plot to a landscape postscript file.
Explanation :
This routine changes the keywords pr, x_min,x_max,y_min,y_max
in order to change the range of a 2-D plot, or to open a
SET_PLOT,'ps' and create a postscript.
This is done basically repeating the sequence of commands in the
calling routine, within a loop.
The routine that calls print2d_plot should have :
window,/free
;;to open a window
x_min=min(lambda) & x_max=max(lambda)
y_min=min(sp) & y_max=max(sp)
;; to set the initial limits of
;; a one-dimensional plot.
pr=''
begin_plot_sp:
plot,lambda,sp,xr=[x_min,x_max],yr=[y_min,y_max],$
xstyle=1,ystyle=1
;; to plot (etc....)
print2d_plot, pr=pr, x_min=x_min,x_max=x_max,$
y_min=y_min,y_max=y_max,$
go_to_line=go_to_line,$
out_name=out_name,/ask_name
or:
print2d_plot, pr=pr, x_min=x_min,x_max=x_max,$
y_min=y_min,y_max=y_max,$
go_to_line=go_to_line,$
out_name='spectrum.ps'
;;to create the ps file spectrum.ps
if go_to_line eq 'y' then goto,begin_plot_sp
If you have an image or a stack of images, the limits cannot be
changed and you should omit the min,max limits.
Use : IDL>
Examples :
Inputs :
Opt. Inputs :
Outputs :
Opt. Outputs:
Keywords :
Calls :
Common : None.
Restrictions: None.
Side effects: None known yet.
Category :
Prev. Hist. :
Written :
Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ),
UCLAN (University of Central Lancashire, UK)
Modified : Version 1, GDZ Fri Jan 30 12:21:59 1998
v.2 GDZ added set_plot, 'ps',/copy ,/inter 02-Feb-2000
Version 3, 21-Dec-2000, William Thompson
Modified for better cross-platform capability.
Ver 4, 1-May-02, GDZ
Modified the setup to go back to display.
Version : Version 4, 1-May-02
NAME
PROTON_DENS()
EXPLANATION
Calculates the ratio of the proton density to electron density using
abundance and ion balance files.
INPUTS
TEMP The logarithm (base 10) of the temperature(s) for which the
ratio is required. Can be an array.
OUTPUT
An array of same size as TEMP containing the proton-to-electron ratio.
KEYWORDS
HYDROGEN If set then the routine computes the ratio of hydrogen to
free electrons.
CALLS
READ_IONEQ, READ_ABUND
COMMON BLOCKS
ELEMENTS
PROGRAMMING NOTES
To work out the proton/electron ratio, an ion balance and abundance
file are required. These can be specified through the common block,
otherwise the default files are assumed (!ioneq_file and !abund_file).
Because the ion balance data is tabulated only for logT from 4.0 to
8.0, the proton/electron ratio can only be calculated for this range.
Above and below these temperatures, the values at 8.0 and 4.0 are
assumed, respectively.
I've added a check to see if the temperatures are tabulated at 0.1
dex intervals (e.g., 4.0, 4.1, etc.). If they are, then a quicker
algorithm is used to calculate p/e ratios. This is useful for
synthetic.pro.
HISTORY
Ver.1, 5-Dec-2001, Peter Young
Ver.2, 3-Dec-2001, Peter Young
Added /hydrogen keyword.
V. 3, 22-May-2002, GDZ:
generalize directory concatenation to work for Unix, Windows
and VMS.
V.4, 06-Aug-02 GDZ
Changed the use of CHIANTI system variables.
VERSION : 4, 06-Aug-02
NAME
R2W()
EXPLANATION
Converts a distance above a star into a dilution factor.
INPUTS
R Distance above a star's surface, measured from the star's
center, in stellar radii units. E.g., R=1 is the surface.
OUTPUT
Radiation dilution factor - a number between 0 and 0.5
HISTORY
Ver.1, 8-Aug-2001, Peter Young
Ver.2, 12-Nov-2001, Peter Young
catches error if r < 1.
CONTACT
Peter Young, CfA, pyoung@cfa.harvard.edu
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
RAD_LOSS
PURPOSE:
Calculates energy loss rate by free-free (ff), radiative
recombination (fb) and by line (bound-bound) radiation.
CATEGORY:
synthetic spectra
CALLING SEQUENCE:
RAD_LOSS,Temperature,Loss_rate
INPUTS:
None: The user will select an elemental abundance file and a
ionization equilibrium file through widgets.
KEYWORDS:
Pressure: pressure in emitting region (cm^-3 K)
density=pressure/temperature(K)
Density: density (cm^-3), constant for all temperatures
if neither density or pressure is set, then a default
constant density of 10^10 cm^-3 is used.
Psfile: to create a postscript plot of the radiative loss in
the file specified by the name assigned to 'Psfile'
Outfile: name of an ascii file where the radiative loss rate
as a function of temperature is output
RADTEMP Specify background radiation temperature (default: 6000 K)
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
OUTPUTS:
Temperature: array of temperatures (K)
Loss_rate: energy loss rate in erg cm^3 s^-1
PROCEDURE:
if keyword pressure is set then calculations performed at constant pressure
if keyword density is set then calculations performed at constant density
otherwise, density is set to 1.e+10
pressure = density * temperature (cm^-3 K)
the user will be asked to select an abundance file and a
ionization balance file.
EXAMPLE:
> rad_loss,t,r
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
January 1999: version 1, adopted from synthetic.pro
Version 2, 21-Dec-2000, William Thompson
Modified for better cross-platform capability.
Ver.3, 6-Dec-2001, Peter Young
Added /noprot, radtemp and dilute keywords.
Removed elvlc, wgfa and upsilon common blocks.
Removed calls to read_ip and read_masterlist (not needed).
Ver.4, 8-Jul-2003, Peter Young
Updated routine header (no changes to code).
V 5, 25-May-2005, GDZ
corrected routine header.
VERSION : 5, 25-May-2005, GDZ
NAME
RATE_COEFF()
PROJECT
CHIANTI
EXPLANATION
Returns the electron rate coefficient in units of cm^3 s^-1.
Either the entire excitation/de-excitation array for the specified
ion or, if the TRANS= keyword is used, the excitation rate for
the specified transition.
INPUTS
IONNAME The CHIANTI ion identifier, e.g., 'o_6' for O VI.
TEMP Specify temperature(s) at which upsilon(s) are required.
Note that this can be an array. Units: K.
KEYWORDS
QUIET Prevents printing of information to the screen.
OPTIONAL INPUTS
TRANS Level indices for transition, e.g., [1,2] for transition
1-2.
PATH If the data files are in a different directory from the
standard CHIANTI distribution, then this keyword should be
set to the directory. E.g., PATH='/home/mydata/o/o_6'
OUTPUTS
Returns the 2D array containing excitation and de-excitation
coefficients. If E(i) < E(j) then CC(i,j) will be the excitation
coefficient and CC(j,i) will be the de-excitation coefficent.
If the keyword TRANS= is set, then the routine only returns the
excitation coefficient for the specified transition.
EXAMPLES
IDL> help,rate_coeff('o_6',3e5)
DOUBLE = Array[40, 40]
IDL> result=rate_coeff('o_6',3e5,trans=[1,3])
Wavelength: 1031.91
Exc. rate coeff: 1.913e-008
De-exc. rate coeff: 1.522e-008
IDL> print,result
1.9130775e-008
CALLS
CONVERTNAME, ZION2FILENAME, ZION2NAME, SETUP_ION, POP_SOLVER,
READ_IONEQ, READ_ABUND, PROTON_DENS
HISTORY
Ver.1, 22-Jun-2004, Peter Young
Ver.2, 5-Jul-2005, Peter Young
updated for v.5 of CHIANTI
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME: RATIO_PLOTTER
PURPOSE:
A widget-based routine to allow the analysis of density or
temperature sensitive ratios.
EXPLANATION:
RATIO_PLOTTER is designed to study temperature and density
sensitive line ratios. For temperature ratios, just use the
keyword /temp; for density ratios just use /dens.
The routine allows line ratios relative to a
particular line (called the 'denominator line') to be viewed. One
can either choose a particular numerator, or one can simply view
all ratios within a specified wavelength range (see the button widget
just above the main plot window).
In the former case, the numerator line can be chosen either from the
strongest lines, or from all lines within a specified wavelength
range.
A wavelength range is selected via the sliders at the lower left of
the main widget.
A default set of emissivity parameters is used initially to create
the first plot that you see. To change the parameters, click on the
'CHANGE PARAMETERS' button near the top of the GUI. This activates
a new set of widgets allowing the user to change whether energy or
photon units are needed, whether proton rates are included, the
temperature/density range, etc. Note that while the parameters are
being changed, the user can not modify the line selection or plot
parameters.
When a particular numerator line has been selected, observed
intensities (and error bars) for both the denominator and numerator
can be input, and the derived density (plus error bars) can be seen
on the plot (click on 'PLOT ERROR BARS'), or in a text widget (see
the 'SHOW DERIVED DENSITIES' button).
The accuracy of the derived density or temperature is limited by the
intervals in the emissivity calculation. The intervals can be
changed on the widget (there are 4 choices given) and if a new
interval is selected, new emissivities should be calculated.
Using the smallest intervals will give the highest accuracy for
the computed density or temperature.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
RATIO_PLOTTER, IZ, ION [, /TEMP, /DENS, EM, PATH=, /NOPROT, $
IONEQ_FILE=, ABUND_FILE= ]
EXAMPLES:
RATIO_PLOTTER, 26, 13, /TEMP ; Fe XIII
RATIO_PLOTTER, 10, 6, /DENS ; Ne VI
RATIO_PLOTTER, 26, 13, /DENS, PATH='/home/new_chianti_data'
INPUTS:
IZ: The atomic number of the ion
ION: The spectroscopic number of the ion (e.g., 12 = XII)
OPT. INPUTS:
EM: Save the displayed emissivities to structure EM. This
structure is simply the structure EMISS_SELECT used in
the routine, with some extra tags. This structure has the
tags:
.lines.emiss Emissivities of line at requested densities
.lines.wavel Wavelength(s) of line (blend)
.dens Log10 electron density/densities
.temp Log10 electron temperature(s)
.rphot Photoexcitation radius
.radt Radiation temperature
.proton String indicating whether proton rates are
included.
.date The date and time at which structure was
created.
.version The version of CHIANTI that created the
structure.
PATH: Data in the CHIANTI format that is not in the CHIANTI
database can be read by specifying the directory in which
it lies through PATH.
ABUND_FILE The name of a CHIANTI abundance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio. Default is
!abund_file.
IONEQ_FILE The name of a CHIANTI ion balance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio and evaluating
the T_max of the ion. Default is !ioneq_file.
KEYWORDS:
DENSITY If set then ratios are plotted as a function of
density rather than temperature.
TEMPERATURE If set then the ratios are plotted as a function of
temperature rather than density.
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
PROGRAMMING NOTES:
RATIO_PLOTTER is actually a collection of several routines....
DENS_FINDER - converts observed ratios into densities
INDEX_EXTRACTOR - a device for extracting indices out of arrays
WAVEL_PLOT - plots the little window in bottom left of GUI
DENS_PLOT - updates the plot window
DENS_MAIN_EVENT - responds to widget actions
SAMPLE_WID - sets up the widgets
RATIO_PLOTTER - loads up various initial parameters
The emissivities of all the ion's lines are stored in the
structure "emiss", while those of the selected lines are stored
in "emiss_sel". This latter can be output into IDL by giving the
"EM" optional input on the command line.
The routine is set up to allow more than one numerator to be
displayed at once, but I've never actually found a need to
implement this yet. (Note that you'll see "Numerator 1" on
the widget.)
CALLS:
EMISS_CALC, READ_IONEQ, EMISS_SELECT, ZION2NAME,
ZION2FILENAME, ZION2SPECTROSCOPIC, PS, PSCLOSE, IS_NUMBER,
CHIANTI_FONT, TRIM
INTERNAL PROCEDURES AND FUNCTIONS
DENS_FINDER, INDEX_EXTRACTOR, DENS_PLOT, DENS_MAIN_EVENT,
SAMPLE_WID, WAVEL_PLOT
COMMON BLOCKS
EMISS_DATA, SELECT, SLIDERS, PLOTTING, RAD_DATA, PROTON_RATES,
EXTRA, ELVLC, FILES, TEMP
HISTORY:
Ver.1: PRY, 15-SEP-97.
Ver.2: PRY, 6-JUL-98, added EM and PATH
Ver.3: PRY, 5-SEP-98, added call to choose_ioneq
Ver.4: PRY, 11-JAN-99, added PROTON keyword and widget to allow
the addition of proton rates
Ver.5: PRY, 3-FEB-99, added a title to the widget, and the name
of the ion to the ratio plot title
Ver.6: PRY, 25-MAR-99, corrected bug for wavelengths > 1000
angstroms
Ver.7: PRY, 1-JUN-99, routine now works in CDS environment
without use_dere_chianti
Ver.8: PRY, 22-FEB-00, corrected colour problem
Ver.9: PRY, 17-AUG-00, added windows identifying the numerator
and denominator transitions. This required an
extra routine (MAKE_STRINGS) and a common block
(ELVLC).
Ver.10: PRY, 25-AUG-00, added buttons to allow a choice between
ratios in energy or photon units.
Ver.11: PRY, 25-AUG-00, can now specify a wavelength range by
directly typing in the numbers
Ver.12: PRY, 30-Nov-00, changed call to emiss_select
Ver.13: PRY, 21-Dec-00, removed set_plot,'x' following help from
Bill Thompson
Ver.14, PRY, 27-Dec-00, changed switch to tst1 for IDL v5.4
Ver.15, PRY, 7-Dec-01, changed /prot keyword to /noprot to be
compatible with other CHIANTI routines.
Added /temperature keyword.
Ver.16, PRY, 28-May-02, removed SPLINE calls, changing them to
SPL_INIT and SPL_INTERP; changed density labels to
temperature labels where appropriate.
Ver.17, PRY, 29-May-02, made treatment of photoexcitation consistent
with other CHIANTI routines.
V. 18, 29-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for Unix,
Windows and VMS.
Now we only call zion2filename.
When creating the ps file, ps and psclose are used.
v.19, 12-Jun-02 GDZ
fixed a small bug when finding the names of the files when the
keyword PATH is given.
v.20, 2-Aug-02, Peter Young
made some cosmetic changes following Giulio's suggestions.
v.21, 5-Aug-02, Peter Young
made various changes:
- the emissivity parameters (at top of widget) can only be
changed independently of line selection now
- the text widgets now check to make sure the user inputs
are numbers.
- extended the number of tags on the output EM structure
v.22, 6-Aug-02, Peter Young
corrected plot problem when viewing all temperature ratios
in a fixed wavelength range.
v.23, 8-Aug-02, Peter Young
a number of cosmetic changes to make the GUI more
user-friendly
v.24, 13-Aug-02, Peter Young
changed the temperature/density text widget so that numbers
are registered even if the return key has not been hit.
v.25, 14-Aug-02, Peter Young
photoexcitation button now works again; also some cosmetic
changes
V.26, 17-Sept-02, GDZ
added scrolling in main frame
V.27, 10-Feb-03, Peter Young
corrected bug related to fonts on Windows PCs
V.28, 13-Feb-03, Peter Young
corrected problem when ion balance data dosen't exist for
an ion
V.29, 18-Feb-03, Peter Young
added call to routine chianti_font to deal with fonts.
V.30, 28-Aug-03, Peter Young
corrected bug when two lines have the same wavelength by
introducing .ind tag to emiss_sel
V.31, 3-Nov-03, Giulio Del Zanna
Added printout of Ne(Te) vs. ratio values
Modified format e8.2 to e9.2 for Windows compatibility.
V.32, 6-Nov-03, Peter Young
Corrected bug when new emissivities are calculated that
prevented the emissivites in emiss_sel from being updated.
Also, the Ne(Te), ratio values are now printed to a pop-up
window through the new 'SHOW RATIO VALUES' button rather
than printed to the text window (see V.31).
V.33, 7-Nov-03, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
Modified the popup widget by calling xpopup and adding
labels. Now it is possible to paste and copy the RATIO
values into a file.
V.34, 12-Dec-03, Peter Young
Lowered the position of the postscript plot on the paper so
that the title isn't chopped off on US letter-size paper.
V.35, 2-Aug-2005, GDZ
Various modifications. Now the routine handles the
dielectronic case. Added printing of line lists in the
line ratio plots. Added the option to print directly to
the PRINTER. Added the option to SAVE a structure
containing the emissivities into an IDL save file (using
SAVEGEN). Added retain=2 to the window. Added
logarithmic or linear plot switch. Added cleaning of the
variables at the start of the routine. Various minor
cosmetic changes.
V.36, 12-Aug-2005, GDZ
Reinstated some previous cosmetic features. Also adjusted
some sizes, added some checks (e.g. minimum is set to 1e-10 if
plot is in log scale -to avoid log(0)-; automatic scaling cannot
be set if log scale is on).
V.37, 15-Aug-2005, Peter Young
Corrected bug with derived densities when the theoretical ratio
is double-valued.
V.38, 15-Aug-2005, Peter Young
Corrected bug introduced by modification above.
V.39, 17-Aug-2005, Peter Young
Adjusted layout of widget, modified printing of wavelengths
in the plot window, and adjusted plot limits for log scale.
VERSION : 39, 17-Aug-2005
This procedure has a dual purpose: (i) to extract `emiss' indices from
`emiss_sel' and, (ii) create labels that will be displayed on the plot
window.
The lines that comprise the blend are contained in emiss_sel.label
as, e.g., '203.79+203.80'. This routine separates this string into
the separate wavelengths and looks in emiss.lambda to see which
indices they correspond to. The set of indices are output through INDEX.
INPUT
I Index of component in emiss_sel. E.g., for the denominator I=0,
for the numerator I=1.
OPTIONAL OUTPUT
INDEX Integer array of same length as the number of lines in the
numerator or denominator (based on value of I). The elements
give the indices of the lines as they appear in the EMISS
structure.
PLOT_LABEL A string containing the index to be used when labelling
the line ratio plots.
KEYWORD
PS Setting this adds an angstrom to the wavelength labels. (Only
works for the postscript device.)
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
READ_ABUND
PURPOSE:
to read CHIANTI abundance files
CATEGORY:
science.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
READ_ABUND,File,Abundance,Reference
INPUTS:
File: the name (string) of the file containing the abundance values
(relative to hydrogen) usually of the form
'!xuvtop/abundance/*.abund'
OUTPUTS:
Abundance: an array of abuncance values
Reference: a string containing the reference to the chosen set
of abundances in the scientific literature
PROCEDURE:
You can describe the foobar superfloatation method being used here.
EXAMPLE:
> read_abund,'allen.abund',abundance,ref
abundance(26) = abundance of iron relative to hydrogen
quoted by C.W. Allen in Astrophysical Quantities
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1996: Version 2.0
V. 3, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
VERSION : 3, 21-May-2002
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
READ_DEM
PURPOSE:
to read values the differential emission measure as a function
of temperature
CATEGORY:
science.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
READ_DEM, File, T, Dem, Ref
INPUTS:
File: the name of the file containing the DEM values, usually in
!xuvtop/dem/*.dem
OUTPUTS:
T: Log10 values of temperature (K)
Dem: Log10 values of the differential emission measure
Ref: the reference to the DEM values in the scientific literature
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
Describe optional outputs here. If the routine doesn't have any,
just delete this section.
EXAMPLE:
> read_dem,!xuvtop+'/dem/active_region.dem',t,dem,ref
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1996: Version 2.0
V. 3, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
Ver.4, 20-Nov-2002, Peter Young
DEM values of -1 caused errors, so this has been corrected.
VERSION : 4, 20-Nov-2002
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
astrophysical emission line spectra. It is a collaborative project
involving Ken Dere (Naval Research Laboratory, Washington DC),
Brunella Monsignori-Fossi and Enrico Landi (Arcetri Observatory,
Florence), and Helen Mason and Peter Young (DAMTP, Cambridge Univ.).
NAME:
READ_ELVLC
PURPOSE:
to read files containing observed and theoretical energy levels
CATEGORY:
science.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
READ_ELVLC, File, L1, Term, Conf, ss, ll, jj, Ecm, Eryd, Ecmth, Erydth, Ref
INPUTS:
File: the name of the file
i.e., !xuvtop+'/si/si_12/si_12.elvlc' for Si XII
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
None:
OUTPUTS: L1 - level index
Term - configuration index
Conf - configuration description
ss - 2S+1
ll - L
jj - J
Ecm - observed energy (cm^-1)
Eryd - observed energy (Rydbergs)
Ecmth - theoretical energy (cm^-1)
Erydth - theoretical energy (Rydbergs)
Ref - reference
note: the theoretical energies are usually those used in the scattering
calculation and are only useful for predicting approximate
wavelengths
EXAMPLE:
> file = !xuvtop+'/si/si_12/si_12.elvlc'
> read_elvlc,file,l1,term,conf,ss,ll,jj,ecm,eryd,ref
>
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1996: Version 2.0
Ver.2, 6-Dec-2001, Peter Young
Modified the form of the "term" output. The J-value is now
represented by a fraction rather than a decimal.
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME:
READ_ELVLC_DIRECT
PURPOSE:
to read files containing observed energy levels
does not reformat some variables like READ_ELVL
CATEGORY:
science.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
READ_ELVLC_DIRECT, File, L1, Term, Conf, ss, ll, spd, jj, Ecm, Eryd, Ecmth, Erydth, Ref
INPUTS:
File: the name of the file
i.e., !xuvtop+'/si/si_12/si_12.elvl' for Si XII
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
None:
OUTPUTS: L1 - level index
Term - configuration index
Conf - configuration description
ss - 2S+1
ll - L
spd - 'S', 'P', etc to denote L value
jj - J
Mult - multiplicity 2J+1
Ecm - energy (cm^-1)
Eryd - energy (Rydbergs)
Ecmth - energy (cm^-1)
Erydth- energy (Rydbergs)
Ref - reference
EXAMPLE:
> file = !xuvtop+'/si/si_12/si_12.elvl'
> read_elvlc_direct,file,l1,term,conf,ss,ll,jj,ecm,eryd,ecmth,erydth,ref
>
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1996: Version 2.0
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
READ_FBLVL
PURPOSE:
To read files containing observed free-bound energy levels
CATEGORY:
Science.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
READ_FBLVL, File, L1, Conf, pqn, ll, spd, mult, Ecm, Ecmth, Ref
INPUTS:
File: the name of the file
e.g., !xuvtop+'/si/si_12/si_12.fblvl' for Si XII
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
None:
OUTPUTS: L1 - level index
CONF - configuration description
PQN - principal quantum number of electron being ionized
LL - L-value of ionized electron
SPD - 'S', 'P', etc to denote L value
MULT - multiplicity 2J+1
ECM - energy (cm^-1)
ECMTH - energy (cm^-1)
REF - reference
EXAMPLE:
> file = !xuvtop+'/si/si_12/si_12.elvlc'
> read_fblvl,file,l1,conf,pqn,ll,mult,ecm,ecmth,ref
>
HISTORY
Ver.1, 31-Jul-2002, Peter Young
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is
a collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME:
READ_GFFGU
PURPOSE:
Read gffgu.dat file containing free-free gaunt factors of
R. S. Sutherland, 1998, MNRAS, 300, 321
note: the file available from the web site are mislabelled
CALLING SEQUENCE:
READ_GFFGU,g2,u,gff
INPUTS:
None
OUTPUTS:
g2,u,gff defined in the paper by Sutherland
COMMON BLOCKS:
None
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
April 2000: Version 3.0
October 2001: Version 4 - Ken Dere -
corrected for the fact that the original
Sutherland file was mislabelled
November 2001: Corrected the address of the gffgu.dat file - Enrico Landi
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME:
READ_GFFINT
PURPOSE:
Read gffint file containing integrated free-free gaunt factors of
R. S. Sutherland, 1998, MNRAS, 300, 321
CALLING SEQUENCE:
READ_GFFINT,g2,gff,s1,s2,s3
INPUTS:
None
OUTPUTS:
g2,gff,s1,s2,s3 defined in the paper by Sutherland
COMMON BLOCKS:
None
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
April 2000: Version 3.0
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
READ_IONEQ
PURPOSE:
to read files containing the ionization equilibrium values
CATEGORY:
science.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
READ_IONEQ, File, T, Ioneq, Ref
INPUTS:
File: for example, !xuvtop+'/ioneq/arnaud_rothenflug.ioneq'
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
None:
OUTPUTS:
T: array of log10 temperatures
Ioneq: 3-d array (T,element,ion)
of the fractional abundance of the ion in
ionization equilibrium.
Ref: reference in the scientific literature
EXAMPLE:
> read_ioneq,!xuvtop+'/ioneq/arnaud_rothenflug.ioneq'
> help,t,ioneq
> T FLOAT = Array(41)
> IONEQ FLOAT = Array(41, 28, 29)
> print, minmax(t)
> 4.00000 8.00000
> print,t(20)
> 6.0000
> print,ioneq(20,25,9)
> 0.269 = fractional abundance of Fe X in
ionization equilibrium
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere (KPD)
March 1996: Version 2.0
March 1999: KPD to read both number of temperature and number
of elements
25-Oct-2000 V. 4, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ).
Corrected to interpret the '-1' as a reference only
if within the first 3 columns
V. 5, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
v.6, 25-Oct-2004, Peter Young
modified format statement so that it will read any number of
temperatures.
V 7, 25-May-2005, GDZ
corrected routine header.
VERSION : 7, 25-May-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME:
READ_IP
PURPOSE:
to read values of ionization potentials
CALLING SEQUENCE:
READ_IP, File, IP, Ref
INPUTS:
File: the name of the file containing the IP values, usually
!xuvtop/ip/chianti.ip
OUTPUTS:
IP: Array values of ionization potential (cm^-1)
Ref: the reference to the IP values in the scientific literature
EXAMPLE:
> read_ip,!xuvtop+'/ip/chianti.ip',ip,ref
ip(2-1,2-1) give the ionization potential of He II (Z=2, Ion=2)
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1998: Version 1.0
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME:
READ_KLGFB
PURPOSE:
to read CHIANTI files file containing the free-bound gaunt factors for n=1-6
from Karzas and Latter, 1961, ApJSS, 6, 167
CATEGORY:
science.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
READ_KLGFB,PE,GFB
INPUTS:
File: none
OUTPUTS:
PE: an array of natural log of 41 values of Photon Energy values relative to
the recombination edge i.e., at the recombination edge, PE=0.
GFB: an array containing the natural log of free-bound gaunt factors indexed
by energy, n and l
PROCEDURE: reads the file: '!xuvtop/continuum/klgfb.dat'
EXAMPLE:
> read_klgfb,pe,klgfb
the free-bound gaunt factor vs. energy for recombination to a hydrogen 2p state
(n=2 and l=1) is given by klgfb(*,n-1,l-1)
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
July 2002: Version 1.0
Version 2, 8-Aug-02, GDZ
corrected a typo.
VERSION : V.2, 8-Aug-02
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME:
READ_MASTERLIST
PURPOSE:
read the masterlist.ions types of file and output a list of ions
CATEGORY:
science.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
READ_MASTERLIST,filename,list
INPUTS:
filename: name of the masterlist file
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
none
OUTPUTS:
list: list of ions
COMMON BLOCKS:
none;
EXAMPLE:
> read_masterlist,'!xuvtop/masterlist.masterlist.ions',list
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
December 1998: first version
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It
is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME:
READ_SPLUPS
PURPOSE:
to read file containing spline fits to the Burgess-Tully scaled
collision strengths
CATEGORY:
science.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
READ_SPLUPS, File, Splstr, Splref
INPUTS:
File: the name of the input file, i.e. !xuvtop/si/si_4/si_4.splups
OUTPUTS:
SPLSTR Structure containing the data from the file. The tags are
as follows:
.lvl1 lower level index
.lvl2 upper level index
.t_type transition type
.gf gf value
.de Delta-E for transition (rydbergs)
.c_ups the scaling parameter
.nspl
.spl Vector of length 9, containing spline points
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS
SPLREF String array containing references.
KEYWORDS
PROT Allows reading of .psplups files for proton rates.
PROCEDURE:
see Burgess and Tully, 1992, Astronomy and Astrophysics, 254, 436.
EXAMPLE:
> read_splups, !xuvtop+'/si/si_4/si_4.splups',splstr,splref
PROGRAMMING NOTES
This routine is marginally quicker (20-25%) reading the .splups
files than Ken's original routine. The improvement in speed is
through minimising the lines of code in the WHILE loop.
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1996: Version 2.0
Ver.3, 23-Jan-01, Peter Young
completely revised. Now reads into a structure and
handles 9 point spline fits.
Ver.4, 26-Jan-01, Peter Young
speeded up routine
Ver.5, 22-Mar-01, Peter Young
now checks if file exists
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME:
READ_WGFA
PURPOSE:
:
CATEGORY:
science
CALLING SEQUENCE:
READ_WGFA, File, Lvl1, Lvl2, Wvl, Gf, A_value, Ref
INPUTS:
File: name of the file containing the radiative data
i.e. !xuvtop/c/c_4/c_4.wgfa
OUTPUTS:
Lvl1: 1D array of indices of the lower level (starting at 1)
Lvl2: 1D array of indices of the upper level (starting at 1)
Wvl: 2D array of transition wavelengths in Angstroms
Gf: 2D array of weighted oscillator strength gf
A_value: 2D array of radiative transition probability (s^-1)
Ref: 1D string array of references to the data in the scientific literature
EXAMPLE:
> read_wgfa,!xuvtop+'/c/c_4/c_4.wgfa',lvl1,lvl2,wvl,gf,a,ref
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1996: Version 2.0
v.3, 6-Mar-02, Peter Young
Changed the way the reference string is read in order to
prevent '-1' problems.
v.4, 12-Mar-02, Peter Young
Corrected bug following above change.
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME:
READ_WGFA2
PURPOSE:
read radiative data files
a modified version of read_wgfa
needed to take account of two types of transitions between the same 2 levels:
for example, the M1 and the 2 photon E1 transition 1s-2s in hydrogenic ions
CATEGORY:
science
CALLING SEQUENCE:
READ_WGFA2, File, Lvl1, Lvl2, Wvl, Gf, A_value, Ref
INPUTS:
File: name of the file containing the radiative data
i.e. !xuvtop/c/c_4/c_4.wgfa
OUTPUTS:
Lvl1: 1D array of indices of the lower level (starting at 1)
Lvl2: 1D array of indices of the upper level (starting at 1)
Wvl: 1D array of transition wavelengths in Angstroms
Gf: 1D array of weighted oscillator strength gf
A_value: 1D array of the total radiative transition probability (s^-1)
Ref: 1D string array of references to the data in the scientific literature
EXAMPLE:
> read_wgfa2,!xuvtop+'/c/c_4/c_4.wgfa',lvl1,lvl2,wvl,gf,a,ref
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1996: Version 2.0
V.3, 3-Nov-03, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
Modified size of input arrays. Now the routine can read a file up to
30 000 lines.
VERSION : 3, 3-Nov-03
function rebinw rebins the input array on a new grid and returns the output array. this routine is preferred over simple INTERPOL or SPLINE because this is guaranteed to e.g., conserve energy while rebinning spectra. syntax ff=rebinw(f,x,y,/perbin,nbin=nbin,wrange=wrange) parameters f [INPUT; required] array values x [INPUT; required] absissae for F 1: if size matches that of F, assumed to be mid-bin values 2: if size is size(F)+1, assumed to be bin boundaries (i.e., all the bin-beginners and a final bin-ender) 3: if neither of the above, this is assumed to be the desired *output* grid, and the absissae of the input are assumed to span the linear range 1..N(F) * Y is ignored on input, but will be overwritten on output y [I/O] the new absissa values 1: if scalar or 1-element vector on input, assumed to be number of bins in output * linear binning if +ve, log binning if -ve 2: if >1-element vector on input, assumed to be the desired output grid of bin boundaries, with the last element defining the final bin-ending value. 3: if not defined, takes value from NBIN NOTE: F extrapolates as zeros. keywords perbin [INPUT] if set, assumes that units of F(X) are [.../bin] nbin [I/O] number of bins in output * overwritten if defined via X or Y * linear binning if +ve, log binning if -ve * default: 1 wrange [INPUT] output grid range * ignored if defined via array Y (or X -- case 3) * overrides if determined via X and CASE 1 of Y * default: [1.,500.] _extra [JUNK] here only to prevent crashing the program restrictions beware that if Y is not sorted in ascending order, on output it will be! requires external procedure FINDEX.PRO history vinay kashyap (Jan98) forced x to be required inputs (Jun98) changed call to INTERPOL to combo call to INTERPOLATE/FINDEX (VK;99Jul) corrected long-standing "feature" of NBIN being useless, changed default behavior of Y=UNDEFINED, NBIN, and X=/=F (VK; MarMM)
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
SETUP_ELEMENTS
PURPOSE: read in ionization equilibrium and abundances
not for general user use
CALLING SEQUENCE:
SETUP_ELEMENTS
INPUTS:
None
OUTPUTS: reads data into common block
COMMON BLOCKS:
common elements,abund,abund_ref,ioneq,ioneq_logt,ioneq_ref
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
Feb. 2000: Version 1.0 for CHIANTI version 3
V. 2, 21-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ):
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V. 3, 16-Apr-2003, Peter Young
I had to use expand_path for DIR in order for the paths to be
recognised in Windows.
VERSION : 3, 16-Apr-2003
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
SETUP_ION
PURPOSE:
Several of the CHIANTI routines require the atomic data for ions
to be read into common blocks, and so this routine performs this
task for individual ions.
Note that the inputs WVLMIN and WVLMAX merely serve to check
whether the ion has lines lying in this wavelength range. If yes,
then the common blocks are filled with the data; if no, then the
common blocks are left empty.
An important point to note is that the
wgfa and upsilon common blocks contain their data in 2-D array
form, suitable for solving the level balance equations. When
dealing with dielectronic files, there will be some transitions
which will have two A-values, one representing autoionisation
rather than radiative decay. For the level balance equations,
these two A-values need to be summed together. However, for
computing the line emissivity, one needs to only use the radiative
decay A-value. For this purpose, the routine outputs the 1-D
arrays read by READ_WGFA2 which contain the two separate A-values,
allowing other routines to pick out just the radiative decay
A-value. These outputs are listed below (LVL1, LVL2, etc.).
CALLING SEQUENCE:
SETUP_ION,Ion,Wvlmin,Wvlmax,Wvltst,Lvl1,Lvl2,Wvl1,Gf1,A_value1
INPUTS
ION String specifying ion, e.g., 'c_2'
WVLMIN Minimum wavelength of interest (angstroms). If there are
no lines with wavelengths between WVLMIN and WVLMAX, then
no data is read into the common blocks. If both WVLMIN
and WVLMAX are set to -1, then no checks are made on the
wavelengths (i.e., the common blocks will be filled).
WVLMAX Maximum wavelength of interest (angstroms). See above.
OPTIONAL INPUT
PATH Can be used to specify a different directory to !xuvtop
for the location of the data files. E.g.,
path='/data/user/chianti/o_4'
KEYWORDS
NOPROT Switches off the inclusion of proton rates.
ALL By default the routine only looks for wavelengths which
are positive when checking if they lie in the wavelength
range. By setting /ALL then negative wavelengths are also
included.
OUTPUTS:
WVLTST The number of transitions lying between WVLMIN and WVLMAX.
If WVLMIN and WVLMAX are both -1, then WVLTST will
be the total number of transitions in the .wgfa file
(including any with zero wavelength).
LVL1 Number of final level of transition (1-D array)
LVL2 Number of initial level of transition (1-D array)
WVL1 Wavelenths (in angstroms) of spectral lines formed by this
ion (1-D array)
GF1 Oscillator strength (1-D array)
A_VALUE1 Radiative transition probability (1-D array)
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS
ANYLINES Contains the indices of the elements of lvl1, lvl2, wvl1,
gf1, a_value1 arrays for which the wavelengths lie in
specified wavelength range.
EXAMPLE:
IDL> setup_ion,'c_2',1000.,1500.,wvltst,Lvl1,Lvl2,Wvl1,Gf1,A_value1
IDL> print,wvltst
17
IDL> setup_ion,'c_2',-1,-1,wvltst,Lvl1,Lvl2,Wvl1,Gf1,A_value1
IDL> print,wvltst
43
IDL> setup_ion,'c_2',-1,0,wvltst,Lvl1,Lvl2,Wvl1,Gf1,A_value1
IDL> print,wvltst
0
COMMON BLOCKS:
common elvlc,l1a,term,conf,ss,ll,jj,ecm,eryd,ecmth,erydth,eref
common wgfa, wvl,gf,a_value
common upsilon,t_type,deu,c_ups,splups
CALLS
READ_WGFA2, READ_SPLUPS, READ_ELVLC, ION2FILENAME
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Ver.1, Sep-99, Ken Dere
Ver.2, 10-Oct-00, Peter Young
Allowed wvlmin and wvlmax to take -1 values.
Removed elements common block.
Removed for-loop.
Added PATH.
Ver.3, 12-Nov-01, Peter Young
Added proton common block and /noprot keyword
Ver.4, 11-Dec-01, Peter Young
Added keyword /all.
V.5, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V.6, 25-Feb-2004, Enrico Landi (EL)
Added call to read_ionrec.pro to read ionization
and recombination files.
VERSION : 6, 25-Feb-2004, EL
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME: SHOW_POPS
PURPOSE:
To display populations of significant levels in a CHIANTI ion
model
CATEGORY:
Scientific analysis
EXPLANATION:
Displays percentage level populations and level IDs for all levels
in the specified ion with populations greater than 0.01%. If the
temperature is not specified, then it is taken to be where the
maximum of the ionisation fraction is.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
SHOW_POPS, IZ, ION [, POPSTR, DENS= , TEMP= , /NOPROT,
RADTEMP= , RPHOT= , /ALL, /DIEL, PATH=,
IONEQ_FILE= , ABUND_FILE= ]
EXAMPLES:
show_pops,26,13,popstr
show_pops,26,13,dens=7.5,temp=6.0,rphot=1.2
INPUTS:
IZ The atomic number of the ion
ION The spectroscopic number of the ion (e.g., 12 = XII)
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
DENS Logarithm of electron density
TEMP Logarithm of electron temperature. If not specified, then
T_max of the ion is used
RADTEMP Specify background radiation temperature (default: 6000 K)
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
PATH Directly specify the path where the ion data is contained,
e.g., path='/home/other_data/fe_13'
N_LEVELS The size of the ion model is automatically determined
from the information in the CHIANTI data files. Setting
this keyword allows the number of levels in the model to
be reduced. E.g., N_LEVELS=14 reduces the model to the
first 14 levels given in the .ELVLC file.
IONEQ_FILE To include proton rates in the level balance equations
requires the number of density of protons to be known,
and this requires an ion balance file and an abundance
file to be specified, which are done through the
IONEQ_FILE and ABUND_FILE keywords. If they are not set
then the default files specified by !ioneq_file and
!abund_file are used.
ABUND_FILE See IONEQ_FILE.
SUM_MWL_COEFFS An array of coefficients of the same length as
the array of temperatures. Electron and proton rate
coefficients will be calculated at each temperature
and then a weighted sum of the coefficients is
performed using SUM_MWL_COEFFS. This allows
non-Maxwellian energy distributions to be
incorporated into the level balance equations.
If this keyword is set for an ion that has ionization
and recombination included in the level balance, then
these processes will be switched off for the
calculation since their rates implicitly assume a
single Maxwellian to describe the ion fractions of
the neighbouring ions.
LEVEL Allows the control of which level populations are displayed
to the screen. If set to a positive scalar or array, then
only those levels are printed. If it is set to a negative
scalar (-n), then all level populations up to level n are
printed. E.g., LEVEL=20 (only level 20); LEVEL=[5,7,20]
(levels 5, 7 and 20); LEVEL=-20 (all levels up to level 20).
RADFUNC The name of a user-defined function that will generate
a radiation spectrum as a function of temperature.
This radiation field will replace the black-body that
is assumed when using the RADTEMP keyword in the call
to pop_solver.
; OPTIONAL OUTPUTS
POPSTR Send level population information to a structure. POPSTR has
the tags:
.dens Density (cm^-3)
.temp Temperature (K). Can be an array if SUM_MWL_COEFFS=
is used.
.radtemp RADTEMP. Set to -1 if RADTEMP not
set.
.rphot RPHOT value. Set to -1 if RPHOT not set.
.proton String set to 'yes' if proton rates included, 'no'
otherwise
.version CHIANTI version used to derive populations.
.date Date and time at which structure created.
.level Structure containing level information. Tags are:
.index CHIANTI level index
.term String containing level identifier.
.pop Population of level
.sumtst Set to 1 if the SUM_MWL_COEFFS keyword has been used.
Set to 0 otherwise.
.sum_mwl_coeffs Contains SUM_MWL_COEFFS. Set to -1 if sumtst=0.
KEYWORDS:
ALL Show populations for all levels.
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
DIEL Use the dielectronic recombination files. E.g., for Fe XXII,
the routine will read in the fe_22d.* files instead of the
fe_22.* files.
COMMON BLOCKS:
ELVLC, WGFA, UPSILON, RADIATIVE, PROTON, ELEMENTS
CALLS:
ZION2FILENAME, POP_SOLVER, SETUP_ION, READ_IONEQ,
READ_ABUND, PROTON_DENS, CONCAT_DIR
HISTORY:
Ver 1, PRY 22-Sep-97
Ver.2, PRY 5-Sep-98 - added call to choose_ioneq
Ver.3, PRY 23-Apr-99 - calls pop_solver now; added DENS keyword
Ver.4, PRY 18-Dec-99 - added deu to upsilon common block to be
consistent with main Chianti routines.
Ver.5, PRY 7-Aug-00 - added /DIEL keyword to allow populations of
the dielectronic recombination files to be studied.
Also changed elvlc common block to match new
version of pop_solver.
Ver 6, PRY 10-Oct-00 - now calls setup_ion to read ion data
Ver 7, PRY 12-Nov-01 - modified for proton rates, photoexcitation,
and 9 pt splines.
Ver 8, PRY 9-Dec-01 - completed modifications for v4 of CHIANTI.
V. 9, 25-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
Now we only call zion2filename
V. 10, 9-Aug-2002, Peter Young
corrected !ioneq_file problem
V. 11, 12-Aug-2002, Peter Young
added POPSTR output, and tidied up header.
V. 12, 4-Oct-2003, GDZ
modified the input to POP_SOLVER, now it is dealt with an
input structure.
V 13, 4-May-2005, Enrico Landi (EL)
Modified in order to include ionization and recombination
data in the input to POP_SOLVER
V.14, 26-May-2005, Peter Young (implemented by GDZ)
added SUM_MWL_COEFFS optional input for allowing
non-Maxwellian distributions to be considered.
added LEVEL= optional input to only print the populations of
a few levels.
V.15, 5-Jul-2005, Peter Young
added RADFUNC= and /QUIET keywords
VERSION : 15, 5-Jul-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
SPECTROSCOPIC2ION
PURPOSE:
provide identification string
CATEGORY:
database.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
SPECTROSCOPIC2ION, snote, Ion, dielectronic=dielectronic
INPUTS:
snote: the spectroscopic notation for the ion, i.e. 'C II'
OPTIONAL INPUTS: none
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
OUTPUTS:
Ion: CHIANTI notation for an ion, i.e., 'c_2' for C II
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS: dielectronic (0/1)
EXAMPLE:
> spectroscopic2ion, 'O VI d', ion,dielectronic=dielectronic
> help, ion, dielectronic
> ION STRING = 'o_6d'
> DIELECTRONIC INT = 1
WRITTEN :
Version 1, Written by: Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ) 25-May-2002
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
V.2, 12-Aug-02, GDZ
Corrected a typo concerning XXII.
VERSION : 2, 12-Aug-02
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
SUTHERLAND
PURPOSE:
Calculate the free-free continuum from an hot, low density plasma
Uses the free-free gaunt factor calculations of Sutherland, 1998,
MNRAS, 300, 321.
Note that Sutherland's Eq.(15) has units of erg/cm^3/s. Comparing
with Rybicki & Lightman's Eq.5.14(a) (in their book 'Radiative
Processes in Astrophysics'), suggests that Sutherland's units
should be erg/cm^3/s/sr/Hz. We are assuming the latter to be
correct in this routine.
When using the DEM_INT optional input, FREEFREE expects the
differential emission measure to have been derived from a product
of N_e*N_H rather than N_e*N_e. This can be important when dealing
with a regime (typically T < 10^4.5) where H and He are not fully
ionised.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
SUTHERLAND,temperature, wavelength, intensity
INPUTS:
T Temperature in degrees Kelvin, can be a 1 D array
WVL Wavelength in Angstroms
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
None
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
NO_SETUP: If the procedure setup_elements has already been called
then the keyword /no_setup should be set to avoid
repeating this step.
MIN_ABUND: If set, calculates the continuum only from those
elements which have an abundance greater than min_abund.
This can speed up the calculations. ;
DEM_INT The intensity array is multiplied by a DEM number for
each temperature. DEM_INT needs to be of the same size
as TEMPERATURE. It is needed for the synthetic spectrum
routines.
PHOTONS The output spectrum is given in photon units rather
than ergs.
SUMT The default is to output the intensity array as an array
of size (nwvl x nT). Setting this keyword performs a sum
over the temperatures to yield a vector of same size as
the input wavelengths, thus producing the complete
free-free spectrum.
OUTPUTS:
RAD Free-free continuum intensity in units
10^-40 erg cm^3 s^-1 str^-1 angstrom^-1 per unit
emission measure [ integral (N_e N_H dh) in cm^-5 ].
If T is given as a 1-D array, then RAD will be output
as a 2-D array, with one element for each temperature
and wavelength (but also see SUMT).
PROGRAMMING NOTES
The gaunt factors from Sutherland (MNRAS 300, 321, 1998) are a
function of uu and gg (see his Eq. 14). uu is a function of both
wavelength and T, while gg is a function of T only.
The gaunt factor (gff) is tabulated for values of uu and gg at
fixed intervals in log(uu) and log(gg). The log(uu) values go from
-4 to 4 in 0.2 steps; the log(gg) values go from -4 to 4 in 0.1 steps.
A particular (input) temperature and wavelength give rise to values
uu0 and gg0, the logs of which lie between -4 and 4. To derive the
corresponding gff0 value, I use the IDL routine BILINEAR.
BILINEAR requires, not uu and gg values as input, but indices.
E.g., the indices corresponding to the tabulated values of uu are
0 (=-4.0), 1 (=-3.8), 2 (=-3.6), etc. Thus, if log(uu0)=-3.76, then
i_uu0=1.20 is the index of uu0.
In order to make significant time-savings, I give BILINEAR all of
the wavelengths and temperatures in the same call for a particular
ion. To do this, I make my i_uu and i_gg values 2-D arrays of size
(nwvl x nT), and BILINEAR then produces a (nwvl x nT) array
containing the gff values.
A problem occurred if nT=1, as BILINEAR will turn the input uu and
gg vectors into 2-D arrays of size (nwvl x nwvl). If there are a
large number of wavelengths, this uses a lot of memory. To solve
this I make a 2 element temperature vector whose values are
identical, and then change this back to a 1 element vector after
BILINEAR has been called. See the parts of the code where I use
'tst1'.
COMMON BLOCKS:
common elements,abund,abund_ref,ioneq,ioneq_t,ioneq_ref
CALLS
READ_IP, READ_GFFGU, SETUP_ELEMENTS
EXAMPLES:
IDL> freefree,1.e+6,wvl,int
IDL> freefree,1.e+6,wvl,int,min_abund=3.e-5
IDL> freefree,1.e+6,wvl,int,/no_setup,min_abund=1.e-6
IDL> wvl=findgen(5001)/10. + 50.
IDL> temp=10.^(findgen(41)/10. +4.)
IDL> freefree,temp,wvl,int
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1999: Version 2.0
September 1999: Version 3.0
Ver.3.1, 11-Aug-00, Peter Young
Improved call to bilinear, allowing routine to solve for
all temperatures in one go. This makes the routine quicker,
and also lowers the memory usage of the routine when dealing
with many wavelengths.
Ver.3.2, 16-Aug-00, Peter Young
Corrected expression for 'gg', replacing ip with z^2.
Ver.3.3, 16-Oct-00, Peter Young
Now deals with dem_int correctly
Ver.3.4, 10-Oct-01, Ken Dere
Corrected for labelling errors in Sutherland's gffgu.dat file
No longer reads ionization potential file
Ver.3.5, 5-Dec-01, Peter Young
Corrected expression for gamma^2
Renamed routine sutherland.pro
Restructured code to make it run quicker.
Ver.3.6, 22-May-01, Peter Young
Re-instated the MIN_ABUND optional input.
Changed ioneq_t to ioneq_logt (GDZ).
Ver.3.7, 18-Aug-03, Peter Young
Activated /PHOTONS keyword
Ver.3.8, 5-Nov-03, Peter Young
Corrected bug found by Jim McTiernan when multiple temperatures
were input. The quantity 'newfactor' was not being calculated
correctly due to indexing problems.
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
SYNTHETIC
PURPOSE:
calculates a synthetic spectrum
PROCEDURE:
Calculations are done assuming either constant density or
constant pressure. See CH_SYNTHETIC for details.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
SYNTHETIC,Wmin, Wmax, Fwhm, Pressure= , Lambda, Spectrum ,List_wvl, List_ident
,[/all, density=, /cont, min_abund=]
INPUTS:
Wmin: lower limit of the wavelength/energy range of interest (Angstroms)
Wmax: upper limit of the wavelength/energy range of interest (Angstroms)
Pressure: pressure in emitting region (cm^-3 K), or
Density: density in emitting region (cm^-3).
Fwhm: gaussian full width at half maximum of the resolution of the output
spectrum, for example, to correspond to an observed spectrum
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
SNGL_ION: specifies a single ion (e.g. SNGL_ION='Fe_10' to include
only Fe X lines) or an array (e.g. SNGL_ION=['Fe_10','Fe_11']
to include only Fe X and Fe XI lines) of ions to be used
instead of the complete set of ions specified in
!xuvtop/masterlist/masterlist.ions
MASTERLIST: string of a specific masterlist file (full path).
If defined as a keyword (i.e. MASTERLIST=1 or /MASTERLIST)
then a widget allows the user to select a user-defined
masterlist file. Shortcut for SNGL_ION.
MIN_ABUND: If set, calculates the continuum only from those elements which
have an abundance greater than min_abund.
DEM_NAME: Name of the DEM file to used. If not passed, then the user
is prompted for it.
ABUND_NAME: Name of the abundance file to use. If not passed, then
the user is prompted for it.
IONEQ_NAME: Name of the ionization equilization name to use. If not
passed, then the user is prompted for it.
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
RADTEMP The blackbody radiation field temperature (default 6000 K).
OUTPUTS:
Lambda: wavelength array of calculated synthetic spectrum
Spectrum: intensity array (erg cm^-2 s^-1 str^-1 Ang^-1),
unless keyword photons is set then output is is
photons cm^-2 s^-1 str^-1 Ang^-1
List_wvl: a list of wavelengths for use with synthetic_plot.pro
List_ident: a list of line identifications for use with
synthetic_plot.pro
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
ALL: if set, then all lines are included. This means that lines for which
only an approximate wavelength is known (only theoretical energy
levels are known) are included.
SNGL_ION: specifies a single ion (e.g. SNGL_ION='Fe_10' to include
only Fe X lines) or an array (e.g. SNGL_ION=['Fe_10','Fe_11']
to include only Fe X and Fe XI lines) of ions to be used
instead of the complete set of ions specified in
!xuvtop/masterlist/masterlist.ions
MASTERLIST: string of a specific masterlist file (full path).
If defined as a keyword (i.e. MASTERLIST=1 or /MASTERLIST)
then a widget allows the user to select a user-defined
masterlist file. Shortcut for SNGL_ION.
CONTINUUM: if set, then the continuum (free-free, free-bound and
two-photon) are included
MIN_ABUND: If set, calculates the continuum only from those elements which
have an abundance greater than min_abund. Can speed up the
calculations. For example, from Allen (1973):
abundance (H) = 1.
abundance (He) = 0.085
abundance (C) = 3.3e-4
abundance (O) = 6.6e-4
abundance (Si) = 3.3e-5
abundance (Fe) = 3.9e-5
PHOTONS: if set, intensities are in photons cm^-2 s^-1 sr^-1 Ang^-1
DEM_NAME: Name of the DEM file to used. If not passed, then the user
is prompted for it.
ABUND_NAME: Name of the abundance file to use. If not passed, then
the user is prompted for it.
IONEQ_NAME: Name of the ionization equilization name to use. If not
passed, then the user is prompted for it.
NOPROT If set, then proton rates are not included.
RADTEMP Specify background radiation temperature (default: 6000 K)
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius units.
I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface. (Default is
infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
CALLS:
CH_SYNTHETIC, MAKE_CHIANTI_SPEC, READ_ABUND, STRPAD
COMMON BLOCKS: None
RESTRICTIONS:
SIDE EFFECTS:
EXAMPLE:
> synthetic,100.,200.,.1, pressure=1.e+16,lambda,spectrum,list_wvl,list_ident
CATEGORY:
spectral synthesis.
WRITTEN :
Version 1, 8-Nov-01, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ).
Rewritten as a wrapper routine using the new procedures.
Compared to the previous SYNTHETIC, these are the main changes:
1-Now the PRESSURE value is a keyword as the DENSITY value
2-The keyword CONT is now renamed CONTINUUM
3-Added keywords PHOTONS, DEM_NAME, ABUND_NAME, IONEQ_NAME
4-MASTERLIST can now be used both as an input string or as a keyword.
5-The description of the line details now has the spectroscopic
designation at the end.
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Version 2, 18-Nov-01, Peter Young
Added /noprot, rphot and radtemp keywords.
Version 3, 11-Dec-01, Peter Young
Changed call to ch_strpad to strpad.
Version 4, 28-Apr-02, GDZ, changed the call to make_chianti_spec and the
continuum keyword.
V. 5, 22-May-2002 GDZ. Removed const_net definitions.
V.6, 14-Feb-2003 GDZ.
Fixed a bug (keyword PHOTONS was not active).
VERSION : 6, 14-Feb-2003
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
synthetic_plot
PURPOSE:
to plot out synthetic spectra calculated with Synthetic
and interactively identify spectral lines
CATEGORY:
spectroscopy
CALLING SEQUENCE:
SYNTHETIC_PLOT,Wvl,Spectrum,List_wvl,List_ident,fwhm
INPUTS:
Wvl: wavelength array from synthetic
Spectrum: spectrum intensity array from synthetic
List_wvl: string array of spectral line wavelengths
List_ident: string array of spectral line identifications
Fwhm: when the cursor is clicked, spectral lines with fwhm
(Angstroms) of the cursor are printed out
KEYWORDS
xrange: similar to IDL keyword to determine wavelength range of plot
OUTPUTS:
None
PROCEDURE:
Click the left mouse button to select a wavelength
Click the right mouse button to exit
EXAMPLE:
> synthetic,100.,200.,.1,1.e+15,wvl,spectrum,list_wvl,list_ident
> synthetic_plot,wvl,spectrum,list_wvl,list_ident,0.1
note: it is not necessary for the two fwhm values to be the same
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
May 1996: Version 2.0
Dec. 1998: revised by Ken Dere
V.4, 23 Oct 2000 GDZ, added the log keyword, and changed a few things
in the plot.
Ver.5, 12-Dec-2001, Peter Young
Changed style of printing, and made method of extracting the
intensity from list_ident compatible with the new version of
isothermal.pro.
VERSION 5 12 Dec 2001 Peter Young
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
TEMPERATURE_RATIOS
PURPOSE:
calculate and display temperature sensitivity of line intensity ratios
CATEGORY:
spectral diagnostics
PROCEDURE :
The intensities (Population of the upper level * A) of the lines within
the selected ion are first calculated, either at constant pressure or
at constant density (however specified in the input). They are plotted
in window 0. The intensities relative to the brightest reference line
are then plotted in window 1. A widget allows the user to select a
number of lines (at least one!) for the numerator of the ratio, and a
number of lines for the denominator. In case of multiple selections, the
line intensities are summed. The ratio values are plotted in window 2, and
optionally also saved in a text file. A postscript file can also be
created. The ratio values, calculated at twice and half the prescribed
density are also calculated and overplotted, to show how the
temperature ratio also depends on the density.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
> temperature_ratios,ion,wmin,wmax,Log10(tempmin),Log10(tempmax),temperature,ratio,description,$
[pressure= ,density= , psfile= , outfile= ]
EXAMPLE:
> temperature_ratios,'c_4',100.,1600.,4.,6.,temp,ratio,desc,density=1.e+10,$
psfile='test.ps', outfile='test.txt'
then select the ratio of (384.17 + 384.19) to 1550.772
INPUTS:
Ion: the CHIANTI style name of the ion, i.e., 'c_5' for C V
Wmin: minimum wavelength limit in Angstroms
Wmax: maximum wavelength limit in Angstroms
Tempmin: log10 of lowest temperature of interest, i.e. 4 for 10.^4 K
Tempmax: log10 of highest temperature of interest
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
Must specify indices of lines which are to form the ratio
RADTEMP The blackbody radiation field temperature (default
6000 K).
RPHOT Distance from the centre of the star in stellar radius
units. I.e., RPHOT=1 corresponds to the star's surface.
(Default is infinity, i.e., no photoexcitation.)
ABUND_FILE The name of a CHIANTI abundance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio. Default is
!abund_file.
IONEQ_FILE The name of a CHIANTI ion balance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio and evaluating
the T_max of the ion. Default is !ioneq_file.
OUTPUTS:
Temperature: an array of temperatures spanning Tempmin to Tempmax
Ratio: an array of the intensity ratio of the selected lines
Desc: a short string description of the selected line ratio
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
Ps and/or text file with the intensity ratio.
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
DENSITY: calculates the intensity ratios for constant density.
If neither density or pressure are specified, a constant
density of 1.e+10 cm^-3 is assumed as default.
OUTFILE: the (optional) name of the output ascii file where a
listing of the line ratio intensities as a function of
temperature is saved.
PSFILE: the (optional) name of the output postscript file
where a plot of the chosen temperature sensitive line
ratio is saved.
NOPROT Switches off inclusion of proton rates.
VERBOSE prints out information
CALLS:
read_ioneq, convertname, ion2spectroscopic,ion2filename,
ch_xmenu_sel, emiss_calc
COMMON:
elvlc,l1a,term,conf,ss,ll,jj,ecm,eryd,ecmth,erydth,eref
wgfa, wvl,gf,a_value
upsilon,t_type,deu,c_ups,splups
proton, pstr, pe_ratio
radiative, radt, dilute
RESTRICTIONS:
SIDE EFFECTS: None known yet.
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
May 1996: Version 2.0, Ken Dere
April 2000: V. 3 Ken Dere modified for V3
14-Jul-2000 V. 4 Peter Young, now calls pop_solver
2-Oct-2000 V. 5 Giulio Del Zanna, corrected an error in the
creation of the string list of the lines in the ratio.
Also corrected a few minor errors.
Removed the device,window_state call, and added a few
other 'cosmetic' adjustments.
Version 6, 21-Dec-2000, William Thompson
Modified for better cross-platform capability.
Ver.7, 6-Dec-2001, Peter Young
Revised to call emiss_calc for the emissivities.
V.8, 21-May-2002, GDZ
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
V.9, 1-Aug-02 GDZ
Fixed label mistake, and changed all the formats.
V.10, 06-Aug-02 GDZ
Changed the use of CHIANTI system variables.
V.11, 15-Aug-02, GDZ
Major revision:
-Added the keyword VERBOSE, to avoid printing out long lists of lines.
-Removed the call to ch_xselect_s, that did not work for long lists.
-Added a '*' in the line lists, to identify 'unobserved' lines.
-Replaced the commands to create PS file, to make it
cross-platform compatible.
-Added a large number of cosmetics, mainly lables to the axes and
titles, that were missing.
-Removed plotting in windows already present.
-Removed the pressure keyword.
-Added the CHIANTI version number in the outputs.
V.12, 3-Nov-03 GDZ
Modified format e8.2 to e9.2 for Windows compatibility.
VERSION : 12, 3-Nov-03
PROJECT
CHIANTI http://wwwsolar.nrl.navy.mil/chianti.html
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME
temp_plotter
PURPOSE:
A widget-based routine to allow the analysis of temperature sensitive
ratios. **** See RATIO_PLOTTER for details. *****
CALLING SEQUENCE:
IDL> temp_plotter, name,$
EM, PATH=PATH, NOPROT=NOPROT, $
IONEQ_FILE=IONEQ_FILE, ABUND_FILE=ABUND_FILE
INPUTS:
The ion name (e.g. 'si_3' for Si III)
OPTIONAL INPUTS : none
OUTPUTS:
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
EM: Save the displayed emissivities to structure EM.
**** See RATIO_PLOTTER for details. *****
KEYWORDS:
PATH: Data in the CHIANTI format that is not in the CHIANTI
database can be read by specifying the directory in which
it lies through PATH.
ABUND_FILE The name of a CHIANTI abundance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio. Default is
!abund_file.
IONEQ_FILE The name of a CHIANTI ion balance file. This is used for
calculating the proton to electron ratio and evaluating
the T_max of the ion. Default is !ioneq_file.
NOPROT If set, then the default setting will be NOT to use
proton rates. This can be changed within the routine.
CALLS: CONVERTNAME RATIO_PLOTTER
COMMON BLOCKS: none
RESTRICTIONS:
SIDE EFFECTS:
CATEGORY:
spectral synthesis.
EXAMPLE:
IDL> temp_plotter, 'fe_13'
WRITTEN :
Ver.1, 18-Apr-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ) written as a wrapper
routine to call RATIO_PLOTTER (written by P. Young).
MODIFIED: V.2, 2-Aug-2005, GDZ
Now the routine handles the dielectronic case
VERSION : 2, 2-Aug-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
TWO_PHOTON
PURPOSE:
Calculate the 2 photon continuum from a hot, low density plasma.
For the hydrogen isoelectronic sequence, A values
Parpia, F. A., and Johnson, W. R., 1982, Phys. Rev. A, 26, 1142.
and distribution function as a function of Z is taken from:
Goldman, S.P. and Drake, G.W.F., 1981, Phys Rev A, 24, 183
For the helium isoelectronic sequence, A values are from:
Drake, G.W.F., 1986, Phys. Rev. A, 34, 2871
and the distribution function as a function of Z is taken from:
Drake, G.W.F., Victor, G.A., Dalgarno, A., 1969, Phys.
Rev. A, 180, 25.
in this paper the distribution is only given up to Z=10 but
extrapolation to higher Z appears to be OK.
Note that, unlike the freefree and freebound routines, two_photon
requies the electron density to be specified. This is because there
is a call to pop_solver
CALLING SEQUENCE:
TWO_PHOTON,temperature, density, wavelength, intensity
INPUTS:
TEMPERATURE Temperature in degrees Kelvin, can be a 1D array
WAVELENGTH Wavelengths in Angstroms.
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
DENSITY Electron density in cm^-3, can also be a 1D array
of the same size as Temperature. If there are several
temperatures specified but only one density, then
density is assumed the same at all temperatures.
If not specified, then default densities of 10^10
electrons/cm^3 are assumed.
DEM_INT An array of same length as TEMP which contains the
differential emission measure values at each temperature.
The emissivity at each temperature is multiplied by the
DEM value and the d(logT) value.
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
NO_SETUP: If the procedure setup_elements has already been called
then the keyword /no_setup should be set to avoid
repeating this step
MIN_ABUND: If set, calculates the continuum only from those
elements which have an abundance greater than min_abund.
Can speed up the
calculations. For example:
abundance (H) = 1.
abundance (He) = 0.085
abundance (C) = 3.3e-4
abundance (Si) = 3.3e-5
abundance (Fe) = 3.9e-5
SUMT If several temperatures have been specified, then /sumt
will sum the emissivities over the different
temperatures, giving an output INTENSITY that has the
same size as WAVELENGTH.
PHOTONS If set the continuum emissivity is output in photon
units rather than erg units.
VERBOSE
OUTPUTS:
RAD 2 photon continuum intensity in units of
10^-40 erg cm^3/s/sr/Angstrom per unit emission measure
( integral(N_H N_e dh) in cm^-5) if a DEM is not defined.
If DEM values are defined, it is assumed that they are given
as N_H N_e dh/dT. The units are
10^-40 erg/cm^2/s/sr/Angstrom
If T is given as a 1-D array, then the output will be a 2-D array,
with one element for each temperature and wavelength
(but also see SUMT).
CALLS
POP_SOLVER, SETUP_ION, SETUP_ELEMENTS, READ_MASTERLIST,
CONVERTNAME
COMMON BLOCKS:
ELEMENTS, ELVLC, WGFA, UPSILON, PROTON
EXAMPLE:
> two_photon,1.e+6,3.e+10,wvl,int
> two_photon,1.e+6,3.e+10,wvl,int,min_abund=3.e-5
> two_photon,1.e+6,3.e+10,wvl,int,/no_setup
PROGRAMMING NOTES
For He 2-photon decays, the distribution function is from Table II
of Drake et al. (1969), except that the values have been divided by
the A-value from Drake (1986).
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
February 2001: Version 1.0
Ver.2, 19-Dec-2001, Peter Young
Now allows an array of temperatures.
Added /SUMT keyword.
Added DEM_INT= optional input.
Switched to using spl_init & spl_interp for the spline fits.
Corrected a small bug.
Ver.3, 20-Dec-2001, Peter Young
Corrected a bug related to density indices.
Ver.4, 23-Apr-2002, Peter Young
Added /photons keyword.
Ver.5, 28-May-2002, Peter Young
Corrected way in which DEM_INT is handled.
V. 6, 28-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS.
Corrected the description of the units and various
inaccuracies in the header.
V.7, 14-Aug-02, GDZ
Added keyword VERBOSE
V.8, 4-Oct-2003, GDZ
modified the input to POP_SOLVER, now it is dealt with an
input structure.
V.9, 8-Jun-2004, EL
modified the input to POP_SOLVER, now it includes ion/rec
V.10, 5-Jul-2005
corrected problems with the input structure for pop_solver
v.11 29-Jul-2005, GDZ
fixed bug, only define ioneq_ionrec when files are
there (it was failing with neutrals)
VERSION : 11 29-Jul-2005
Project : CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
Name : USE_CHIANTI
Purpose : Sets up system variables for use of CHIANTI routines
Explanation : The CHIANTI software uses system variables
that have to be defined. This routine is called by the
CHIANTI routines if these system variables are not defined.
** If one is using the solar-soft package, these should
already be defined*****.
** If the CHIANTI package is used as stand-alone, then
this routine can be used for the setup with e.g.:
use_chianti,'/home/data/chianti/'
if /home/data/chianti/ points to the actual place where
the CHIANTI top directory is.
Use : IDL> use_chianti, '/home/data/chianti/', $
[ioneq= , abund=]
Inputs : None
Opt. Inputs : The full pathname of the CHIANTI top directory.
Outputs : None
Opt. Outputs: None
Keywords : IONEQ - to define the default ionization eq. file to be used.
ABUND - to define the default abundance file to be used.
Calls : None
Common : None
Restrictions: None
Side effects: None
Category :
Prev. Hist. : Based on use_dere_chianti, written by C D Pike, RAL
Written : Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ) DAMTP (University of Cambridge, UK)
Modified : Version 1, GDZ 10-Oct-2000
Version 2, GDZ 10-Jan-2001
added the definition of the !abund_file
V. 3, GDZ, 2-May-2002 Modified substantially, adding a new
system variable.
V.4, 10-July-2002 GDZ
Removed the definition of !chianti_top, upon request.
V.5, 25-July-2002, GDZ
Fixed a problem with IDL versions earlier than 5.3 (the routine
would not compile). ALso, introduced the use of concat_dir for
cross-platform compatibility.
V.6, 06-Aug-02 GDZ
Changed the use of CHIANTI system variables. Added comments on
the which CHIANTI version is used.
V.7 12-Aug-02 GDZ Changed default abundance file. Removed '***'
V.8, GDZ 13-Feb-2003
Changed default ioneq file, to include ALL the elements.
V.9, 12-Aug-2005, GDZ
Changed default ioneq file from mazzotta_etal_ext to
mazzotta_etal_9.ioneq where ion fractions have been extended
up to 10^9 K. This is useful to avoid steps in the
emissivities at high-temperatures.
Version : V.9, 12-Aug-2005
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME
VERNER_XS()
EXPLANATION
Reads the Verner & Yakovlev (A&AS 109, 125, 1995) photoionization
cross-section data and generates the values of the cross-section at
the wavelengths WVL
INPUTS
IZ Atomic number of ion (e.g., 26 = Fe)
ION Spectroscopic number of ion (e.g., 13 = XIII)
WVL Wavelengths (in angstroms) for which cross-sections are
required (1-D array).
OPTIONAL INPUTS
DATA By default VERNER_XS reads the Verner & Yakovlev data file when
it is called. Through the DATA keyword the data array can be
sent to VERNER_XS instead.
OUTPUT
The photoionization cross-section for the ionization of the outer
electron in units of mega-barns (Mb = 10^-18 cm^2) at the input
wavelengths. E.g., for Fe XIII (ground configuration
1s2.2s2.2p6.3s2.3p2) it is the cross-section for the removal of the
3p electron.
HISTORY
Ver.1, 24-Jul-2002, Peter Young
NAME
W2R()
EXPLANATION
Converts a dilution factor into a distance above a star.
INPUTS
W Radiation dilution factor.
OUTPUT
Distance from star -- a number greater than 1.
HISTORY
Ver.1, 7-Dec-2001, Peter Young
CONTACT
Peter Young, CfA, pyoung@cfa.harvard.edu
NAME
WHICH_LINE
PROJECT
CHIANTI
PURPOSE:
Upon given an ion name and wavelength, this routine prints out a list
of possible line IDs for the wavelength. Wavelengths within 1% of the
input wavelength are searched for.
INPUTS
IONNAME Name of an ion in the CHIANTI format. E.g., 'fe_13' for Fe XIII.
WVL A wavelength in angstroms.
OUTPUTS (to screen)
Prints a list of atomic transitions and wavelengths for lines close to
the input wavelength. A '*' is placed next to the closest wavelength
match.
KEYWORDS
NARROW Narrows the search range to 0.02% of the specified wavelength.
EXAMPLE
IDL> which_line,'o_6',1032
Wavelength i j Lower level Upper level A-value
1037.615 1 2 1s2.2s 2S1/2 - 1s2.2p 2P1/2 4.21e+008
1031.914 1 3 1s2.2s 2S1/2 - 1s2.2p 2P3/2 4.28e+008
CALLS
CONVERTNAME, ZION2FILENAME, READ_WGFA2, READ_ELVLC
HISTORY
Ver.1, 22-Jun-2004, Peter Young
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an atomic database package for the calculation of
continuum and emission line spectra from astrophysical plasmas. It is a
collaborative project involving the Naval Research Laboratory
(Washington DC, USA), the Arcetri Observatory (Firenze, Italy), and the
Cambridge University (United Kingdom).
NAME:
Z2ELEMENT
PURPOSE:
provide identification strings
CATEGORY:
database.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
Z2ELEMENT, Iz, Name
INPUTS:
Iz: nuclear charge of ion of interest, i.e. 26 for Fe
OUTPUTS:
Name: a string identifying the element
EXAMPLE:
> z2element,2,name
> print,name
> He
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1996: Version 2.0
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
ZION2FILENAME
PURPOSE:
help locate CHIANTI database files
CATEGORY:
database.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
ZION2FILENAME, Iz, Ion, Filename
INPUTS:
Iz: nuclear charge of ion of interest, i.e. 26 for Fe
Ion: charge state of ion of interest, i.e. 2 for Fe II
KEYWORDS:
diel: set if excitation of this ion is by dielectronic
recombination
OUTPUTS:
Filename: the complete filename and path specification for generic
CHIANTI database file, i.e. '.elvlc' suffix is not included
RESTRICTIONS:
!xuvtop must be set
EXAMPLE:
> zion2filename,26,2,filename
> print,filename
> /data1/xuv/fe/fe_2/fe_2 assuming !xuvtop = '/data1/xuv'
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Written by: Ken Dere
March 1996: Version 2.0
Sept 1996: Modified for use with VMS
December 1998: Modified to diel keyword
V.5, 29-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
generalized directory concatenation to work for
Unix, Windows and VMS. Added keyword name to output just
the name of the file and changed the dielectronic keyword.
VERSION : 5, 29-May-2002
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics of
Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving the Naval
Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence (Italy), the
University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
ZION2SPECTROSCOPIC
PURPOSE:
provide identification strings
CATEGORY:
database.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
ZION2SPECTROSCOPIC, Iz, Ion, Name
INPUTS:
Iz: nuclear charge of ion of interest, i.e. 26 for Fe
Ion: charge state of ion of interest, i.e. 2 for Fe II
OUTPUTS:
Name: the spectroscopic notation for the ion, i.e. 'Fe II'
EXAMPLE:
> zion2spectroscopic,26,2,name
> print,name
> Fe II
WRITTEN : Ken Dere
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
March 1996: Version 2.0
V.3, 25-May-2002, Giulio Del Zanna (GDZ)
added the DIELECTRONIC keyword.
VERSION : 3, 25-May-2002
NAME:
CHIANTI_FONT
PURPOSE:
Generates standard fonts for CHIANTI GUIs suitable for both Unix and
Windows operating systems.
CATEGORY:
Widgets, fonts
CALLING SEQUENCE:
CHIANTI_FONT, FONT [, /BIG, /FIXED ]
INPUTS:
None.
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
None.
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
BIG Output a descriptor for a large font.
FIXED Output a descriptor for a fixed-width font.
OUTPUTS:
FONT A descriptor for a font suitable for passing to IDL widget
routines.
OPTIONAL OUTPUTS:
None.
COMMON BLOCKS:
None.
SIDE EFFECTS:
None.
RESTRICTIONS:
Has not been tried with a MAC OS.
PROCEDURE:
CHIANTI_FONT, FONT [, /BIG, /FIXED ]
EXAMPLE:
IDL> chianti_font,font
IDL> print,font
Arial*bold*16
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Ver.1, 6-Aug-2003, Peter Young
PROJECT: CHIANTI
CHIANTI is an Atomic Database Package for Spectroscopic Diagnostics
of Astrophysical Plasmas. It is a collaborative project involving
the Naval Research Laboratory (USA), the University of Florence
(Italy), the University of Cambridge and the Rutherford Appleton
Laboratory (UK).
NAME:
FB_RAD_LOSS
PURPOSE:
Calculate the total radiative losses of a plasma due to the
free-bound (radiative recombination) continuum.
EXPLANATION
This routine does not use the same method of calculating the ion
continuum emissivities as the FREEBOUND routine. This is because a
modified version of FREEBOUND would be very slow for this purpose.
Instead, we use the method of Mewe et al. (A&AS 65, 511, 1986) which
is outlined in their Sect.2.2. The integration over the quantity
P_c(lambda,T) is very simple as the gaunt factor, G_c, has no
intrinsic lambda dependence other than through the limits.
Comparisons between the wavelength-resolved continuum emission
derived from the Mewe et al. method with the more sophisticated
method employed in FREEBOUND show excellent agreement with at most
10% differences at specific wavelengths.
CALLING SEQUENCE:
fb_rad_loss, temp, int, min_abund=min_abund, /no_setup
OUTPUTS
TEMP Temperatures (K). These are the temperatures at which the
ion fractions are defined (typically 10^4 to 10^8 in 0.1
dex intervals).
INT The emissivity in units of erg cm^3 s^-1.
OPTIONAL INPUTS:
MIN_ABUND Exclude elements whose abundances are less than MIN_ABUND.
(Note that Ab(H)=1.)
KEYWORD PARAMETERS:
NO_SETUP If the procedure setup_elements has already been called
then the keyword /nosetup should be set to avoid
repeating this step
PROGRAMMING NOTES
This routine computes the free-bound gaunt factor following the
prescription set out in Sect.2.2 of Mewe et al. (1986). The
expression for f_2 (Eq. 16 of Mewe et al.) contains several
quantities that need to be computed. Zeta_0 is computed internally
by the function ZETA_0 through a prescription evident from browsing
Table I of Mewe et al. Z_0 is computed from the ionization potential
of the recombined ion which is contained in the .ip file within the
database. The quantity n_0 (also used in deriving Z_0) is derived
using the routine CONF2N which extracts the highest n value from
the configuration description of the ground term of each ion.
The quantity Z is just the charge on the recombined ion; E_0 is the
ionization potential of the recombined ion, while E_n_0+1 is derived
from Mewe's Eq.7 with the prescription that z_n=Z and n=n_0+1.
The ions that are considered for the continuum are those for which
.fblvl files exist.
COMMON BLOCKS:
common elements,abund,abund_ref,ioneq,ioneq_t,ioneq_ref
INTERNAL FUNCTIONS
ZETA_0
CALLS
READ_IP, ZION2FILENAME, SETUP_ELEMENTS, FILE_EXIST,
READ_FBLVL, CONCAT_DIR, GET_IEQ
EXAMPLES
IDL> fb_rad_loss,temp,int
IDL> plot,temp,int,/xlog,/ylog
MODIFICATION HISTORY:
Ver.1, 1-Aug-2002, Peter Young
Completely new version of fb_rad_loss. Incorporates code from
a version of freebound not available in CHIANTI.
V 2, 25-May-2005, GDZ
corrected routine header.
VERSION: 2, 25-May-2005